Developing Consumer Marketing Claims within the Clinical
... Propulsid (cisapride) Rezulin (troglitazone) Lotronex (alosetron HCl) Raplon (rapcuronium) Baycol (cerivaxtatin) Vioxx (rofecoxib) 92 NME’s from 1998-2000 ...
... Propulsid (cisapride) Rezulin (troglitazone) Lotronex (alosetron HCl) Raplon (rapcuronium) Baycol (cerivaxtatin) Vioxx (rofecoxib) 92 NME’s from 1998-2000 ...
Lecture 19
... Catecholamines: -They work at two receptors (α,β) -α receptor are excitatory (constriction effect) -β receptor inhibitory on smooth muscle -β1 found in the heart -β2 found in the lung this not from the lecture it can help you to understand the receptors : -α1 : mainly effect is constriction -α2: mai ...
... Catecholamines: -They work at two receptors (α,β) -α receptor are excitatory (constriction effect) -β receptor inhibitory on smooth muscle -β1 found in the heart -β2 found in the lung this not from the lecture it can help you to understand the receptors : -α1 : mainly effect is constriction -α2: mai ...
Prescription_Drugs_Information_Fact_Sheet
... (sedatives). The most commonly misused classes of prescription drugs in Australia are benzodiazepines and opioid analgesics. The benzodiazepines are prescribed to relieve anxiety and to treat panic attacks and insomnia. Some sedatives contain barbiturates but benzodiazepines are more commonly used n ...
... (sedatives). The most commonly misused classes of prescription drugs in Australia are benzodiazepines and opioid analgesics. The benzodiazepines are prescribed to relieve anxiety and to treat panic attacks and insomnia. Some sedatives contain barbiturates but benzodiazepines are more commonly used n ...
Epinephrine
... inc. blood return to heart, inc. circulation, inc. BP 2. Alpha-2 = inhibits release of norepinephrine dec. in vasoconstriction, dec. BP 3. Beta-1 = inc. in heart rate & force on contraction 4. Beta-2 = relaxation of smooth muscle in bronchi, ...
... inc. blood return to heart, inc. circulation, inc. BP 2. Alpha-2 = inhibits release of norepinephrine dec. in vasoconstriction, dec. BP 3. Beta-1 = inc. in heart rate & force on contraction 4. Beta-2 = relaxation of smooth muscle in bronchi, ...
Psychoactive Drugs - Hinsdale Central High School
... yellowish crystals are crushed and smoked, injected, or inhaled. The effects last for hours. Effects = euphoria, loss of appetite, increased alertness, hyperactivity. Extremely addictive! Dangers = permanent brain damage, kidney and liver damage. Cocaine (snow, rock) = comes from the coca plant. As ...
... yellowish crystals are crushed and smoked, injected, or inhaled. The effects last for hours. Effects = euphoria, loss of appetite, increased alertness, hyperactivity. Extremely addictive! Dangers = permanent brain damage, kidney and liver damage. Cocaine (snow, rock) = comes from the coca plant. As ...
Adolescent Drug Trends “It Wasn’t Like That when You were A Teen….”
... 1 in 5 teens has abused a prescription (Rx) pain medication 1 in 5 report abusing prescription stimulants and tranquilizers Many teens think these drugs are safe because they have legitimate uses, but taking them without a prescription to get high or “self-medicate” can be as dangerous – and addi ...
... 1 in 5 teens has abused a prescription (Rx) pain medication 1 in 5 report abusing prescription stimulants and tranquilizers Many teens think these drugs are safe because they have legitimate uses, but taking them without a prescription to get high or “self-medicate” can be as dangerous – and addi ...
2014.9.16 What do synapses learn from stress?
... The physiological response to stress requires coordinated behavioral and visceral responses. The latter rely on the release of corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) from the terminals of neurons located in the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) of the hypothalamus. The long-term effects of stress on the ...
... The physiological response to stress requires coordinated behavioral and visceral responses. The latter rely on the release of corticotropin releasing hormone (CRH) from the terminals of neurons located in the paraventricular nucleus (PVN) of the hypothalamus. The long-term effects of stress on the ...
Chapter 16
... • Increase drowsiness and sedation • Produce mild state of euphoria, reduction in inhibitions, feeling of relaxation • May impair mood, speech, and motor coordination ...
... • Increase drowsiness and sedation • Produce mild state of euphoria, reduction in inhibitions, feeling of relaxation • May impair mood, speech, and motor coordination ...
Miriam AsgadomeSammanf
... structures and target areas, but what they all have in common is that they have the ability to increase the concentration of dopamine in the brain. This is a signal substance in the brain that causes a pleasant sensation in the reward pathway. This pathway is important in the human brain because it ...
... structures and target areas, but what they all have in common is that they have the ability to increase the concentration of dopamine in the brain. This is a signal substance in the brain that causes a pleasant sensation in the reward pathway. This pathway is important in the human brain because it ...
Risk Lists for Informed Consent
... The drugs used in this study may have side effects, some of which are listed below. Please note that these lists do not include all the side effects seen with these drugs. These lists include the more serious or common side effects with a known or possible relationship. If you have questions concern ...
... The drugs used in this study may have side effects, some of which are listed below. Please note that these lists do not include all the side effects seen with these drugs. These lists include the more serious or common side effects with a known or possible relationship. If you have questions concern ...
Common Drugs and Their Effects
... •blurred vision, nausea, muscle tension, teeth grinding •faintness, chills, sweating; increased heart rate and blood pressure, elevated body temperature •(in high doses) distortions in perception, thinking and memory, as well as hallucinations •death from dehydration and hypothermia in the context o ...
... •blurred vision, nausea, muscle tension, teeth grinding •faintness, chills, sweating; increased heart rate and blood pressure, elevated body temperature •(in high doses) distortions in perception, thinking and memory, as well as hallucinations •death from dehydration and hypothermia in the context o ...
hypnosis and drugs
... of the central nervous system, reducing anxiety but impairing memory and judgement ...
... of the central nervous system, reducing anxiety but impairing memory and judgement ...
Alzheimer*s and Parkinson*s Disease
... Patients with Alzheimer’s may be neglectful of their dental health and oral hygiene, because of their forgetfulness. Medications they are taking can cause Xerostomia, which can lead to an increase in caries. ...
... Patients with Alzheimer’s may be neglectful of their dental health and oral hygiene, because of their forgetfulness. Medications they are taking can cause Xerostomia, which can lead to an increase in caries. ...
Chapter 1 Opener
... Bind to post synaptic receptor and cause effects, or increase effectiveness of NT ...
... Bind to post synaptic receptor and cause effects, or increase effectiveness of NT ...
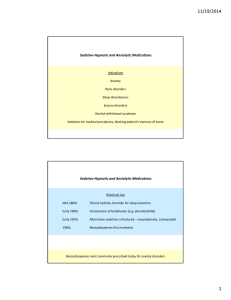
11/19/2014 Sedative‐Hypnotic and Anxiolytic Medications
... Activation of GABA neurons in other regions of CNS, including brain stem and cerebral cortex ...
... Activation of GABA neurons in other regions of CNS, including brain stem and cerebral cortex ...
Benzodiazepines - Dr Anthony (Tony) Mander
... If someone is both anxious and sleeping badly, the longer-acting benzodiazepines can be taken at night - they will improve sleep but still be present the next day to help with the anxiety. What can I do to help myself ? Self-help treatments for anxiety and insomnia are available from psychologists, ...
... If someone is both anxious and sleeping badly, the longer-acting benzodiazepines can be taken at night - they will improve sleep but still be present the next day to help with the anxiety. What can I do to help myself ? Self-help treatments for anxiety and insomnia are available from psychologists, ...
Role of Dopamine
... important for “liking” (NAcc shell) vs “wanting” (NAcc core). Therefore, tolerance may occur in the shell region, and craving may result from changes in the core. Also, different types of receptors may be important. ...
... important for “liking” (NAcc shell) vs “wanting” (NAcc core). Therefore, tolerance may occur in the shell region, and craving may result from changes in the core. Also, different types of receptors may be important. ...
to see the medication guide for Danabol supplement.
... Other ingredients: Microcrystalline cellulose, magnesium stearate Mode of action: Danabol is thought to act through binding to androgen receptors, displacement of glucocorticoids from their receptor, increases in the ...
... Other ingredients: Microcrystalline cellulose, magnesium stearate Mode of action: Danabol is thought to act through binding to androgen receptors, displacement of glucocorticoids from their receptor, increases in the ...
File - NorthStar Mental Wellness
... What Is Its Function? Neurotransmitter • One of the most important functions of norepinephrine is its role as the neurotransmitter released from the sympathetic neurons affecting the heart. An increase in norepinephrine from the sympathetic nervous system increases the rate of contractions 1 Hormon ...
... What Is Its Function? Neurotransmitter • One of the most important functions of norepinephrine is its role as the neurotransmitter released from the sympathetic neurons affecting the heart. An increase in norepinephrine from the sympathetic nervous system increases the rate of contractions 1 Hormon ...
Toxicology Power Point
... Nervous System • Stimulants: stimulates brain activity (amphetamines, cocaine, methamphetamines) • Depressants: Inhibits brain activity (Alcohol, barbiturates, heroin, GHB, Rohypnol, huffing) • Hallucinogens: alterations in perception and mood without affecting brain activity (Ecstasy, LSD, PCP, can ...
... Nervous System • Stimulants: stimulates brain activity (amphetamines, cocaine, methamphetamines) • Depressants: Inhibits brain activity (Alcohol, barbiturates, heroin, GHB, Rohypnol, huffing) • Hallucinogens: alterations in perception and mood without affecting brain activity (Ecstasy, LSD, PCP, can ...
39- Antituberculosis drugs
... 1. First-line drugs: Isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, ethambutol and streptomycin Second-line drugs : Aminosalicylic acid(PAS), kanamycin 2. Isoniazid : 1952, the most active drug for the treatment of tuberculosis (1)Mechanism of action Inhibit the synthesis of mycolic acid which is essential comp ...
... 1. First-line drugs: Isoniazid, rifampin, pyrazinamide, ethambutol and streptomycin Second-line drugs : Aminosalicylic acid(PAS), kanamycin 2. Isoniazid : 1952, the most active drug for the treatment of tuberculosis (1)Mechanism of action Inhibit the synthesis of mycolic acid which is essential comp ...
Students list DRUGS
... Synapse is between nerves and neuroeffecter junctions are between a nerve and any other cell types. Neurotransmitters bind to specific receptor site like key and lock. Many drugs and other xenobiotics also fit into various types of receptors and elicit a response – agonists. Those that block the rec ...
... Synapse is between nerves and neuroeffecter junctions are between a nerve and any other cell types. Neurotransmitters bind to specific receptor site like key and lock. Many drugs and other xenobiotics also fit into various types of receptors and elicit a response – agonists. Those that block the rec ...
Psychopharmacology

Psychopharmacology (from Greek ψῡχή, psȳkhē, ""breath, life, soul""; φάρμακον, pharmakon, ""drug""; and -λογία, -logia) is the scientific study of the effects drugs have on mood, sensation, thinking, and behavior. It is distinguished from neuropsychopharmacology, which emphasizes the correlation between drug-induced changes in the functioning of cells in the nervous system and changes in consciousness and behavior.The field of psychopharmacology studies a wide range of substances with various types of psychoactive properties, focusing primarily on the chemical interactions with the brain.Psychoactive drugs interact with particular target sites or receptors found in the nervous system to induce widespread changes in physiological or psychological functions. The specific interaction between drugs and their receptors is referred to as ""drug action"", and the widespread changes in physiological or psychological function is referred to as ""drug effect"". These drugs may originate from natural sources such as plants and animals, or from artificial sources such as chemical synthesis in the laboratory.