Proteins - Clayton State University
... Hydrogen bonds • Hydrogen bonds form in water and between amino acids in a polypeptide chain via their R groups • Hydrogen bond donors (e.g., hydroxyl or amino groups) have hydrogen atoms covalently linked to more electronegative atoms • Hydrogen bond acceptors (e.g., carbonyl or sulfhydryl groups) ...
... Hydrogen bonds • Hydrogen bonds form in water and between amino acids in a polypeptide chain via their R groups • Hydrogen bond donors (e.g., hydroxyl or amino groups) have hydrogen atoms covalently linked to more electronegative atoms • Hydrogen bond acceptors (e.g., carbonyl or sulfhydryl groups) ...
Creating a Standard Curve Protein Concentration (µg/mL
... These DO NOT have to be points that you plotted from the data table. Choose two points whose coordinates are easily determined with confidence. Use these two points (WITH UNITS!!!) to calculate the slope of your line. Now determine equation for this line (Remember that b, the y-intercept) in this ca ...
... These DO NOT have to be points that you plotted from the data table. Choose two points whose coordinates are easily determined with confidence. Use these two points (WITH UNITS!!!) to calculate the slope of your line. Now determine equation for this line (Remember that b, the y-intercept) in this ca ...
BICH 303 Exam #1 Fall 2005 1. Amphiphilic or amphipathic
... B. S protein C. H solvent D. H protein E G protein for unfolded native conformations. 23. What are the advantages of forming quaternary structure? a. stability: a decrease in the surface to volume ratio and shielding of hydrophobic residues from the solvent. b genomic economy: less DNA required to c ...
... B. S protein C. H solvent D. H protein E G protein for unfolded native conformations. 23. What are the advantages of forming quaternary structure? a. stability: a decrease in the surface to volume ratio and shielding of hydrophobic residues from the solvent. b genomic economy: less DNA required to c ...
Biochemistry 304 2014 Student Edition Membranes
... Peripheral (Extrinsic) Proteins Can be dissociated by mild treatment from membrane, e.g. high ionic strength or pH changes. Do not bind lipid hydrophobic regions. Bind at membrane surface to certain lipid head groups or integral proteins. Capable of reversible binding that may vary with conditions. ...
... Peripheral (Extrinsic) Proteins Can be dissociated by mild treatment from membrane, e.g. high ionic strength or pH changes. Do not bind lipid hydrophobic regions. Bind at membrane surface to certain lipid head groups or integral proteins. Capable of reversible binding that may vary with conditions. ...
Protein Creation Pathway Tutorial
... 4. What is the function of the nucleolus? ____________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. In general, what are small parts of the cell called? _______________________________________________ ...
... 4. What is the function of the nucleolus? ____________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________________________________ 5. In general, what are small parts of the cell called? _______________________________________________ ...
Macromolecules in Organisms
... Color the glycerol molecule using the same colors for carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen as you did before. The fatty acid chains may be saturated (only single bonds between carbons) or unsaturated (contain at least one double bond). A carboxyl functional group (-COOH) is found on the end of the fatty aci ...
... Color the glycerol molecule using the same colors for carbon, hydrogen, and oxygen as you did before. The fatty acid chains may be saturated (only single bonds between carbons) or unsaturated (contain at least one double bond). A carboxyl functional group (-COOH) is found on the end of the fatty aci ...
2nd Amino Acid Workshop - Maastricht Proteomics Center
... the isotopic dilution of precursor amino acids in the samples, mass spectrometry (MS)3 was used to analyze crudely purified target proteins to confirm their identity and to estimate their enrichment by measuring a protein specific peptide fraction. This new approach incorporates a number of benefits ...
... the isotopic dilution of precursor amino acids in the samples, mass spectrometry (MS)3 was used to analyze crudely purified target proteins to confirm their identity and to estimate their enrichment by measuring a protein specific peptide fraction. This new approach incorporates a number of benefits ...
L -2 Sample preparation Before crystallization (first step
... Deterrent to microbial growth, which prevents the possibility of microbial agents growing and secreting proteases into the sample solution. Typically add 1mM sodium azide. Note: Sodium azide and thymol can sometimes bind the sample, are toxic and in some cases do not live well with heavy atoms Our L ...
... Deterrent to microbial growth, which prevents the possibility of microbial agents growing and secreting proteases into the sample solution. Typically add 1mM sodium azide. Note: Sodium azide and thymol can sometimes bind the sample, are toxic and in some cases do not live well with heavy atoms Our L ...
Immunology: Specific Immunity
... • Belong to class of proteins called immunoglobulins (Ig), subclass of globulins. • Y-shaped molecule with hinges – Ends include variable regions where antigen binding occurs. – Antibodies made by a single B cell are all the same, differ from those made by another in variable region. ...
... • Belong to class of proteins called immunoglobulins (Ig), subclass of globulins. • Y-shaped molecule with hinges – Ends include variable regions where antigen binding occurs. – Antibodies made by a single B cell are all the same, differ from those made by another in variable region. ...
Transport - AllenDWPScience
... Tell whether each of these molecules crosses the cell membrane easily with NO energy required: macromolecules non-charged small molecules water charged molecules lipid-soluble molecules ...
... Tell whether each of these molecules crosses the cell membrane easily with NO energy required: macromolecules non-charged small molecules water charged molecules lipid-soluble molecules ...
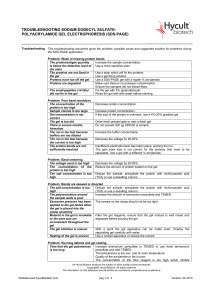
Troubleshooting SDS-PAGE-0410
... Quality of the acrylamide or bis is poor. Quality of the acrylamide or bis is poor. There is too little crosslinker, increase the amount of bisacrylamide. The bis concentration is too high, recheck the amount that is used. There is too much crosslinker, decrease the amount of bisacrylamide. The uppe ...
... Quality of the acrylamide or bis is poor. Quality of the acrylamide or bis is poor. There is too little crosslinker, increase the amount of bisacrylamide. The bis concentration is too high, recheck the amount that is used. There is too much crosslinker, decrease the amount of bisacrylamide. The uppe ...
File
... • Misfolded proteins are tagged with ubiquitin • Protein with more than one tag is taken to a proteasome, a tunnel-like multiprotein structure – As the protein moves through the tunnel, it is straightened and dismantled – Proteasomes also destroy properly-folded proteins that are in excess or no lon ...
... • Misfolded proteins are tagged with ubiquitin • Protein with more than one tag is taken to a proteasome, a tunnel-like multiprotein structure – As the protein moves through the tunnel, it is straightened and dismantled – Proteasomes also destroy properly-folded proteins that are in excess or no lon ...
Gunawardena, Shanti : Proteomics for the Discovery of Biomarkers and Diagnosis of Diseases
... subsequent protein identification by peptide mass fingerprinting (Gras, Muller et al. 1999). The samples used in this technique are usually cellular lysates from disease and normal tissues or serum. Direct comparison of protein expression to identify differentially expressed proteins between the ce ...
... subsequent protein identification by peptide mass fingerprinting (Gras, Muller et al. 1999). The samples used in this technique are usually cellular lysates from disease and normal tissues or serum. Direct comparison of protein expression to identify differentially expressed proteins between the ce ...
What is biochemistry?
... a certain carbohydrate to food to change its texture or flavour – such as pectin, which is used as a gelling agent in jam-making. Alternatively, a biochemist might find a substitute for common biological molecules. For example, they help to develop artificial sweeteners to replace sugar in your tea ...
... a certain carbohydrate to food to change its texture or flavour – such as pectin, which is used as a gelling agent in jam-making. Alternatively, a biochemist might find a substitute for common biological molecules. For example, they help to develop artificial sweeteners to replace sugar in your tea ...
Chemistry Membranes Transport across membrane
... - molecules of water are connected by hydrogen bond - negative end attracts positive ions or positive end of other polar molecules very well, it is able to dissolve many substances = water is called universal solvent hydrophile substances - dissolved in water (salts, sugars, proteins, acids, alkalis ...
... - molecules of water are connected by hydrogen bond - negative end attracts positive ions or positive end of other polar molecules very well, it is able to dissolve many substances = water is called universal solvent hydrophile substances - dissolved in water (salts, sugars, proteins, acids, alkalis ...
Does Cell Growth Predict Protein Productivity? - Cell-Ess
... When the goal is to increase protein titer, VCD is a valuable metric to gauge the proliferative capacity of the cell, but it is not the only indicator of protein yield. Experimental conditions (such as media or feeds) that increase per cell productivity may have equal or lower VCD than the control, ...
... When the goal is to increase protein titer, VCD is a valuable metric to gauge the proliferative capacity of the cell, but it is not the only indicator of protein yield. Experimental conditions (such as media or feeds) that increase per cell productivity may have equal or lower VCD than the control, ...
Food Microbiology-Single Cell Protein-UNIT-2-2012
... • Some strains produce mycotoxins and hence they should be screened. 3. Bacteria • These have more than 80% protein. They are poor in sulphur containing amino acids. • Brevibacterium uses hydrocarbons as substratum and Methylophilus methylitropous uses methanol. • It has high nucleic acid content Di ...
... • Some strains produce mycotoxins and hence they should be screened. 3. Bacteria • These have more than 80% protein. They are poor in sulphur containing amino acids. • Brevibacterium uses hydrocarbons as substratum and Methylophilus methylitropous uses methanol. • It has high nucleic acid content Di ...
proteins
... called its secondary structure; common secondary structures are the alpha-helix and the pleated-sheet. The secondary structure is formed when amino acids hydrogen bond to other amino acids farther along the polypeptide chain. The tertiary structure is the three-dimensional shape of the entire polype ...
... called its secondary structure; common secondary structures are the alpha-helix and the pleated-sheet. The secondary structure is formed when amino acids hydrogen bond to other amino acids farther along the polypeptide chain. The tertiary structure is the three-dimensional shape of the entire polype ...
What is a protein?
... 3. Distinguish the protein of interest 4. Separate the protein of interest 5. Retrieve the protein of interest ...
... 3. Distinguish the protein of interest 4. Separate the protein of interest 5. Retrieve the protein of interest ...
Western blot

The western blot (sometimes called the protein immunoblot) is a widely used analytical technique used to detect specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract. It uses gel electrophoresis to separate native proteins by 3-D structure or denatured proteins by the length of the polypeptide. The proteins are then transferred to a membrane (typically nitrocellulose or PVDF), where they are stained with antibodies specific to the target protein. The gel electrophoresis step is included in western blot analysis to resolve the issue of the cross-reactivity of antibodies.There are many reagent companies that specialize in providing antibodies (both monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies) against tens of thousands of different proteins. Commercial antibodies can be expensive, although the unbound antibody can be reused between experiments. This method is used in the fields of molecular biology, immunogenetics and other molecular biology disciplines. A number of search engines, such as CiteAb, Antibodypedia, and SeekProducts, are available that can help researchers find suitable antibodies for use in western blotting.Other related techniques include dot blot analysis, immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry where antibodies are used to detect proteins in tissues and cells by immunostaining, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).The method originated in the laboratory of Harry Towbin at the Friedrich Miescher Institute. The name western blot was given to the technique by W. Neal Burnette and is a play on the name Southern blot, a technique for DNA detection developed earlier by Edwin Southern. Detection of RNA is termed northern blot and was developed by George Stark at Stanford.