Analyses for Molecular Interactions in Living Cells
... complementation of the lacZ locus of E. coli, demonstrating that fragments of b-galactosidase that have no enzyme activity can associate spontaneously to generate an active complex GFP fragments fused to peptide sequences capable of producing an antiparallel coiled coil produced flurescent complexes ...
... complementation of the lacZ locus of E. coli, demonstrating that fragments of b-galactosidase that have no enzyme activity can associate spontaneously to generate an active complex GFP fragments fused to peptide sequences capable of producing an antiparallel coiled coil produced flurescent complexes ...
Response - Dublin City Schools
... as a gas (ethylene gas) Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
... as a gas (ethylene gas) Copyright © 2008 Pearson Education, Inc., publishing as Pearson Benjamin Cummings ...
Lecture 11
... interactions relay signals from receptors to target molecules in the cell • Signal transduction usually involves multiple steps • Multistep pathways can amplify a signal: A few molecules can produce a large cellular response • Multistep pathways provide more opportunities for coordination and regula ...
... interactions relay signals from receptors to target molecules in the cell • Signal transduction usually involves multiple steps • Multistep pathways can amplify a signal: A few molecules can produce a large cellular response • Multistep pathways provide more opportunities for coordination and regula ...
CKIP-1, a proinflammatory protein in macrophages interferes with
... Therefore, TNF reverse signaling appeared to have a negative regulatory role in inflammation, which is supported by the fact that reverse signaling has been shown to induce a temporary LPS resistance in monocytic cells. TNF reverse signaling has been shown to activate both proapoptotic and antiapopt ...
... Therefore, TNF reverse signaling appeared to have a negative regulatory role in inflammation, which is supported by the fact that reverse signaling has been shown to induce a temporary LPS resistance in monocytic cells. TNF reverse signaling has been shown to activate both proapoptotic and antiapopt ...
Vascular Smooth Muscle Cells activation revealed by quantitative
... Vascular smooth-muscle cells (VSMCs) are the main components of the artery medial layer and if activated by growth factors as a consequence of vessel injuries, acquire the ability to proliferate and migrate contributing to the formation of neointima. In the early phase/events of VSMC stimulation a c ...
... Vascular smooth-muscle cells (VSMCs) are the main components of the artery medial layer and if activated by growth factors as a consequence of vessel injuries, acquire the ability to proliferate and migrate contributing to the formation of neointima. In the early phase/events of VSMC stimulation a c ...
The Sevenless signaling pathway
... interact with SOS. Since STY expression is dependent on activity of the same pathway that it regulates, this provides an e¤cient way to terminate or modulate RTK signaling and thereby preventing inappropriate cellular responses due to sustained signaling. 4. Downstream of Ras Signal propagation from ...
... interact with SOS. Since STY expression is dependent on activity of the same pathway that it regulates, this provides an e¤cient way to terminate or modulate RTK signaling and thereby preventing inappropriate cellular responses due to sustained signaling. 4. Downstream of Ras Signal propagation from ...
Figure 17.12 Translation: the basic concept
... Figure 17.5 A tobacco plant expressing a firefly gene ...
... Figure 17.5 A tobacco plant expressing a firefly gene ...
Regulation of Muscle Protein Synthesis and
... through the IkB kinase (IKK) complex that functions to phosphorylate and induce IkB degradation to release NF-κB to the nucleus where it binds its cognate DNA sequences to regulate gene expression. One gene related to the ubiquitin proteasome system that it is thought to be regulated by NF-κB is MuR ...
... through the IkB kinase (IKK) complex that functions to phosphorylate and induce IkB degradation to release NF-κB to the nucleus where it binds its cognate DNA sequences to regulate gene expression. One gene related to the ubiquitin proteasome system that it is thought to be regulated by NF-κB is MuR ...
3.B-C-D Expectations
... DEFINE morphogenesis DEFINE apoptosis DEFINE insertion sequence DEFINE transposon DEFINE prophage and provirus DEFINE phage DEFINE phosphorylation STATE that most signal molecules are water soluble and bind to receptors on the plasma membrane STATE that testosterone (a steroid) is a lipid soluble ch ...
... DEFINE morphogenesis DEFINE apoptosis DEFINE insertion sequence DEFINE transposon DEFINE prophage and provirus DEFINE phage DEFINE phosphorylation STATE that most signal molecules are water soluble and bind to receptors on the plasma membrane STATE that testosterone (a steroid) is a lipid soluble ch ...
Jan06_Alpha_Project_Retreat
... Custom (simpler) transcriptional control – Get rid of cell-cycle regulation – Get rid of feedback loops – Express genes from custom constitutive or inducible/repressible promoters Simpler response – Remove genes known to be involved in, but not essential to, mating Easier to manipulate – Put all gen ...
... Custom (simpler) transcriptional control – Get rid of cell-cycle regulation – Get rid of feedback loops – Express genes from custom constitutive or inducible/repressible promoters Simpler response – Remove genes known to be involved in, but not essential to, mating Easier to manipulate – Put all gen ...
Thyroid Hormone Receptor: Dimers, Dimers, Dimers
... Nuclear reactors are intracellular receptors as well as transcription factors. They respond through physical interactions with their respective ligands. These ligands are small, hydrophobic signaling molecules such as steroid hormones. Once the ligand is bound, co-activators or co-repressors may be ...
... Nuclear reactors are intracellular receptors as well as transcription factors. They respond through physical interactions with their respective ligands. These ligands are small, hydrophobic signaling molecules such as steroid hormones. Once the ligand is bound, co-activators or co-repressors may be ...
Understanding Embryonic Development: A
... embryo, some of which are localized by cytoplasmic movements following fertilization (reviewed by Gerhart, 1987), but there is no evidence at all for such determinants in mammalian eggs. Certain particular forms of regulatory requirement are implied by the biological processes of higher vertebrate e ...
... embryo, some of which are localized by cytoplasmic movements following fertilization (reviewed by Gerhart, 1987), but there is no evidence at all for such determinants in mammalian eggs. Certain particular forms of regulatory requirement are implied by the biological processes of higher vertebrate e ...
Chapter 11 - My Teacher Site
... • The G protein is loosely attached to cytoplasmic side of membrane • It functions as a molecular switch that is either “on” or “off” • Inactive form: GDP (guanosine diphosphate) is bound to G protein • Active form: GTP (guanosine triphosphate) is bound to G protein • The receptor and G protein work ...
... • The G protein is loosely attached to cytoplasmic side of membrane • It functions as a molecular switch that is either “on” or “off” • Inactive form: GDP (guanosine diphosphate) is bound to G protein • Active form: GTP (guanosine triphosphate) is bound to G protein • The receptor and G protein work ...
Cell communication
... initiate a signal-transduction system 2. Compare and contrast G protein-coupled receptors, tyrosine kinase receptors, and ligandgated ion channels 3. List two advantages of a multistep pathway in the transduction stage of cell signaling 4. Explain how an original signal molecule can produce a cellul ...
... initiate a signal-transduction system 2. Compare and contrast G protein-coupled receptors, tyrosine kinase receptors, and ligandgated ion channels 3. List two advantages of a multistep pathway in the transduction stage of cell signaling 4. Explain how an original signal molecule can produce a cellul ...
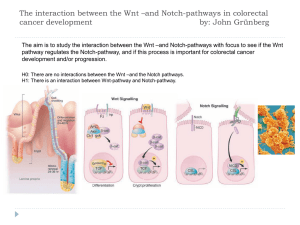
The interaction between the Wnt –and Notch-pathways in
... other way around, between Notch inhibition and Wnt pathway through β-catenin signalling. Using gamma-secretase inhibitors may provide a targeted-drug strategy for treating human colorectal cancer, because of the close correlation between the Notch and Wnt pathway ...
... other way around, between Notch inhibition and Wnt pathway through β-catenin signalling. Using gamma-secretase inhibitors may provide a targeted-drug strategy for treating human colorectal cancer, because of the close correlation between the Notch and Wnt pathway ...
lecture 4
... - greater than 50% of all cellular proteins assemble into higher-order structures - either oligomers of identical proteins (homo-oligomers) or of different proteins (hetero-oligomers) - activity of most oligomers strictly depend on their proper assembly - example of what can go wrong: - von Hippel-L ...
... - greater than 50% of all cellular proteins assemble into higher-order structures - either oligomers of identical proteins (homo-oligomers) or of different proteins (hetero-oligomers) - activity of most oligomers strictly depend on their proper assembly - example of what can go wrong: - von Hippel-L ...
Mapping functional regions of the segment
... subfamily of proteins that have very similar zinc fingers and which recognize identical or very closely related GC-rich sequences. So far, three other members have been identified: Krox-24 (also known as Egr-1, Zif268, NGFI-A and TIS8 (8-12)), EGR-3 (13) and NGFI-C (14). Although these proteins are ...
... subfamily of proteins that have very similar zinc fingers and which recognize identical or very closely related GC-rich sequences. So far, three other members have been identified: Krox-24 (also known as Egr-1, Zif268, NGFI-A and TIS8 (8-12)), EGR-3 (13) and NGFI-C (14). Although these proteins are ...
Chapter 8 Principles of Development
... actively dividing cytoplasm confined to narrow shaped disc mass on yolk cleavage is partial (meroblastic): furrow does not cut through the yolk birds, reptiles, most fishes & few amphibians ...
... actively dividing cytoplasm confined to narrow shaped disc mass on yolk cleavage is partial (meroblastic): furrow does not cut through the yolk birds, reptiles, most fishes & few amphibians ...
Control of Metabolism and Growth Through Insulin-Like
... (CC) of the ring gland, and constitute a small population of neuroendocrine cells that oppose the action of the IPCs (2,6). These two neuroendocrine cell populations differentiate during embryogenesis and project axons that contact the open hemolymph circulation as well as each other. Together, they ...
... (CC) of the ring gland, and constitute a small population of neuroendocrine cells that oppose the action of the IPCs (2,6). These two neuroendocrine cell populations differentiate during embryogenesis and project axons that contact the open hemolymph circulation as well as each other. Together, they ...
Racial differences in B cell receptor signaling pathway activation
... Background: Single-cell network profiling (SCNP) is a multi-parametric flow cytometry-based approach that simultaneously measures basal and modulated intracellular signaling activity in multiple cell subpopulations. Previously, SCNP analysis of a broad panel of immune signaling pathways in cell subs ...
... Background: Single-cell network profiling (SCNP) is a multi-parametric flow cytometry-based approach that simultaneously measures basal and modulated intracellular signaling activity in multiple cell subpopulations. Previously, SCNP analysis of a broad panel of immune signaling pathways in cell subs ...
Document
... • Remember: a single B-cell makes a single type of antibody – or, more precisely, a single idiotype ...
... • Remember: a single B-cell makes a single type of antibody – or, more precisely, a single idiotype ...
Calcium signaling in polycystic kidney disease
... the mid 1990s, two genes, PKD1 and PKD2, were identified as the sites of mutations responsible for ADPKD, with virtually indistinguishable pathologies. The molecular characterization of these genes was achieved by positional cloning [2,3], facilitated by early phases of the human genome project. The ...
... the mid 1990s, two genes, PKD1 and PKD2, were identified as the sites of mutations responsible for ADPKD, with virtually indistinguishable pathologies. The molecular characterization of these genes was achieved by positional cloning [2,3], facilitated by early phases of the human genome project. The ...
Snails, Synapses and Smokers
... Roel Nusse Signals that guide embryonic cells through development are often under the control of inhibitors. It now seems that one such inhibitor does not bind to the signal itself, but rather to the receptor that detects the signal. typical cell’s network of signal-transduction pathways has so many ...
... Roel Nusse Signals that guide embryonic cells through development are often under the control of inhibitors. It now seems that one such inhibitor does not bind to the signal itself, but rather to the receptor that detects the signal. typical cell’s network of signal-transduction pathways has so many ...
Hedgehog signaling pathway

The Hedgehog signaling pathway (or signalling pathway; see spelling differences) is a signaling pathway that transmits information to embryonic cells required for proper development. Different parts of the embryo have different concentrations of hedgehog signaling proteins. The pathway also has roles in the adult. Diseases associated with the malfunction of this pathway include basal cell carcinoma.The Hedgehog signaling pathway is one of the key regulators of animal development and is present in all bilaterians. The pathway takes its name from its polypeptide ligand, an intercellular signaling molecule called Hedgehog (Hh) found in fruit flies of the genus Drosophila. Hh is one of Drosophila's segment polarity gene products, involved in establishing the basis of the fly body plan. The molecule remains important during later stages of embryogenesis and metamorphosis.Mammals have three Hedgehog homologues, DHH, IHH, and SHH, of which Sonic (SHH) is the best studied. The pathway is equally important during vertebrate embryonic development. In knockout mice lacking components of the pathway, the brain, skeleton, musculature, gastrointestinal tract and lungs fail to develop correctly. Recent studies point to the role of Hedgehog signaling in regulating adult stem cells involved in maintenance and regeneration of adult tissues. The pathway has also been implicated in the development of some cancers. Drugs that specifically target Hedgehog signaling to fight this disease are being actively developed by a number of pharmaceutical companies.