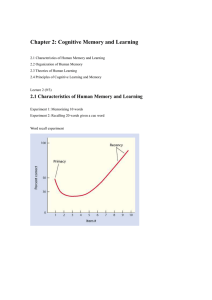
4 - University of Oklahoma
... 1. Preconscious attention is the highly automatic, largely unconscious selection of certain stimuli for simple cognitive processing 2. Focal attention is a controlled, conscious level of attention that focuses cognitive processes on relevant or prominent stimuli in the environment 3. Selective atten ...
... 1. Preconscious attention is the highly automatic, largely unconscious selection of certain stimuli for simple cognitive processing 2. Focal attention is a controlled, conscious level of attention that focuses cognitive processes on relevant or prominent stimuli in the environment 3. Selective atten ...
Lecture Note
... “Children tends to remember well who bought them the toys when and where” Episodic memory (explicit) ...
... “Children tends to remember well who bought them the toys when and where” Episodic memory (explicit) ...
encoding - WordPress.com
... A major figure in the history of encoding is Hermann Ebbinghaus (1850–1909). Ebbinghaus was a pioneer in the field of memory research. Using himself as a subject he studied how we learn and forget information by repeating a list of nonsense syllables to the rhythm of a metronome until they were comm ...
... A major figure in the history of encoding is Hermann Ebbinghaus (1850–1909). Ebbinghaus was a pioneer in the field of memory research. Using himself as a subject he studied how we learn and forget information by repeating a list of nonsense syllables to the rhythm of a metronome until they were comm ...
Chapter3
... Personal information management • Personal information management (PIM) is a growing problem for most users – Who have vast numbers of documents, images, music files, video clips, emails, attachments, bookmarks, etc., – Major problem is deciding where and how to save them all, then remembering what ...
... Personal information management • Personal information management (PIM) is a growing problem for most users – Who have vast numbers of documents, images, music files, video clips, emails, attachments, bookmarks, etc., – Major problem is deciding where and how to save them all, then remembering what ...
Unit VII: Cognition - Rapid City Area Schools
... c. Stress tends to increase the chance than an event will be remembered, but excitement decreases the chance than an event will be remembered. d. The effect of emotion on memory depends on the interpretation of the event in the frontal lobes. e. Emotion enhances memory because it is important for ou ...
... c. Stress tends to increase the chance than an event will be remembered, but excitement decreases the chance than an event will be remembered. d. The effect of emotion on memory depends on the interpretation of the event in the frontal lobes. e. Emotion enhances memory because it is important for ou ...
Memory - My Haiku
... Unit 3: Memory (Cognition) Essential Task 3-1: Describe the information processing model of memory with specific attention to the following steps: - Encoding: external stimuli, sensory registers, selective attention, reticular formation, short-term memory - Storage: long-term memory, explicit memory ...
... Unit 3: Memory (Cognition) Essential Task 3-1: Describe the information processing model of memory with specific attention to the following steps: - Encoding: external stimuli, sensory registers, selective attention, reticular formation, short-term memory - Storage: long-term memory, explicit memory ...
Working memory
... Baddeley’s experiments: • Procedure 1 (control condition): – The subject was given items to remember (e.g., a sequence of numbers or letters) – The subject report the item given in the first task (recalling). – The subject carried out a cognitive task (e.g., verifying a sentence) ...
... Baddeley’s experiments: • Procedure 1 (control condition): – The subject was given items to remember (e.g., a sequence of numbers or letters) – The subject report the item given in the first task (recalling). – The subject carried out a cognitive task (e.g., verifying a sentence) ...
2320Lecture22
... Capacity • For example: what if recalling interferes with memory? What if they forgot the information before they could report it? • How could you modify the experiment to measure the instantaneous capacity, before any forgetting can occur? ...
... Capacity • For example: what if recalling interferes with memory? What if they forgot the information before they could report it? • How could you modify the experiment to measure the instantaneous capacity, before any forgetting can occur? ...
U Eyewitness Testimony
... 5. In the Cognitive Interview, the interviewer seeks to reconstruct the external, emotional, and cognitive conditions surrounding the event. Why are each of these important in remembering events? ...
... 5. In the Cognitive Interview, the interviewer seeks to reconstruct the external, emotional, and cognitive conditions surrounding the event. Why are each of these important in remembering events? ...
Lec 18 - Forgetting
... Forgetting (retention loss) refers to apparent loss of information already encoded and stored in an individual's long term memory. It is a spontaneous or gradual process in which oldmemories are unable to be recalled from memory storage. It is subject to delicately balanced optimization that ensures ...
... Forgetting (retention loss) refers to apparent loss of information already encoded and stored in an individual's long term memory. It is a spontaneous or gradual process in which oldmemories are unable to be recalled from memory storage. It is subject to delicately balanced optimization that ensures ...
You - Ashton Southard
... mention of relevant facts about those individuals (they were wearing a funny hat or they had long red hair) When older adults are directed to use the memory strategy of elaboration during both study and retrieval, the difference between young and old adults nearly disappears › Clearly, elders’ ass ...
... mention of relevant facts about those individuals (they were wearing a funny hat or they had long red hair) When older adults are directed to use the memory strategy of elaboration during both study and retrieval, the difference between young and old adults nearly disappears › Clearly, elders’ ass ...
lecture 16 - Illinois State University Department of Psychology
... • Participants viewed words and were asked to make three different types of judgments: • Visual processing (e.g. “Is LOG in upper case?” Y/N) • Phonological (e.g. “Does DOG rhyme with LOG?” Y/N) • Semantic (e.g. “Does DOG fit in the sentence: ‘The ___ chased the cat’?” Y/N) ...
... • Participants viewed words and were asked to make three different types of judgments: • Visual processing (e.g. “Is LOG in upper case?” Y/N) • Phonological (e.g. “Does DOG rhyme with LOG?” Y/N) • Semantic (e.g. “Does DOG fit in the sentence: ‘The ___ chased the cat’?” Y/N) ...
Chap 6 RR
... proposes that the information at the end of the list is remembered due to the fact that it is still in shortterm memory. Recognition is usually a much easier task than recall since the retrieval cue is the actual piece of information you are trying to remember, yet retrieval errors are still made wh ...
... proposes that the information at the end of the list is remembered due to the fact that it is still in shortterm memory. Recognition is usually a much easier task than recall since the retrieval cue is the actual piece of information you are trying to remember, yet retrieval errors are still made wh ...
Cognitive
... Capacity - Very limited and in some models considered a "bottleneck" in human information processing. The classic work of Miller (1956) determined the number of units that can be processed at any one time as 7 + 2. Subsequent studies have indicated that 5 + 2 may apply to most of the items we wish t ...
... Capacity - Very limited and in some models considered a "bottleneck" in human information processing. The classic work of Miller (1956) determined the number of units that can be processed at any one time as 7 + 2. Subsequent studies have indicated that 5 + 2 may apply to most of the items we wish t ...
Memory
... but no barn. 17% in the experimental group (the group asked the leading questions) reported seeing a barn. Only 3% in the control group (not asked leading questions) made this error. ...
... but no barn. 17% in the experimental group (the group asked the leading questions) reported seeing a barn. Only 3% in the control group (not asked leading questions) made this error. ...
Economic Attention Networks: Associative Memory and Resource
... • conserved quantities (except for unusual circumstances – e.g. Economic Stimulus Package) • STI: the immediate urgency of an Atom • LTI: measure of importance for quick recall of Atom • Forgetting process: uses low-LTI and other factors to remove Atoms from quick memory ...
... • conserved quantities (except for unusual circumstances – e.g. Economic Stimulus Package) • STI: the immediate urgency of an Atom • LTI: measure of importance for quick recall of Atom • Forgetting process: uses low-LTI and other factors to remove Atoms from quick memory ...
Chap 5: The Cognitive Approach II
... In the whole report condition, participants attempted to recall the entire array but could only remember several letters. In the partial-report condition, they were cued after the display to report the letters in one row only. They could remember all the letters. This shows iconic memory has a high ...
... In the whole report condition, participants attempted to recall the entire array but could only remember several letters. In the partial-report condition, they were cued after the display to report the letters in one row only. They could remember all the letters. This shows iconic memory has a high ...
PDF
... Event must be encoded in memory Cues important in aiding recall Cues may come from wording of question, lists, context Recall takes time. The more time the better the recall ...
... Event must be encoded in memory Cues important in aiding recall Cues may come from wording of question, lists, context Recall takes time. The more time the better the recall ...
on Memory
... events of our own life. • Declarative memory: stored knowledge that can be called forth consciously as needed. • Procedural memory: permanent storage of learned skills that does not require conscious recollection. (swimming, driving, tying a tie) ...
... events of our own life. • Declarative memory: stored knowledge that can be called forth consciously as needed. • Procedural memory: permanent storage of learned skills that does not require conscious recollection. (swimming, driving, tying a tie) ...
05powerpoint
... Memory is the capacity to retain information over time. Memory allows us to learn from previous experiences. Memory systems can be characterized by duration, capacity, and coding. ...
... Memory is the capacity to retain information over time. Memory allows us to learn from previous experiences. Memory systems can be characterized by duration, capacity, and coding. ...
The stress model of Yerkes-Dodson law suggests that at low and
... degree to which an event is perceived stressful, the less likely it is for a person to recollect memory accurately, thus the presence of the misinformation effect. Strengths of this experiment included a careful selection of similar video clips, and a thorough literature review that which enabled th ...
... degree to which an event is perceived stressful, the less likely it is for a person to recollect memory accurately, thus the presence of the misinformation effect. Strengths of this experiment included a careful selection of similar video clips, and a thorough literature review that which enabled th ...