Final Exam Study Guide Spring 2003 FAMR 380
... A researcher wants to know whether college students start saving more money for postcollege life as they near the end of the college careers. The researcher surveys a random sample of 1,000 undergraduate students enrolled in 100 different four-year colleges. Each student was asked to report (a) how ...
... A researcher wants to know whether college students start saving more money for postcollege life as they near the end of the college careers. The researcher surveys a random sample of 1,000 undergraduate students enrolled in 100 different four-year colleges. Each student was asked to report (a) how ...
Section 1-3
... display quantitative data, the boxplot. • Draw and label a number line that includes the range of the distribution. • Draw a central box from Q1 to Q3. • Note the median M inside the box. ...
... display quantitative data, the boxplot. • Draw and label a number line that includes the range of the distribution. • Draw a central box from Q1 to Q3. • Note the median M inside the box. ...
Chapter 1 Descriptive Statistics
... numbers; the lower and upper class which is called class. Class is in first column for frequency distribution table. *Classes always represent a variable, non-overlapping; each value is belong to one and only one class. The numbers listed in second column are called frequencies, which gives the numb ...
... numbers; the lower and upper class which is called class. Class is in first column for frequency distribution table. *Classes always represent a variable, non-overlapping; each value is belong to one and only one class. The numbers listed in second column are called frequencies, which gives the numb ...
Document
... • From the approximation we observe the bellshaped appearance of the distribution. • In practice, we select only one simple random sample from the population. • We repeated the sampling process 500 times in this section simply to illustrate that many different samples are possible and that the diffe ...
... • From the approximation we observe the bellshaped appearance of the distribution. • In practice, we select only one simple random sample from the population. • We repeated the sampling process 500 times in this section simply to illustrate that many different samples are possible and that the diffe ...
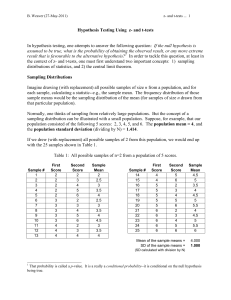
Statistical Inference - Complementary Course of
... based on a sample taken from the population. The process of making inferences about the population based on samples taken from it is called statistical inference or inferential statistics. We have already discussed the sampling theory which deals with the methods of selecting samples from the given ...
... based on a sample taken from the population. The process of making inferences about the population based on samples taken from it is called statistical inference or inferential statistics. We have already discussed the sampling theory which deals with the methods of selecting samples from the given ...
6/25/97 502as1
... 2. How would your results change if the sample of 21 had been taken from a population of 100? 3. Assume that the population standard deviation is 6.00 (and that the sample of 21 is taken from a very large population). Find z .0005 using the Normal table (If you have several values of z that you can ...
... 2. How would your results change if the sample of 21 had been taken from a population of 100? 3. Assume that the population standard deviation is 6.00 (and that the sample of 21 is taken from a very large population). Find z .0005 using the Normal table (If you have several values of z that you can ...
Measures of Position
... 5) You will see a list of numerical values for the data, including x Med 7.35 . The median value of the birthweights for sample of babies was 7.35 pounds. Properties of the Median: 1) The median is used when one must find the center or middle value of a data set. 2) The median is used when one m ...
... 5) You will see a list of numerical values for the data, including x Med 7.35 . The median value of the birthweights for sample of babies was 7.35 pounds. Properties of the Median: 1) The median is used when one must find the center or middle value of a data set. 2) The median is used when one m ...
Lecture4
... We want a measure which shows how far away most of the data points are from the mean. One option is to keep track of the average distance each point is from the mean. ...
... We want a measure which shows how far away most of the data points are from the mean. One option is to keep track of the average distance each point is from the mean. ...
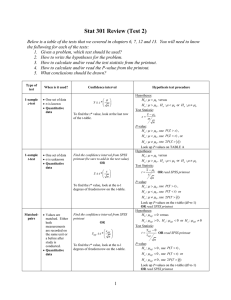
Chapter 6: Confidence Intervals
... The t-Distribution When a sample size is less than 30, and the random variable x is approximately normally distributed, it follow a t-distribution. t x μ s n Properties of the t-distribution 1. The t-distribution is bell shaped and symmetric about the mean. 2. The t-distribution is a family of cu ...
... The t-Distribution When a sample size is less than 30, and the random variable x is approximately normally distributed, it follow a t-distribution. t x μ s n Properties of the t-distribution 1. The t-distribution is bell shaped and symmetric about the mean. 2. The t-distribution is a family of cu ...
QNT 561 Final Exam - Assignment
... Want to check other classes..?? Visit http://www.studentehelp.com ...
... Want to check other classes..?? Visit http://www.studentehelp.com ...
Bootstrapping (statistics)

In statistics, bootstrapping can refer to any test or metric that relies on random sampling with replacement. Bootstrapping allows assigning measures of accuracy (defined in terms of bias, variance, confidence intervals, prediction error or some other such measure) to sample estimates. This technique allows estimation of the sampling distribution of almost any statistic using random sampling methods. Generally, it falls in the broader class of resampling methods.Bootstrapping is the practice of estimating properties of an estimator (such as its variance) by measuring those properties when sampling from an approximating distribution. One standard choice for an approximating distribution is the empirical distribution function of the observed data. In the case where a set of observations can be assumed to be from an independent and identically distributed population, this can be implemented by constructing a number of resamples with replacement, of the observed dataset (and of equal size to the observed dataset).It may also be used for constructing hypothesis tests. It is often used as an alternative to statistical inference based on the assumption of a parametric model when that assumption is in doubt, or where parametric inference is impossible or requires complicated formulas for the calculation of standard errors.