Normal Distribution
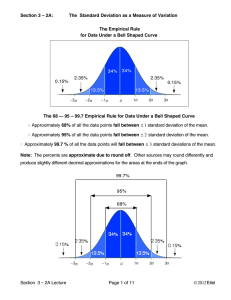
... It is good to know the standard deviation, because we can say that any value is: likely to be within 1 standard deviation (68 out of 100 should be) very likely to be within 2 standard deviations (95 out of 100 should be) almost certainly within 3 standard deviations (997 out of 1000 should be) ...
... It is good to know the standard deviation, because we can say that any value is: likely to be within 1 standard deviation (68 out of 100 should be) very likely to be within 2 standard deviations (95 out of 100 should be) almost certainly within 3 standard deviations (997 out of 1000 should be) ...
Document
... Formula - = (X) / N English: To calculate the mean, first add up all the scores, then divide by the number of scores you added up. ...
... Formula - = (X) / N English: To calculate the mean, first add up all the scores, then divide by the number of scores you added up. ...
Chapter 6 Section 2
... The null hypothesis is about the population mean not the sample mean. The sample mean only provides evidence about what is the value of the population mean. (b) A change is made that should improve student satisfaction with the way grades are processed- The null hypothesis, that there is an improvem ...
... The null hypothesis is about the population mean not the sample mean. The sample mean only provides evidence about what is the value of the population mean. (b) A change is made that should improve student satisfaction with the way grades are processed- The null hypothesis, that there is an improvem ...
Topic 14: Unbiased Estimation
... Topic 14: Unbiased Estimation∗ October 27, 2011 When we look to estimate the distribution mean µ, we typically use the sample mean x̄. For the variance σ 2 , we have been presented with two choices: n ...
... Topic 14: Unbiased Estimation∗ October 27, 2011 When we look to estimate the distribution mean µ, we typically use the sample mean x̄. For the variance σ 2 , we have been presented with two choices: n ...
Stochastic Simulation - University of Kentucky College of Engineering
... The precision was originally described for f , so a variance estimate for this value is needed before the relationship between precision and number of independent runs can be determined. So, preliminary runs can be generated to get an idea of the variance magnitude. The worst case will be the broad ...
... The precision was originally described for f , so a variance estimate for this value is needed before the relationship between precision and number of independent runs can be determined. So, preliminary runs can be generated to get an idea of the variance magnitude. The worst case will be the broad ...
Communicate your thinking clearly and completely.
... just been discovered that an observation which was erroneously recorded as “30” actually had a value of “35.” If we make this correction to the data, then (a) the mean remains the same, but the median is increased. (b) the mean and median remain the same. (c) the median remains the same, but the mea ...
... just been discovered that an observation which was erroneously recorded as “30” actually had a value of “35.” If we make this correction to the data, then (a) the mean remains the same, but the median is increased. (b) the mean and median remain the same. (c) the median remains the same, but the mea ...
Estimating the sample mean and standard deviation from the
... frequently encountered scenarios, respectively. For the first two scenarios, our method greatly improves existing methods and provides a nearly unbiased estimate of the true sample standard deviation for normal data and a slightly biased estimate for skewed data. For the third scenario, our method s ...
... frequently encountered scenarios, respectively. For the first two scenarios, our method greatly improves existing methods and provides a nearly unbiased estimate of the true sample standard deviation for normal data and a slightly biased estimate for skewed data. For the third scenario, our method s ...
Class 4. Leverage, residuals and influence
... A new plot. Leverage vs. studentized residual. Points that drive the regression have big leverage and extreme studentized residuals. The delete one idea works pretty well, except when there is a second data point lying close by. In this case the second point can drive the regression line, masking th ...
... A new plot. Leverage vs. studentized residual. Points that drive the regression have big leverage and extreme studentized residuals. The delete one idea works pretty well, except when there is a second data point lying close by. In this case the second point can drive the regression line, masking th ...
File
... This is clearly greater than 1.0, but is it sufficiently greater to infer that the null hypothesis of equal variances must be rejected? We need a sampling distribution for F'. This is found in Appendix 3 (pp. 544546). Notice that the tables in this appendix are threedimensional tables, i.e., their ...
... This is clearly greater than 1.0, but is it sufficiently greater to infer that the null hypothesis of equal variances must be rejected? We need a sampling distribution for F'. This is found in Appendix 3 (pp. 544546). Notice that the tables in this appendix are threedimensional tables, i.e., their ...
32. STATISTICS 32. Statistics 1
... a probabilistic model, e.g., to assess the model’s validity or to determine the values of its parameters. There are two main approaches to statistical inference, which we may call frequentist and Bayesian. In frequentist statistics, probability is interpreted as the frequency of the outcome of a rep ...
... a probabilistic model, e.g., to assess the model’s validity or to determine the values of its parameters. There are two main approaches to statistical inference, which we may call frequentist and Bayesian. In frequentist statistics, probability is interpreted as the frequency of the outcome of a rep ...
Bootstrapping (statistics)

In statistics, bootstrapping can refer to any test or metric that relies on random sampling with replacement. Bootstrapping allows assigning measures of accuracy (defined in terms of bias, variance, confidence intervals, prediction error or some other such measure) to sample estimates. This technique allows estimation of the sampling distribution of almost any statistic using random sampling methods. Generally, it falls in the broader class of resampling methods.Bootstrapping is the practice of estimating properties of an estimator (such as its variance) by measuring those properties when sampling from an approximating distribution. One standard choice for an approximating distribution is the empirical distribution function of the observed data. In the case where a set of observations can be assumed to be from an independent and identically distributed population, this can be implemented by constructing a number of resamples with replacement, of the observed dataset (and of equal size to the observed dataset).It may also be used for constructing hypothesis tests. It is often used as an alternative to statistical inference based on the assumption of a parametric model when that assumption is in doubt, or where parametric inference is impossible or requires complicated formulas for the calculation of standard errors.