Hypothesis Testing: Example
... employees are superior and that, if we gave this test to our current employees, the mean of the test would be more than 500. The company which designs the test cannot help us directly as, although they know the typical performance of a test taker, they do not know the typical performance of our empl ...
... employees are superior and that, if we gave this test to our current employees, the mean of the test would be more than 500. The company which designs the test cannot help us directly as, although they know the typical performance of a test taker, they do not know the typical performance of our empl ...
A Little Stats Won't Hurt You
... quantify what happened (“What is the effect of X on Y ?”). But before any of these more complex methods can be used, the first step is always to look at the data in many different ways. The idea is to effectively describe (or summarize) the data, and then look for “interesting” features. Note, howev ...
... quantify what happened (“What is the effect of X on Y ?”). But before any of these more complex methods can be used, the first step is always to look at the data in many different ways. The idea is to effectively describe (or summarize) the data, and then look for “interesting” features. Note, howev ...
252y0552 - On-line Web Courses
... IV. Do sections adding to at least 20 points - Anything extra you do helps, and grades wrap around) . Show your work! State H 0 and H 1 where appropriate. You have not done a hypothesis test unless you have stated your hypotheses, run the numbers and stated your conclusion. (Use a 95% confidence lev ...
... IV. Do sections adding to at least 20 points - Anything extra you do helps, and grades wrap around) . Show your work! State H 0 and H 1 where appropriate. You have not done a hypothesis test unless you have stated your hypotheses, run the numbers and stated your conclusion. (Use a 95% confidence lev ...
Chapters 6 -7 - Department of Agriculture and Water Resources
... inference (e.g. analysis of variance, t-tests, F tests, etc.). These methods have served researchers from a variety of backgrounds and disciplines extremely well over many years. However, there is growing concern about their utility for environmental sampling and assessment. When natural ecosystems ...
... inference (e.g. analysis of variance, t-tests, F tests, etc.). These methods have served researchers from a variety of backgrounds and disciplines extremely well over many years. However, there is growing concern about their utility for environmental sampling and assessment. When natural ecosystems ...
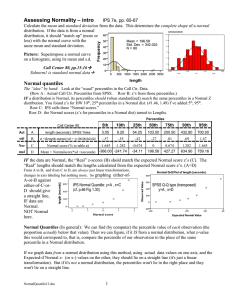
Normal quantile plots
... distances from the line, reversed! Does this help in interpreting? I’m not sure. ...
... distances from the line, reversed! Does this help in interpreting? I’m not sure. ...
Minitab Orientation - Austin Community College
... house size less than or equal to 2 was 0.251 + 0.321 = 0.572. Since a sample size of 1000 is quite large, we would expect that the observed proportion from our simulation would be close to the value of the probability from the population, and it is, since 0.575 is very close to 0.572. ...
... house size less than or equal to 2 was 0.251 + 0.321 = 0.572. Since a sample size of 1000 is quite large, we would expect that the observed proportion from our simulation would be close to the value of the probability from the population, and it is, since 0.575 is very close to 0.572. ...
Graphical Representations of Data
... Often, when the data are numeric, there are too many different data values for a listing of the raw data to be of use in seeing the characteristics of the data. It is common to divide the interval of values of the data into a relatively small number of subintervals, called classes, and to tabulate t ...
... Often, when the data are numeric, there are too many different data values for a listing of the raw data to be of use in seeing the characteristics of the data. It is common to divide the interval of values of the data into a relatively small number of subintervals, called classes, and to tabulate t ...
SSG3 230 - public.asu.edu
... 3. Based on only two scores; 4. A crude measure and is not recommended for descriptive statistics; 5. Rarely used in inferential statistics. The standard deviation is: 1. A measure of the positive square root of the average squared distance of scores from the mean; 2. Calculated in 3 steps--(a) find ...
... 3. Based on only two scores; 4. A crude measure and is not recommended for descriptive statistics; 5. Rarely used in inferential statistics. The standard deviation is: 1. A measure of the positive square root of the average squared distance of scores from the mean; 2. Calculated in 3 steps--(a) find ...
Bootstrapping (statistics)

In statistics, bootstrapping can refer to any test or metric that relies on random sampling with replacement. Bootstrapping allows assigning measures of accuracy (defined in terms of bias, variance, confidence intervals, prediction error or some other such measure) to sample estimates. This technique allows estimation of the sampling distribution of almost any statistic using random sampling methods. Generally, it falls in the broader class of resampling methods.Bootstrapping is the practice of estimating properties of an estimator (such as its variance) by measuring those properties when sampling from an approximating distribution. One standard choice for an approximating distribution is the empirical distribution function of the observed data. In the case where a set of observations can be assumed to be from an independent and identically distributed population, this can be implemented by constructing a number of resamples with replacement, of the observed dataset (and of equal size to the observed dataset).It may also be used for constructing hypothesis tests. It is often used as an alternative to statistical inference based on the assumption of a parametric model when that assumption is in doubt, or where parametric inference is impossible or requires complicated formulas for the calculation of standard errors.