A Review and Comparison of Methods for Detecting Outliers in
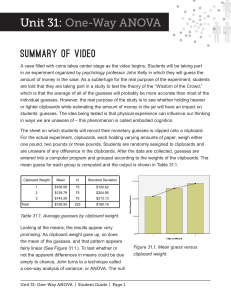
... analyses such as the t-test, ANOVA, and regression, but mainly to find the extreme values away from the majority of the data regardless of the distribution, the outlier labeling methods may be applicable. In addition, for a large data set that is statistically problematic, e.g., when it is difficult ...
... analyses such as the t-test, ANOVA, and regression, but mainly to find the extreme values away from the majority of the data regardless of the distribution, the outlier labeling methods may be applicable. In addition, for a large data set that is statistically problematic, e.g., when it is difficult ...
Variability
... - Count on fingers from low number to high number 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 = 8 numbers Problem: range only takes into account two scores These data sets have the same range: A) 1 1 2 2 98 98 99 100 B) 1 99 99 99 99 99 100 C) 1 10 30 50 70 90 100 C. Standard Deviation Measure of the typical distance score ...
... - Count on fingers from low number to high number 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 = 8 numbers Problem: range only takes into account two scores These data sets have the same range: A) 1 1 2 2 98 98 99 100 B) 1 99 99 99 99 99 100 C) 1 10 30 50 70 90 100 C. Standard Deviation Measure of the typical distance score ...
Statistical versus Practical Significance
... strong that it would happen no more than 5% of the time (1 time in 20) when H0 is true. ...
... strong that it would happen no more than 5% of the time (1 time in 20) when H0 is true. ...
Understanding Variability and Statistical Decision
... ‘spread’ of the distribution is a function of unsystematic variability, and can be estimated using the SDs for the sample. ...
... ‘spread’ of the distribution is a function of unsystematic variability, and can be estimated using the SDs for the sample. ...
Business Statistics: A First Course -
... over the 5 year life cycle of the product will be $1.5 million. If moderately successful, net profit will reach $1.2 million. If unsuccessful, the firm anticipates zero cash inflows. The firms assigns the following probabilities to the 5-year prospects for this product: successful, .60; moderately s ...
... over the 5 year life cycle of the product will be $1.5 million. If moderately successful, net profit will reach $1.2 million. If unsuccessful, the firm anticipates zero cash inflows. The firms assigns the following probabilities to the 5-year prospects for this product: successful, .60; moderately s ...
Bootstrapping (statistics)

In statistics, bootstrapping can refer to any test or metric that relies on random sampling with replacement. Bootstrapping allows assigning measures of accuracy (defined in terms of bias, variance, confidence intervals, prediction error or some other such measure) to sample estimates. This technique allows estimation of the sampling distribution of almost any statistic using random sampling methods. Generally, it falls in the broader class of resampling methods.Bootstrapping is the practice of estimating properties of an estimator (such as its variance) by measuring those properties when sampling from an approximating distribution. One standard choice for an approximating distribution is the empirical distribution function of the observed data. In the case where a set of observations can be assumed to be from an independent and identically distributed population, this can be implemented by constructing a number of resamples with replacement, of the observed dataset (and of equal size to the observed dataset).It may also be used for constructing hypothesis tests. It is often used as an alternative to statistical inference based on the assumption of a parametric model when that assumption is in doubt, or where parametric inference is impossible or requires complicated formulas for the calculation of standard errors.