Autonomic Nervous System
... 1. Cholinergic neurons - release at their ends acetylcholine. a. Parasympathetic pre- and post-ganglionic neurons. b. Sympathetic preganglionic neurons. c. A few sympathetic postganglionic neurons. d. Somatic efferent (motor) neurons to the skeletal muscle. 2. Adrenergic neurons - release at their e ...
... 1. Cholinergic neurons - release at their ends acetylcholine. a. Parasympathetic pre- and post-ganglionic neurons. b. Sympathetic preganglionic neurons. c. A few sympathetic postganglionic neurons. d. Somatic efferent (motor) neurons to the skeletal muscle. 2. Adrenergic neurons - release at their e ...
DOPAMINE ANTAGONISTS: PHENOTHIAZINE/THIOXANTHENE SAR
... antisychotics are dopamine receptor antagonists with a higher affinity for D2 over D1 receptors. They also exhibit varying degrees of selectivity among the cortical dopamine tracts; nigrostriatal (movement disorders), mesolimbic (relief of hallucinations and delusions), mesocortical (relief of psych ...
... antisychotics are dopamine receptor antagonists with a higher affinity for D2 over D1 receptors. They also exhibit varying degrees of selectivity among the cortical dopamine tracts; nigrostriatal (movement disorders), mesolimbic (relief of hallucinations and delusions), mesocortical (relief of psych ...
Dr. Ali Famous Shelf Review
... it was 10, then go to 5 and see the time, it is 4 hours B. Volume of distribution is equal to dose divided by concentration C. T1/2 = 0.7 x Vd divided by clearance D. T1/2 is .7/K, or its .7Vd/Cl E. Css = 1.5 x Cp F. Therapeutic index: LD50/ED50, be careful same units NERVOUS SYSTEM A. Questions 1. ...
... it was 10, then go to 5 and see the time, it is 4 hours B. Volume of distribution is equal to dose divided by concentration C. T1/2 = 0.7 x Vd divided by clearance D. T1/2 is .7/K, or its .7Vd/Cl E. Css = 1.5 x Cp F. Therapeutic index: LD50/ED50, be careful same units NERVOUS SYSTEM A. Questions 1. ...
10 Pharmacologic Management Of Parkinsonism
... Ergot derivatives e.g. bromocriptine & pergolide 2. Non-ergot derivatives e.g. apomorphine, pramipexole, ropinirole, and rotigotine ...
... Ergot derivatives e.g. bromocriptine & pergolide 2. Non-ergot derivatives e.g. apomorphine, pramipexole, ropinirole, and rotigotine ...
Click here for handout
... Amphetamine abuse incidence has declined since 2002: 11% to 7% (Adderall > Ritalin), but not as much as new prescription use has increased. ...
... Amphetamine abuse incidence has declined since 2002: 11% to 7% (Adderall > Ritalin), but not as much as new prescription use has increased. ...
INSILICO Research Article S. AMUTHALAKSHMI* AND A. ANTON SMITH
... The DPP-IV binding site is highly druggable in the sense that tight, specific binding to the enzyme can be achieved with small molecules with drug-like physicochemical properties [14]. The two key binding-site areas for the intermolecular interaction of DPP-IV and reversible inhibitors of non-peptid ...
... The DPP-IV binding site is highly druggable in the sense that tight, specific binding to the enzyme can be achieved with small molecules with drug-like physicochemical properties [14]. The two key binding-site areas for the intermolecular interaction of DPP-IV and reversible inhibitors of non-peptid ...
Molecular determinants of drug–receptor binding kinetics
... stabilizing the transition state increases rates. Destabilizing the bound state weakens affinity and increases the off-rate without altering the on-rate, whereas altering the energy of the unbound state affects the on-rate and the affinity only. In practice, however, achieving any of these ‘corner c ...
... stabilizing the transition state increases rates. Destabilizing the bound state weakens affinity and increases the off-rate without altering the on-rate, whereas altering the energy of the unbound state affects the on-rate and the affinity only. In practice, however, achieving any of these ‘corner c ...
... using the scoring function (4). Uses of CADD in developing specific drugs for many diseases were reported. The notable example which can serve as a proof of principle of the in silico approach involves a Type I TGF β receptors kinase inhibitor. The same molecule (HTS-466284/Ly364947), a 27nM inhibit ...
Opioid Agonist
... treatment of acute, severe pain. Rapid absorption from GIT, wide distribution, The analgesic effect is greater when the drug is administered IM or IV compare with oral route and rapid clearance from plasma. Peak effect after IV bolus is 15 min. Duration of action is between 2 and 3 h. Both liver and ...
... treatment of acute, severe pain. Rapid absorption from GIT, wide distribution, The analgesic effect is greater when the drug is administered IM or IV compare with oral route and rapid clearance from plasma. Peak effect after IV bolus is 15 min. Duration of action is between 2 and 3 h. Both liver and ...
A REVIEW ON ANTHELMINTIC DRUGS AND THEIR FUTURE SCOPE Review Article PIYUSH YADAV*, RUPALI SINGH
... The first thiabendazole was discovered in 1961 and it is a broad spectrum anthelmintics. There is an extensive literature on benzimidazole compounds which showed a number of different biochemical effects. The anthelmintic efficacy of benzimidazoles is due to the ...
... The first thiabendazole was discovered in 1961 and it is a broad spectrum anthelmintics. There is an extensive literature on benzimidazole compounds which showed a number of different biochemical effects. The anthelmintic efficacy of benzimidazoles is due to the ...
IB Bio / Neurobiology and Behavior Unit “Drugs of Abuse” Chart
... car to speed ahead. The result is to make VTA neurons fire more & release more dopamine. Among its many effects on the brain: Like benzodiazepines, ethanol inhibits the release of GABA onto VTA neurons, leading to the VTA neurons firing more rapidly and releasing more dopamine in the reward system ...
... car to speed ahead. The result is to make VTA neurons fire more & release more dopamine. Among its many effects on the brain: Like benzodiazepines, ethanol inhibits the release of GABA onto VTA neurons, leading to the VTA neurons firing more rapidly and releasing more dopamine in the reward system ...
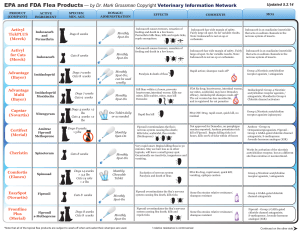
EPA and FDA Flea Products — by Dr. Mark Grossman
... Caution with cat indirect exposure; imidacloprid shampoo wash-off* ...
... Caution with cat indirect exposure; imidacloprid shampoo wash-off* ...
Cover 1 - Fast Facts
... in exhaled air, a value that gives an accurate index of CO in the blood and is used to measure the amount of cigarette smoke inhaled while smoking and to verify claims of abstinence (in which case the value should be less than 10 parts per million) ...
... in exhaled air, a value that gives an accurate index of CO in the blood and is used to measure the amount of cigarette smoke inhaled while smoking and to verify claims of abstinence (in which case the value should be less than 10 parts per million) ...
Corticotropin-releasing factor-1 receptor activation mediates nicotine
... of CRF2 receptors contributes to the anti-stress effects of nonspecific CRF1/CRF2 receptor antagonists such as D-Phe CRF(12-41). During the last decade, several small-molecule CRF1 receptor antagonists have been developed that can cross the blood brain barrier and display efficacy in clinical trials ...
... of CRF2 receptors contributes to the anti-stress effects of nonspecific CRF1/CRF2 receptor antagonists such as D-Phe CRF(12-41). During the last decade, several small-molecule CRF1 receptor antagonists have been developed that can cross the blood brain barrier and display efficacy in clinical trials ...
CNS Acting Drugs
... Alzheimer’s disease: is a brain disorder in elderly due to acetylcholine deficiency. It is characterized by pre-senile dementia with hyaline degeneration of smaller brain blood vessels ...
... Alzheimer’s disease: is a brain disorder in elderly due to acetylcholine deficiency. It is characterized by pre-senile dementia with hyaline degeneration of smaller brain blood vessels ...
Nicotinic agonist

A nicotinic agonist is a drug that mimics the action of acetylcholine (ACh) at nicotinic acetylcholine receptors (nAChRs). The nAChR is named for its affinity for nicotine.Examples include nicotine (by definition), acetylcholine (the endogenous agonist of nAChRs), choline, epibatidine, lobeline, varenicline and cytisine.