Biol115_2014_Lecture 8_Protein Structure
... • Sickle-cell disease, an inherited blood disorder, results from a single amino acid substitution in the haemoglobin protein. ...
... • Sickle-cell disease, an inherited blood disorder, results from a single amino acid substitution in the haemoglobin protein. ...
Solubilization of Membrane Proteins into Functional Lipid‐Bilayer
... reflects the nanoscale size of DIBMALPs and SMALPs, the decrease in calorimetric enthalpy must result from a fraction of DMPC being in contact with the polymer scaffolds along the rim of the nanodiscs. In sharp contrast with the situation encountered in SMALPs, the transition temperature was not dow ...
... reflects the nanoscale size of DIBMALPs and SMALPs, the decrease in calorimetric enthalpy must result from a fraction of DMPC being in contact with the polymer scaffolds along the rim of the nanodiscs. In sharp contrast with the situation encountered in SMALPs, the transition temperature was not dow ...
Levels of Organization
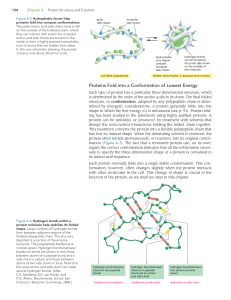
... amino acid is joined to the carbon of the carboxyl group (-COOH) of another amino acid by a single covalent bond, this bond is called a peptide bond. • And the resulting chain of two amino acids is called a peptide. • More amino acids are added one by one, until the protein is complete. ...
... amino acid is joined to the carbon of the carboxyl group (-COOH) of another amino acid by a single covalent bond, this bond is called a peptide bond. • And the resulting chain of two amino acids is called a peptide. • More amino acids are added one by one, until the protein is complete. ...
The Structure and Function of Large Biological Molecules 1. Polymers What are Polymers?
... vertebrate blood, transports oxygen from the lungs to other parts of the body. Other proteins transport molecules across cell membranes. ...
... vertebrate blood, transports oxygen from the lungs to other parts of the body. Other proteins transport molecules across cell membranes. ...
TUTORIAL FOR PROTEIN TECHNOLOGY: Ion-exchange
... When two non-polar solutes interact, there is less surface area for the water molecules to bind to the non-polar solutes. The water molecules will move to the area of bulk water, where it is less structured, and therefore more thermodynamically favourable. Certain ions-the ones high in the Hoffmeist ...
... When two non-polar solutes interact, there is less surface area for the water molecules to bind to the non-polar solutes. The water molecules will move to the area of bulk water, where it is less structured, and therefore more thermodynamically favourable. Certain ions-the ones high in the Hoffmeist ...
Macromolecules in your Food! – Info Sheet
... composed of triglycerides. Moreover, triglycerides that are solid at room temperature are called “fats” while those that remain liquid at room temperature are called “oils.” Triglycerides are also composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms, but in different ratios than in carbohydrates. Triglycer ...
... composed of triglycerides. Moreover, triglycerides that are solid at room temperature are called “fats” while those that remain liquid at room temperature are called “oils.” Triglycerides are also composed of carbon, hydrogen and oxygen atoms, but in different ratios than in carbohydrates. Triglycer ...
“Characterization of Proteins Interacting with Cystinosin” – Lay
... Indeed, we identified galectin-3, a protein known to be able to interact with sugar appended to certain proteins, especially lysosomal proteins, and with various proteins all shown to be involved in the mTOR complex. This is a large group of proteins that integrate stimuli from growth factors and nu ...
... Indeed, we identified galectin-3, a protein known to be able to interact with sugar appended to certain proteins, especially lysosomal proteins, and with various proteins all shown to be involved in the mTOR complex. This is a large group of proteins that integrate stimuli from growth factors and nu ...
Chapter 2 Molecules to enzymes Short Answer
... l. enables conservation of information transfer from DNA to RNA to polypeptide; ...
... l. enables conservation of information transfer from DNA to RNA to polypeptide; ...
A Major Root Protein of Carrots with High Homology to Intracellular
... amino acid residues. Protein domain analysis also indicated that two possible phosphorylation sites are involved in the CR16 protein, the putative phosphorylation sites are located at the amino terminal half (52(TVR)54 and 68(TVR)70). The calculated pi of the CR16 was estim ...
... amino acid residues. Protein domain analysis also indicated that two possible phosphorylation sites are involved in the CR16 protein, the putative phosphorylation sites are located at the amino terminal half (52(TVR)54 and 68(TVR)70). The calculated pi of the CR16 was estim ...
Test 1
... exported out of cell smooth ER - membrane sac distal from rough Er, proteins inside Er have now been synthesized and are now being processed, lipid synthesis. Golgi apparatus - used in final processing of secretory proteins Peroxisome - membrane bound organelle used to isolate chemical reaction invo ...
... exported out of cell smooth ER - membrane sac distal from rough Er, proteins inside Er have now been synthesized and are now being processed, lipid synthesis. Golgi apparatus - used in final processing of secretory proteins Peroxisome - membrane bound organelle used to isolate chemical reaction invo ...
Begrebet ”økologi” er i sig selv ikke ensbetydende med en bedre
... In few years Danish organic protein crops may be used as ingredients in feed for organic fish in partial replacement of fish meal protein. Fish meal is currently the primary protein source in feed for organic fish. Fish meal is manufactured by industrial fish caught among sustainable stocks, but eve ...
... In few years Danish organic protein crops may be used as ingredients in feed for organic fish in partial replacement of fish meal protein. Fish meal is currently the primary protein source in feed for organic fish. Fish meal is manufactured by industrial fish caught among sustainable stocks, but eve ...
INSILICO MODELING OF CAPSULAR POLYSACCHARIDE BIOSYNTHESIS PROTEIN STREPTOCOCCUS PNEUMONIAE LIGAND IDENTIFICATION
... cpsC, and cpsD were the genes which are responsible for a part of a regulatory system containing tyrosine phosphorylation and these genes are also involved in modulation of capsule synthesis in Streptococcus pneumonia[2]. These genes codes capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis proteins. Proteins code ...
... cpsC, and cpsD were the genes which are responsible for a part of a regulatory system containing tyrosine phosphorylation and these genes are also involved in modulation of capsule synthesis in Streptococcus pneumonia[2]. These genes codes capsular polysaccharide biosynthesis proteins. Proteins code ...
Essential Cell Biology Chapter 4 excerpt
... the complexity of intact tissues and organs is a major disadvantage when trying to purify particular molecules, because a long series of chromatography steps is generally required. These procedures not only take weeks to perform but they also yield only a few milligrams of pure protein. Nowadays, pr ...
... the complexity of intact tissues and organs is a major disadvantage when trying to purify particular molecules, because a long series of chromatography steps is generally required. These procedures not only take weeks to perform but they also yield only a few milligrams of pure protein. Nowadays, pr ...
Crystallization Laboratory
... Heavy atoms are useful because they are electron dense. Bottom of periodic table. High electron density is useful because X-rays are diffracted from electrons. When the heavy atom is bound to discrete sites in a protein crystal (a derivative), it alters the X-ray diffraction pattern slightly. Compar ...
... Heavy atoms are useful because they are electron dense. Bottom of periodic table. High electron density is useful because X-rays are diffracted from electrons. When the heavy atom is bound to discrete sites in a protein crystal (a derivative), it alters the X-ray diffraction pattern slightly. Compar ...
Chapter 6
... Proteasomes are a major mechanism by which cells regulate the concentration of particular proteins and degrade misfolded proteins. ...
... Proteasomes are a major mechanism by which cells regulate the concentration of particular proteins and degrade misfolded proteins. ...
Surface expression of the conserved ribosomal protein P0 on
... essential for the ribosomal activity and cell viability in yeast [9]. Through deletion analysis of the P0 protein, the ribosomal function has been mapped to amino acid position 185 –230 in yeast P0 [10]. Since P0 is a very conserved protein [5], we wondered whether the surface expression of P0 is an ...
... essential for the ribosomal activity and cell viability in yeast [9]. Through deletion analysis of the P0 protein, the ribosomal function has been mapped to amino acid position 185 –230 in yeast P0 [10]. Since P0 is a very conserved protein [5], we wondered whether the surface expression of P0 is an ...
PDF - Bioinformation
... Structure elucidation is an expensive and time consuming process and also requires extensive expertise. Currently used techniques to reveal 3D structures are X-ray crystallography and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Imaging. Due to the techniques being expensive and time consuming, there has been a ...
... Structure elucidation is an expensive and time consuming process and also requires extensive expertise. Currently used techniques to reveal 3D structures are X-ray crystallography and Nuclear Magnetic Resonance (NMR) Imaging. Due to the techniques being expensive and time consuming, there has been a ...
Cellular Localization Data - SGD-Wiki
... critical to helping you discern between possible functions you have uncovered so far and in proposing a final protein function or action based on where it is localized and what els ...
... critical to helping you discern between possible functions you have uncovered so far and in proposing a final protein function or action based on where it is localized and what els ...
Amino Acids
... • Results in unfolding and disorganization of proteins’ 2º and 3º structures, not accompanied by hydrolysis of peptide bonds • Denaturing agents include heat, organic solvents, mechanical mixing, strong acids or bases, detergents and ions of heavy metals e.g., lead and mercury • Denaturation may und ...
... • Results in unfolding and disorganization of proteins’ 2º and 3º structures, not accompanied by hydrolysis of peptide bonds • Denaturing agents include heat, organic solvents, mechanical mixing, strong acids or bases, detergents and ions of heavy metals e.g., lead and mercury • Denaturation may und ...
Assignment CHE-09 TMA-01,02 Year 2005
... What is meant by a spontaneous reaction? How does coupling in biochemical reactions help these proceed in forward direction? ' values at 298 K. Take the help of For the following reaction calculate G°΄ and K eq Table 8.3 given in Unit 8. ...
... What is meant by a spontaneous reaction? How does coupling in biochemical reactions help these proceed in forward direction? ' values at 298 K. Take the help of For the following reaction calculate G°΄ and K eq Table 8.3 given in Unit 8. ...
Basic virology
... the important distinction between the protein found in infected and uninfected cells. There is evidence that a change in the conformation from the normal alpha-helical form to the abnormal beta-pleated sheet form is the important modification. The abnormal form then recruits additional normal form ...
... the important distinction between the protein found in infected and uninfected cells. There is evidence that a change in the conformation from the normal alpha-helical form to the abnormal beta-pleated sheet form is the important modification. The abnormal form then recruits additional normal form ...
Protein Synthesis - Beaver Local High School
... three bases complementary to the codon of mRNA Amino acids floating freely in the cytosol are transported to the ribosomes by tRNA molecules ...
... three bases complementary to the codon of mRNA Amino acids floating freely in the cytosol are transported to the ribosomes by tRNA molecules ...
Western blot

The western blot (sometimes called the protein immunoblot) is a widely used analytical technique used to detect specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract. It uses gel electrophoresis to separate native proteins by 3-D structure or denatured proteins by the length of the polypeptide. The proteins are then transferred to a membrane (typically nitrocellulose or PVDF), where they are stained with antibodies specific to the target protein. The gel electrophoresis step is included in western blot analysis to resolve the issue of the cross-reactivity of antibodies.There are many reagent companies that specialize in providing antibodies (both monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies) against tens of thousands of different proteins. Commercial antibodies can be expensive, although the unbound antibody can be reused between experiments. This method is used in the fields of molecular biology, immunogenetics and other molecular biology disciplines. A number of search engines, such as CiteAb, Antibodypedia, and SeekProducts, are available that can help researchers find suitable antibodies for use in western blotting.Other related techniques include dot blot analysis, immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry where antibodies are used to detect proteins in tissues and cells by immunostaining, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).The method originated in the laboratory of Harry Towbin at the Friedrich Miescher Institute. The name western blot was given to the technique by W. Neal Burnette and is a play on the name Southern blot, a technique for DNA detection developed earlier by Edwin Southern. Detection of RNA is termed northern blot and was developed by George Stark at Stanford.