... Give an example of either one from oxygen transport and state its importance or role in oxygen transport. Choice B: What are the significant structural differences between myoglobin and hemoglobin and why is/are these difference(s) important in oxygen transport? Choice A (6 pts) Homotropic – affects ...
exam2_2011_key
... Give an example of either one from oxygen transport and state its importance or role in oxygen transport. Choice B: What are the significant structural differences between myoglobin and hemoglobin and why is/are these difference(s) important in oxygen transport? Choice A (6 pts) Homotropic – affects ...
... Give an example of either one from oxygen transport and state its importance or role in oxygen transport. Choice B: What are the significant structural differences between myoglobin and hemoglobin and why is/are these difference(s) important in oxygen transport? Choice A (6 pts) Homotropic – affects ...
Characteristics of the caspase-like catalytic domain of
... virus and orthopoxvirus processing proteases and a family of de-sumoylating proteases; and clan CD encompassing the five families, caspases, legumains, gingipains, clostripain, and separase. Recently, bioinformatics approaches have identified two further families within this clan: the paracaspases a ...
... virus and orthopoxvirus processing proteases and a family of de-sumoylating proteases; and clan CD encompassing the five families, caspases, legumains, gingipains, clostripain, and separase. Recently, bioinformatics approaches have identified two further families within this clan: the paracaspases a ...
... 14. (10 pts) Please answer one of the following three choices: Choice A: How does the presence of cis double bonds in unsaturated fatty acids affect the phase transition of the membrane? What intermolecular interaction is affected by the presence of these groups in the bilayer? Choice B: Compare and ...
Plasma membrane - HCC Learning Web
... (known as a 9 0 array). A pair of centrioles orientated at right angles to one another occupies the centrosome. This micrograph, produced by a transmission electron microscope, is called a TEM. ...
... (known as a 9 0 array). A pair of centrioles orientated at right angles to one another occupies the centrosome. This micrograph, produced by a transmission electron microscope, is called a TEM. ...
The potato tuber mitochondrial proteome
... specific set of conditions (Millar et al. 2005, Millar et al., 2006, Cui et al., 2011). To ...
... specific set of conditions (Millar et al. 2005, Millar et al., 2006, Cui et al., 2011). To ...
Hemoglobin
... unloaded and the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen is reduced. Thus at the lowest oxygen tensions found in very active tissues the binding affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen is very low allowing maximal delivery of oxygen to the tissue. In contrast the oxygen binding curve for myoglobin is hyperbolic ...
... unloaded and the affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen is reduced. Thus at the lowest oxygen tensions found in very active tissues the binding affinity of hemoglobin for oxygen is very low allowing maximal delivery of oxygen to the tissue. In contrast the oxygen binding curve for myoglobin is hyperbolic ...
mbe.oxfordjournals.org - Oxford Academic
... this region plays a vital role in the 40S subunit assembly and/or ribosomal function. The b-galactosidase fusion construct containing the fragment S6(3–183) was inefficiently targeted to the nucleus, which was attributed to the weak nature of NLS1 (Schmidt et al. 1995). Appending the C-terminal segm ...
... this region plays a vital role in the 40S subunit assembly and/or ribosomal function. The b-galactosidase fusion construct containing the fragment S6(3–183) was inefficiently targeted to the nucleus, which was attributed to the weak nature of NLS1 (Schmidt et al. 1995). Appending the C-terminal segm ...
Rat Leptin ELISA Kit wako
... Grade: for Biochemistry Summary This product is for research use only. Do not administer it to human. For Research on Diabetic Complications & For Accurate Quantification of Sorbitol Sorbitol Dehydrogenase is an essential enzyme involved in polyol metabolism. Sorbitol Dehydrogenase, isolated from mi ...
... Grade: for Biochemistry Summary This product is for research use only. Do not administer it to human. For Research on Diabetic Complications & For Accurate Quantification of Sorbitol Sorbitol Dehydrogenase is an essential enzyme involved in polyol metabolism. Sorbitol Dehydrogenase, isolated from mi ...
Chapter 12 Role of tunnels, channels and gates in enzymatic catalysis
... the last 10-15 years, and currently it is possible to observe the dynamics of proteins at the atomic level by using specific methods, in the timescales ranging from picoseconds to seconds57–59. Therefore, NMR spectroscopy has the potential to supply relevant information regarding not only the perman ...
... the last 10-15 years, and currently it is possible to observe the dynamics of proteins at the atomic level by using specific methods, in the timescales ranging from picoseconds to seconds57–59. Therefore, NMR spectroscopy has the potential to supply relevant information regarding not only the perman ...
Biochem 330 Fall 2011 Problem Set II Enzyme Catalysis, Glycolysis
... glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (GAP) tritiated at C2. The dihydroxyacetone phospate (DHAP) product had lost the label at the middle carbon and showed less than 5% labelling at the C1 carbon. Which of the following is true. Explain. a) This experiment suggests that a single catalytic group on the enzyme ...
... glyceraldehyde 3-phosphate (GAP) tritiated at C2. The dihydroxyacetone phospate (DHAP) product had lost the label at the middle carbon and showed less than 5% labelling at the C1 carbon. Which of the following is true. Explain. a) This experiment suggests that a single catalytic group on the enzyme ...
MND Australia International Research Update December 2016
... Our cells have two major systems for removal of unwanted proteins, the ubiquitinproteasome system (UPS) and the autophagy-lysosome system. In both of these systems, a cascade of special enzymes direct little proteins, called ubiquitin, to unwanted or old proteins to target them for removal. This cas ...
... Our cells have two major systems for removal of unwanted proteins, the ubiquitinproteasome system (UPS) and the autophagy-lysosome system. In both of these systems, a cascade of special enzymes direct little proteins, called ubiquitin, to unwanted or old proteins to target them for removal. This cas ...
The key to life at the atomic level
... tRNA, there is an anticodon which is paired with a matching codon on the mRNA molecule in the ribosome (figure 3). At the other end, there is the specific amino acid which matches the codon. Thus emerged an image of the most fundamental process of life: the manner in which information flows from DNA ...
... tRNA, there is an anticodon which is paired with a matching codon on the mRNA molecule in the ribosome (figure 3). At the other end, there is the specific amino acid which matches the codon. Thus emerged an image of the most fundamental process of life: the manner in which information flows from DNA ...
Authors` pre-proof version - University of Connecticut
... Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (aaRS), together with tRNA, define the alphabet and syntax of the genetic code, upon which all protein synthesis depends. Aminoacylation of all 20 universal amino acids is partitioned between two major aaRS folds (class I and class II). Within each class, the aaRSs with di ...
... Aminoacyl-tRNA synthetases (aaRS), together with tRNA, define the alphabet and syntax of the genetic code, upon which all protein synthesis depends. Aminoacylation of all 20 universal amino acids is partitioned between two major aaRS folds (class I and class II). Within each class, the aaRSs with di ...
Unit 2, Lesson 13: Polymers Polymers are very large organic
... • starch, a polymer of glucose molecules • DNA, a polymer of nucleotides • protein, a polymer of amino acids • cellulose (wood and paper), a polymer of glucose molecules • wool, hair, fingernails, silk etc. One of the most useful achievements of modern chemistry has been the development of technique ...
... • starch, a polymer of glucose molecules • DNA, a polymer of nucleotides • protein, a polymer of amino acids • cellulose (wood and paper), a polymer of glucose molecules • wool, hair, fingernails, silk etc. One of the most useful achievements of modern chemistry has been the development of technique ...
Removal of SDS from biological protein digests for proteomic
... the suitable selection of their building blocks (metal and organic linker). Apart from these features, the lower acidity of the active centers in MOFs makes these materials even very attractive compared Zeolites (highly acidic centers). Also, MOFs may be changing the interactions of adsorbing reacta ...
... the suitable selection of their building blocks (metal and organic linker). Apart from these features, the lower acidity of the active centers in MOFs makes these materials even very attractive compared Zeolites (highly acidic centers). Also, MOFs may be changing the interactions of adsorbing reacta ...
Multiple Sequence Alignments and Sequence Profiles
... Might want to add different pseudocounts depending on the actual count (add more to smaller counts, especially 0) Can use substitution matrices to estimate ...
... Might want to add different pseudocounts depending on the actual count (add more to smaller counts, especially 0) Can use substitution matrices to estimate ...
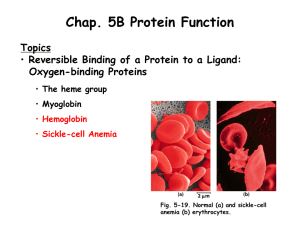
Chapter 5B Lecture
... allosteric (Greek for “other shape”) proteins. The ligands themselves are broadly called structural modulators. Modulators for allosteric proteins can be either inhibitors or activators. When the normal ligand and modulator are identical as they are with Hb (i.e., O2), the modulator is termed homotr ...
... allosteric (Greek for “other shape”) proteins. The ligands themselves are broadly called structural modulators. Modulators for allosteric proteins can be either inhibitors or activators. When the normal ligand and modulator are identical as they are with Hb (i.e., O2), the modulator is termed homotr ...
Kinesin superfamily proteins and their various functions and dynamics
... KIF17 from the cell body to the postsynaptic sites [24,25]. That KIF17 plays an important role in memory has been demonstrated by the fact that transgenic mice overexpressing KIF17 show enhanced working or episode-like memory and spatial learning and memory [26]. Moreover, the gene expressions of KI ...
... KIF17 from the cell body to the postsynaptic sites [24,25]. That KIF17 plays an important role in memory has been demonstrated by the fact that transgenic mice overexpressing KIF17 show enhanced working or episode-like memory and spatial learning and memory [26]. Moreover, the gene expressions of KI ...
Brew Day Presentation
... vigorous open rolling boil for at least one hour. The strong open boil will evaporate the SMM. ...
... vigorous open rolling boil for at least one hour. The strong open boil will evaporate the SMM. ...
Western blot

The western blot (sometimes called the protein immunoblot) is a widely used analytical technique used to detect specific proteins in a sample of tissue homogenate or extract. It uses gel electrophoresis to separate native proteins by 3-D structure or denatured proteins by the length of the polypeptide. The proteins are then transferred to a membrane (typically nitrocellulose or PVDF), where they are stained with antibodies specific to the target protein. The gel electrophoresis step is included in western blot analysis to resolve the issue of the cross-reactivity of antibodies.There are many reagent companies that specialize in providing antibodies (both monoclonal and polyclonal antibodies) against tens of thousands of different proteins. Commercial antibodies can be expensive, although the unbound antibody can be reused between experiments. This method is used in the fields of molecular biology, immunogenetics and other molecular biology disciplines. A number of search engines, such as CiteAb, Antibodypedia, and SeekProducts, are available that can help researchers find suitable antibodies for use in western blotting.Other related techniques include dot blot analysis, immunohistochemistry and immunocytochemistry where antibodies are used to detect proteins in tissues and cells by immunostaining, and enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay (ELISA).The method originated in the laboratory of Harry Towbin at the Friedrich Miescher Institute. The name western blot was given to the technique by W. Neal Burnette and is a play on the name Southern blot, a technique for DNA detection developed earlier by Edwin Southern. Detection of RNA is termed northern blot and was developed by George Stark at Stanford.