intelligence without reason
... 1943, and others less known to the modern Artificial Intelligence world as early as 1941, about using a computer to play chess. He and others developed the idea of minimizing a tree of moves, and of static evaluation, and carried out elaborate hand simulations against human opponents. In a paper tit ...
... 1943, and others less known to the modern Artificial Intelligence world as early as 1941, about using a computer to play chess. He and others developed the idea of minimizing a tree of moves, and of static evaluation, and carried out elaborate hand simulations against human opponents. In a paper tit ...
Management and Artificial Intelligence: Note
... Artificial intelligence is branch of Computer Science working similar to human brain. It gives rise to human intelligence through the machine perspective. The research in Artificial intelligence started in 1956. The ...
... Artificial intelligence is branch of Computer Science working similar to human brain. It gives rise to human intelligence through the machine perspective. The research in Artificial intelligence started in 1956. The ...
Document
... concerned with designing intelligent computer systems, that is, systems that exhibit the characteristics we associate with intelligence in human behavior - understanding language, reasoning, solving problems, and so on. ...
... concerned with designing intelligent computer systems, that is, systems that exhibit the characteristics we associate with intelligence in human behavior - understanding language, reasoning, solving problems, and so on. ...
AI-01a- Intro - Computer Engineering
... You are trying to come up with an algorithm to solve a problem using other algorithms you are familiar with. You have meta-knowledge about how one should think about algorithms, and you use this knowledge to critique your algorithm as you create it. A stranger passing you on the street notices your ...
... You are trying to come up with an algorithm to solve a problem using other algorithms you are familiar with. You have meta-knowledge about how one should think about algorithms, and you use this knowledge to critique your algorithm as you create it. A stranger passing you on the street notices your ...
Vorlesung Grundlagen der Künstlichen Intelligenz
... successful knowledge-based program for scientific reasoning. Joel Moses (PhD work at MIT) demonstrated the power of symbolic reasoning for integration problems in the Macsyma program. First successful knowledge-based program in mathematics. Richard Greenblatt at MIT built a knowledge-based chess-pla ...
... successful knowledge-based program for scientific reasoning. Joel Moses (PhD work at MIT) demonstrated the power of symbolic reasoning for integration problems in the Macsyma program. First successful knowledge-based program in mathematics. Richard Greenblatt at MIT built a knowledge-based chess-pla ...
On The Intersection Of Human-Computer
... When Lieberman published an opinion piece about the relationship between the fields of human-computer interaction and artificial intelligence, he concluded that they ultimately have the same goal - making user interfaces more effective and easier for people to use – and that together, the community ...
... When Lieberman published an opinion piece about the relationship between the fields of human-computer interaction and artificial intelligence, he concluded that they ultimately have the same goal - making user interfaces more effective and easier for people to use – and that together, the community ...
Artificial Intelligence - SVIT
... Variables, Iteration and Recursion, Property Lists and Arrays, Miscellaneous Topics, LISP and Other AI Programming Languages. ...
... Variables, Iteration and Recursion, Property Lists and Arrays, Miscellaneous Topics, LISP and Other AI Programming Languages. ...
Metody Inteligencji Obliczeniowej
... Hilbert delivered what is now considered the most important talk ever given in the history of mathematics, proposing 23 major problems worth working at in future. 100 years later the impact of this talk is still strong: some problems have been solved, new problems have been added, but the direction ...
... Hilbert delivered what is now considered the most important talk ever given in the history of mathematics, proposing 23 major problems worth working at in future. 100 years later the impact of this talk is still strong: some problems have been solved, new problems have been added, but the direction ...
What is computing? Counting, calculating The discipline of
... SC consists of several computing paradigms including: NN Fuzzy set theory Approximate reasoning ...
... SC consists of several computing paradigms including: NN Fuzzy set theory Approximate reasoning ...
NEW TRENDS IN NEUROCYBERNETICS
... A very interesting path of development of modern neurocybernetics is the so-called "embodied cognition" and the enactivism concept (Barsalou, 2009). Adherents of this approach use a converted version of a well-known drawing by Leonardo da Vinci (figure 6) to argue that intelligence is shaped in acti ...
... A very interesting path of development of modern neurocybernetics is the so-called "embodied cognition" and the enactivism concept (Barsalou, 2009). Adherents of this approach use a converted version of a well-known drawing by Leonardo da Vinci (figure 6) to argue that intelligence is shaped in acti ...
Programming and Problem Solving with Java: Chapter 14
... This is the view that a sufficiently programmed computer would actually be intelligent and would think in the same way that a human does. ...
... This is the view that a sufficiently programmed computer would actually be intelligent and would think in the same way that a human does. ...
Evaluation of the Program 2008
... interdisciplinary approach to studies of the brain and mind, and remains one of the few that have managed to do so successfully. It integrates Basic Neurobiology with Computational Neuroscience, Artificial Intelligence, and Social/Cognitive Neuroscience, and it trains the next generation of scientis ...
... interdisciplinary approach to studies of the brain and mind, and remains one of the few that have managed to do so successfully. It integrates Basic Neurobiology with Computational Neuroscience, Artificial Intelligence, and Social/Cognitive Neuroscience, and it trains the next generation of scientis ...
SVIZBOOK - Department of Intelligent Systems
... (Merton system: intelligent system: computer-human tandem) Peter F. Drucker: The best way to predict the future is to make it. Herbert A. Simon: Bounded rationality: agents have limited knowledge (information and cognitive) to optimize their expected benefits; behavioral economics; Nobel Prize for d ...
... (Merton system: intelligent system: computer-human tandem) Peter F. Drucker: The best way to predict the future is to make it. Herbert A. Simon: Bounded rationality: agents have limited knowledge (information and cognitive) to optimize their expected benefits; behavioral economics; Nobel Prize for d ...
SVIZBOOK - Department of Intelligent Systems
... agents"[2] where an intelligent agent is a system that perceives its environment and takes actions that maximize its chances of success. [3] John McCarthy, who coined the term in 1956,[4] defines it as "the science and engineering of making intelligent machines."[5] (Artificial intelligence has been ...
... agents"[2] where an intelligent agent is a system that perceives its environment and takes actions that maximize its chances of success. [3] John McCarthy, who coined the term in 1956,[4] defines it as "the science and engineering of making intelligent machines."[5] (Artificial intelligence has been ...
Introduction to Artificial Intelligence
... Doesn't necessarily (but often) involve thinking Doesn’t necessarily have anything to do with how humans solve the same problem. ...
... Doesn't necessarily (but often) involve thinking Doesn’t necessarily have anything to do with how humans solve the same problem. ...
Phil 212 2008 - UKZN: Philosophy - University of KwaZulu
... Briefly outline the theory of evolution by natural selection and then explain in detail how evolutionary psychology employs evolution to understand the mind. Make sure to mention what evolutionary psychologists presume about (a) the period to which humans are adapted and (b) the connection between t ...
... Briefly outline the theory of evolution by natural selection and then explain in detail how evolutionary psychology employs evolution to understand the mind. Make sure to mention what evolutionary psychologists presume about (a) the period to which humans are adapted and (b) the connection between t ...
Intelligent Mobile Robotics
... Living Autonomously • An autonomous robot acts on its own decisions • Robots are not directly controlled by humans – Can take input and advice from humans ...
... Living Autonomously • An autonomous robot acts on its own decisions • Robots are not directly controlled by humans – Can take input and advice from humans ...
Autonomous Intelligent Mobile Robotics Presentation
... Living Autonomously • An autonomous robot acts on its own decisions • Robots are not directly controlled by humans – Can take input and advice from humans ...
... Living Autonomously • An autonomous robot acts on its own decisions • Robots are not directly controlled by humans – Can take input and advice from humans ...
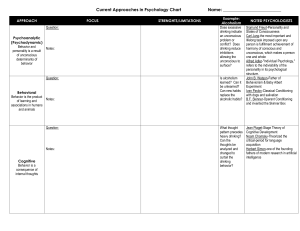
Current Approaches in Psychology Chart Name
... drinking indicate an unconscious problem or conflict? Does drinking reduce inhibitions allowing the unconscious to surface? Is alcoholism learned? Can it be unlearned? Can new habits replace the alcoholic habits? ...
... drinking indicate an unconscious problem or conflict? Does drinking reduce inhibitions allowing the unconscious to surface? Is alcoholism learned? Can it be unlearned? Can new habits replace the alcoholic habits? ...
Turing Test as a Defining Feature of AI-Completeness
... Now that Turing Test has been proven to be AI-Complete we have an additional way of showing other problems to be AI-Complete. We can either show that a problem is both in the set of AI problems and all other AI problem can be converted into it by some polynomial time algorithm or we can reduce any i ...
... Now that Turing Test has been proven to be AI-Complete we have an additional way of showing other problems to be AI-Complete. We can either show that a problem is both in the set of AI problems and all other AI problem can be converted into it by some polynomial time algorithm or we can reduce any i ...
2/3 MCA Second Semester CA4T3 ARTIFICIAL INTELLIGENCE
... introduce the basic principles in artificial intelligence research. It will cover simple representation schemes, problem solving paradigms, constraint propagation, and search strategies. Areas of application such as knowledge representation, natural language processing, expert systems, vision and ro ...
... introduce the basic principles in artificial intelligence research. It will cover simple representation schemes, problem solving paradigms, constraint propagation, and search strategies. Areas of application such as knowledge representation, natural language processing, expert systems, vision and ro ...
AIAI Presentation - Artificial Intelligence Applications Institute
... SONAT ENP data base extended with Binni data Direct DAML file processing from I-X to SONAT via HP JENA Toolkit SOAP Access to SAR Resources from KAoS and I-X via CMU MatchMaker and sample MM client code KAoS policy-governed access to SAR Resources Initial demonstration framework with CoSAR and US-SA ...
... SONAT ENP data base extended with Binni data Direct DAML file processing from I-X to SONAT via HP JENA Toolkit SOAP Access to SAR Resources from KAoS and I-X via CMU MatchMaker and sample MM client code KAoS policy-governed access to SAR Resources Initial demonstration framework with CoSAR and US-SA ...
chap.1
... explorers. The book is also big because we go into some depth in presenting results, although we strive to cover only the most central ideas in the main part of each chapter. Pointers are given to further results in the bibliographical notes at the end of each chapter. The subtitle of this book is " ...
... explorers. The book is also big because we go into some depth in presenting results, although we strive to cover only the most central ideas in the main part of each chapter. Pointers are given to further results in the bibliographical notes at the end of each chapter. The subtitle of this book is " ...
MIQ Understanding a Machine through Multiple Perspectives Analysis
... person is not allowed any other form of information from the outside but is allowed only to manipulate both the symbol and the appropriate story by referencing the instruction, that directs each answer to a corresponding question and story. He or she is also permitted to answer to those outside the ...
... person is not allowed any other form of information from the outside but is allowed only to manipulate both the symbol and the appropriate story by referencing the instruction, that directs each answer to a corresponding question and story. He or she is also permitted to answer to those outside the ...
Philosophy of artificial intelligence

The philosophy of artificial intelligence attempts to answer such questions as: Can a machine act intelligently? Can it solve any problem that a person would solve by thinking? Are human intelligence and machine intelligence the same? Is the human brain essentially a computer? Can a machine have a mind, mental states and consciousness in the same sense humans do? Can it feel how things are?These three questions reflect the divergent interests of AI researchers, cognitive scientists and philosophers respectively. The scientific answers to these questions depend on the definition of ""intelligence"" and ""consciousness"" and exactly which ""machines"" are under discussion.Important propositions in the philosophy of AI include:Turing's ""polite convention"": If a machine behaves as intelligently as a human being, then it is as intelligent as a human being. The Dartmouth proposal: ""Every aspect of learning or any other feature of intelligence can be so precisely described that a machine can be made to simulate it."" Newell and Simon's physical symbol system hypothesis: ""A physical symbol system has the necessary and sufficient means of general intelligent action."" Searle's strong AI hypothesis: ""The appropriately programmed computer with the right inputs and outputs would thereby have a mind in exactly the same sense human beings have minds."" Hobbes' mechanism: ""Reason is nothing but reckoning.""↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑ ↑