Protein mteabolism
... Conversion of aromatic acids into specialized products 1- Phenylalanine amino acid Essential amino acid Converted into tyrosine (major pathway ) ...
... Conversion of aromatic acids into specialized products 1- Phenylalanine amino acid Essential amino acid Converted into tyrosine (major pathway ) ...
Biochemistry: A Short Course
... Phosphoglucose Isomerase (PGI) G6P Conversion via Acid-Base Catalysis Base catalyzes ring closure ...
... Phosphoglucose Isomerase (PGI) G6P Conversion via Acid-Base Catalysis Base catalyzes ring closure ...
Chem*3560 Lecture 11: Regulation by proteolytic cleavage
... 15 and Ile 16, at a location which is structurally equivalent to Lys6 and Ile7 in trypsinogen. The newly exposed N-terminal Ile is similarly positioned to make an ion pair with Asp 194, and the mechanism of activation is the same as for trypsin. The immediate product is called π -chymotrypsin and is ...
... 15 and Ile 16, at a location which is structurally equivalent to Lys6 and Ile7 in trypsinogen. The newly exposed N-terminal Ile is similarly positioned to make an ion pair with Asp 194, and the mechanism of activation is the same as for trypsin. The immediate product is called π -chymotrypsin and is ...
Inborn error in metabolism of amino acids
... acid involves loss of the α-amino acid by transamination followed by oxidative decarboxylation of the respective keto acids. . The decarboxylation step is catalysed by branched chain α keto acid decarboxylase. In approximately 1 in 300,000 live birth in the general US population are affected by this ...
... acid involves loss of the α-amino acid by transamination followed by oxidative decarboxylation of the respective keto acids. . The decarboxylation step is catalysed by branched chain α keto acid decarboxylase. In approximately 1 in 300,000 live birth in the general US population are affected by this ...
- UM Research Repository
... findings showed the addition of these two amino acids in conventional ECM containing serum proteins may not be useful and may even be harmful. This suggests the practice of supplementing ECM with aspartate and serine be ...
... findings showed the addition of these two amino acids in conventional ECM containing serum proteins may not be useful and may even be harmful. This suggests the practice of supplementing ECM with aspartate and serine be ...
The 20 amino acids
... residue, but you don’t have a good plan about what to replace it with, take alanine because it is a subset of all other amino acids ...
... residue, but you don’t have a good plan about what to replace it with, take alanine because it is a subset of all other amino acids ...
Cell Respiration Student Notes
... http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072437316/student_view0/chapter8/animations.html ...
... http://highered.mcgraw-hill.com/sites/0072437316/student_view0/chapter8/animations.html ...
... The change in entropy suggests that there is also a difference in exposure of non-polar groups in the unfolded proteins - specifically with the Threonine containing protein, since So is lower, there must be more ordered water - therefore a larger non-polar sidechaim becomes solvent exposed in the u ...
Protein_Structure_Final_Powerpoint
... Molecular interactions determine tertiary and quaternary structures DNA mutations can affect protein function Unconserved regions are predicted to serve as key sites where ...
... Molecular interactions determine tertiary and quaternary structures DNA mutations can affect protein function Unconserved regions are predicted to serve as key sites where ...
Pathways of Pyrimidine and Purine Metabolism in E.coli
... Background: Escherichia coli has multiple pathways for the salvage of nucleosides. One of these pathways consists of a group of hydrolases capable of breaking down nucleosides to ribose and the corresponding base. E. coli has three different genes for these hydrolases, one of which, rihC, is capable ...
... Background: Escherichia coli has multiple pathways for the salvage of nucleosides. One of these pathways consists of a group of hydrolases capable of breaking down nucleosides to ribose and the corresponding base. E. coli has three different genes for these hydrolases, one of which, rihC, is capable ...
Lecture 12 - Biocatalysis
... cold water fish will die at 30°C, because their enzymes denature • A few bacteria have enzymes that can withstand very high temperatures up to 100°C • Most enzymes however are fully denatured at 70°C ...
... cold water fish will die at 30°C, because their enzymes denature • A few bacteria have enzymes that can withstand very high temperatures up to 100°C • Most enzymes however are fully denatured at 70°C ...
Enzyme Mechanisms
... Some enzymes are so efficient that the limiting factor in completion of the reaction is diffusion of the substrates into the active site: These are diffusion-controlled reactions. Ultra-high turnover rates: kcat ~ 109 s-1. We can describe kcat / Km as catalytic efficiency (or the specificity constan ...
... Some enzymes are so efficient that the limiting factor in completion of the reaction is diffusion of the substrates into the active site: These are diffusion-controlled reactions. Ultra-high turnover rates: kcat ~ 109 s-1. We can describe kcat / Km as catalytic efficiency (or the specificity constan ...
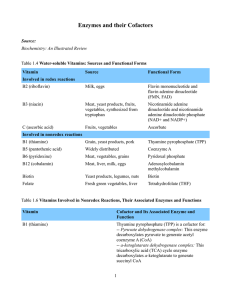
Enzymes and their Cofactors Source: Biochemistry: An Illustrated
... in a reaction that is part of the pathway that degrades odd-numbered fatty acids -- Methionine synthase/homocysteine methyltransferase: This enzyme transfers a methyl group from 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (N5-methylTHF) onto homocysteine to form methionine. Methionine reacts with adenosine triphosphat ...
... in a reaction that is part of the pathway that degrades odd-numbered fatty acids -- Methionine synthase/homocysteine methyltransferase: This enzyme transfers a methyl group from 5-methyltetrahydrofolate (N5-methylTHF) onto homocysteine to form methionine. Methionine reacts with adenosine triphosphat ...
Organic Chemistry Answer Key
... monosaccharides form a polysaccharide, such as starch, cellulose, or chitin. Part C: Describe how the functions of proteins differ from the functions of carbohydrates ...
... monosaccharides form a polysaccharide, such as starch, cellulose, or chitin. Part C: Describe how the functions of proteins differ from the functions of carbohydrates ...
Problem 1
... (a) From these data, describe the native protein in terms of the number of subunits present, their molecular weight, stoichiometry of subunits, and the kinds of bonding (covalent, noncovalent) existing between the subunits. The protein consists of 3 subunits with molecular weights: 30,000 Da (one su ...
... (a) From these data, describe the native protein in terms of the number of subunits present, their molecular weight, stoichiometry of subunits, and the kinds of bonding (covalent, noncovalent) existing between the subunits. The protein consists of 3 subunits with molecular weights: 30,000 Da (one su ...
Organic Chemistry
... substrates on which they act often much smaller molecules than the enzymes themselves. Each protein enzyme has a unique three-dimensional shape arising from its primary, secondary, tertiary and (sometimes) quaternary structure. On the surface of each enzyme molecule there is one small area called th ...
... substrates on which they act often much smaller molecules than the enzymes themselves. Each protein enzyme has a unique three-dimensional shape arising from its primary, secondary, tertiary and (sometimes) quaternary structure. On the surface of each enzyme molecule there is one small area called th ...
Catalytic triad

A catalytic triad refers to the three amino acid residues that function together at the centre of the active site of some hydrolase and transferase enzymes (e.g. proteases, amidases, esterases, acylases, lipases and β-lactamases). An Acid-Base-Nucleophile triad is a common motif for generating a nucleophilic residue for covalent catalysis. The residues form a charge-relay network to polarise and activate the nucleophile, which attacks the substrate, forming a covalent intermediate which is then hydrolysed to regenerate free enzyme. The nucleophile is most commonly a serine or cysteine amino acid, but occasionally threonine. Because enzymes fold into complex three-dimensional structures, the residues of a catalytic triad can be far from each other along the amino-acid sequence (primary structure), however, they are brought close together in the final fold.As well as divergent evolution of function (and even the triad's nucleophile), catalytic triads show some of the best examples of convergent evolution. Chemical constraints on catalysis have led to the same catalytic solution independently evolving in at least 23 separate superfamilies. Their mechanism of action is consequently one of the best studied in biochemistry.