Morphine
... Opioid is a generic term for natural or synthetic substances that bind to specific opioid receptors in the CNS, producing an agonist action. Mechanism of action Opioids act to reduce the intensity and unpleasantness of pain. They produce their effects by activating specific G protein-coupled recepto ...
... Opioid is a generic term for natural or synthetic substances that bind to specific opioid receptors in the CNS, producing an agonist action. Mechanism of action Opioids act to reduce the intensity and unpleasantness of pain. They produce their effects by activating specific G protein-coupled recepto ...
1 - Yimg
... Histamine H1-receptor antagonists • Competitive; some are antimuscarinic, some block -adrenoceptors, and receptors for bradykinin, serotonin, and some have local anesthetic properties. • First generation antihistamines: lipid soluble → sedative (children may experience excitation) ...
... Histamine H1-receptor antagonists • Competitive; some are antimuscarinic, some block -adrenoceptors, and receptors for bradykinin, serotonin, and some have local anesthetic properties. • First generation antihistamines: lipid soluble → sedative (children may experience excitation) ...
dose-effect relationship
... biochemical details of the signaling response. The Kd of the agonist-receptor interaction determines what fraction (B/Bmax) of total receptors will be occupied at a given free concentration (C) of agonist regardless of the receptor concentration: Thus, it is possible to change the sensitivity of tis ...
... biochemical details of the signaling response. The Kd of the agonist-receptor interaction determines what fraction (B/Bmax) of total receptors will be occupied at a given free concentration (C) of agonist regardless of the receptor concentration: Thus, it is possible to change the sensitivity of tis ...
analg_opioide_Engl_2013
... • the pharmacological effects of Pethidine is similar to morphine, primarily at the mu receptor •it has less potent analgesics than morphine and has a shorter duration of action •Pethidine dosn`t delay delivery ...
... • the pharmacological effects of Pethidine is similar to morphine, primarily at the mu receptor •it has less potent analgesics than morphine and has a shorter duration of action •Pethidine dosn`t delay delivery ...
CLONIDINE PREMEDICATION AND ANESTHETIC EFFECTS
... to α1 receptor ratio of 200:1). Alpha-2 receptors are adrenoreceptors that are located primarily on presynaptic nerve terminals. Activation of these receptors inhibits adenylate cyclase activity, which in turn decreases the entry of calcium into the neuronal terminal, which limits norepinephrine rel ...
... to α1 receptor ratio of 200:1). Alpha-2 receptors are adrenoreceptors that are located primarily on presynaptic nerve terminals. Activation of these receptors inhibits adenylate cyclase activity, which in turn decreases the entry of calcium into the neuronal terminal, which limits norepinephrine rel ...
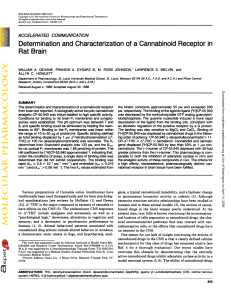
Determination and Characterization of a Cannabinoid Receptor in
... greater potency than the (+)-isomer. This pharmacology is comparable to both the inhibition of adenylate cyclase in vitro and the analgetic activity of these compounds in vivo. The criteria for a high affinity, ...
... greater potency than the (+)-isomer. This pharmacology is comparable to both the inhibition of adenylate cyclase in vitro and the analgetic activity of these compounds in vivo. The criteria for a high affinity, ...
Development of morphine analogue • The Opium Analgesics •Variation of subtituen
... • With a large group such as a pentyl a hexyl group, activity recover slightly • When a phenethyl group is attached, the activity increases 14-fold, a strong indication that a hydrophobic binding region has been located which interacts favourably with the new aromatic ring ...
... • With a large group such as a pentyl a hexyl group, activity recover slightly • When a phenethyl group is attached, the activity increases 14-fold, a strong indication that a hydrophobic binding region has been located which interacts favourably with the new aromatic ring ...
CNS 2 anxiolytics
... • B. A hypnotic drug produces drowsiness and facilitates the onset and maintenance of a state of sleep that resembles natural sleep, and from which the patient can be easily aroused. ...
... • B. A hypnotic drug produces drowsiness and facilitates the onset and maintenance of a state of sleep that resembles natural sleep, and from which the patient can be easily aroused. ...
narcotics - The Podiatry Institute
... The term narcotic was obsolete long before the discovery of endogenous opioid-like ligands and receptofs for these substances. "Narcotic", derived from the Greek word for stupor and at one time applied to any drug that induced sleep, was for a number of years used to refer to morphine-like analgesic ...
... The term narcotic was obsolete long before the discovery of endogenous opioid-like ligands and receptofs for these substances. "Narcotic", derived from the Greek word for stupor and at one time applied to any drug that induced sleep, was for a number of years used to refer to morphine-like analgesic ...
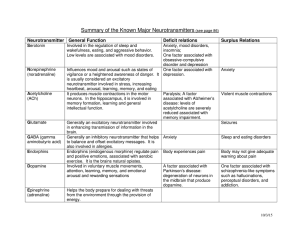
Summary of the Known Major Neurotransmitters (see page 86)
... LSD: Impairs the reuptake of serotonin, making more serotonin available. MDMA (ecstasy): Destroys serotonin nerve cells in animals with moderate and large doses. Prozac: Prevents the reuptake of serotonin, making more serotonin available Amphetamines: Increases dopamine and norepinephrine, and inhib ...
... LSD: Impairs the reuptake of serotonin, making more serotonin available. MDMA (ecstasy): Destroys serotonin nerve cells in animals with moderate and large doses. Prozac: Prevents the reuptake of serotonin, making more serotonin available Amphetamines: Increases dopamine and norepinephrine, and inhib ...
Antiulcer Drugs - Dr. Brahmbhatt`s Class Handouts
... HCl and reducing pepsin activity • Rapid onset and short duration of action • Interact with other drugs – By adsorption or binding the other drugs – By increasing stomach pH (decrease of absorption of certain drugs) – By increasing urinary pH (inhibit elimination of ...
... HCl and reducing pepsin activity • Rapid onset and short duration of action • Interact with other drugs – By adsorption or binding the other drugs – By increasing stomach pH (decrease of absorption of certain drugs) – By increasing urinary pH (inhibit elimination of ...
Pharmacologyonline 3: 7-22 (2011) Newsletter Tamboli et al.
... nicotine-evoked DA release, indicating that it acts as an antagonist at nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) [24]. Application of lobeline releases norepinephrine (NE) from the cytoplasm which may be due to the vesicular uptake inhibition and a reversal of the plasma membrane carrier. Lobeline a ...
... nicotine-evoked DA release, indicating that it acts as an antagonist at nicotinic acetylcholine receptor (nAChR) [24]. Application of lobeline releases norepinephrine (NE) from the cytoplasm which may be due to the vesicular uptake inhibition and a reversal of the plasma membrane carrier. Lobeline a ...
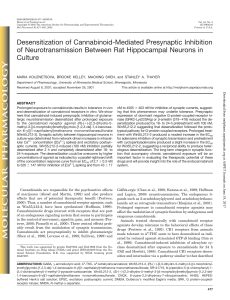
Desensitization of Cannabinoid-Mediated Presynaptic Inhibition of
... Received August 8, 2001; accepted November 26, 2001 ...
... Received August 8, 2001; accepted November 26, 2001 ...
hypnotics and sedatives
... Compounds with a shorter t1/2 are favored in patients with sleep-onset insomnia but without significant daytime anxiety who need to function at full effectiveness during the day. • These compounds also appropriate for the elderly because of a decreased risk of falls and respiratory depression. • One ...
... Compounds with a shorter t1/2 are favored in patients with sleep-onset insomnia but without significant daytime anxiety who need to function at full effectiveness during the day. • These compounds also appropriate for the elderly because of a decreased risk of falls and respiratory depression. • One ...
Antipsychotics - TOP Recommended Websites
... D2- receptors (in chemoreceptor trigger zone) important role in nausea and vomiting drugs that dopamine release in the brain nausea and vomiting D-antagonists (phenotiazines, metoclopramide) antiemetic activity ...
... D2- receptors (in chemoreceptor trigger zone) important role in nausea and vomiting drugs that dopamine release in the brain nausea and vomiting D-antagonists (phenotiazines, metoclopramide) antiemetic activity ...
Document
... The enlarged air sacs (alveoli) of the lungs reduces the surface area available for the movement of gases during respiration. This can cause breathlessness in severe cases. The exact mechanism for the development of emphysema is not understood, although it it known to be linked with smoking and age. ...
... The enlarged air sacs (alveoli) of the lungs reduces the surface area available for the movement of gases during respiration. This can cause breathlessness in severe cases. The exact mechanism for the development of emphysema is not understood, although it it known to be linked with smoking and age. ...
Dr Richard Stevenson
... ***duration 24 – 48 hours*** Treatments Benzodiazepines +/- haloperidol ...
... ***duration 24 – 48 hours*** Treatments Benzodiazepines +/- haloperidol ...
Cholinergic Receptors - .:: سایت تخصصی پزشکی
... • consists of 2 Ach molecules end-to-end • produces a depolarizing block – phase I - depolarizes the end-plate & adjacent muscle – phase II - with continued presence, it desensitizes the end-plate to Ach ...
... • consists of 2 Ach molecules end-to-end • produces a depolarizing block – phase I - depolarizes the end-plate & adjacent muscle – phase II - with continued presence, it desensitizes the end-plate to Ach ...
Rickett Benkiser - American Osteopathic Association
... Chemically different than THC Hundreds of analogs synthesized Urine does not test positive for TCA ...
... Chemically different than THC Hundreds of analogs synthesized Urine does not test positive for TCA ...
Chapter_005
... 1, Cell membrane–embedded enzyme. 2, Ligand-gated ion channel. 3, G protein–coupled receptor system (G = G protein). 4, Transcription factor. (See text for details.) ...
... 1, Cell membrane–embedded enzyme. 2, Ligand-gated ion channel. 3, G protein–coupled receptor system (G = G protein). 4, Transcription factor. (See text for details.) ...
Slide 1
... because the patients weren't taking it and not because the drug didn't work, an analysis of the study results suggests. • A subsequent analysis of urine samples retained from the study showed that fewer than 40 percent of 53 patients in the vigabatrin arm who completed the 12-week study had urine dr ...
... because the patients weren't taking it and not because the drug didn't work, an analysis of the study results suggests. • A subsequent analysis of urine samples retained from the study showed that fewer than 40 percent of 53 patients in the vigabatrin arm who completed the 12-week study had urine dr ...
Midterm review - February 26, 2004
... Anesthetics come in two basic chemical flavors. They are composed of an aromatic group linked to an amine by either an ester bond or an amide bond. Esters: Procaine, Tetracaine, Benzocaine (topical), Cocaine (vasoconstrictor!) Amides: Bupivicaine, Lidocaine, Mepivacaine, Etidocaine (amides always ha ...
... Anesthetics come in two basic chemical flavors. They are composed of an aromatic group linked to an amine by either an ester bond or an amide bond. Esters: Procaine, Tetracaine, Benzocaine (topical), Cocaine (vasoconstrictor!) Amides: Bupivicaine, Lidocaine, Mepivacaine, Etidocaine (amides always ha ...
Cannabinoid receptor antagonist

The discovery of the endogenous cannabinoid system led to the development of CB1 receptor antagonists. The first cannabinoid receptor antagonist, rimonabant, was described in 1994. Rimonabant blocks the CB1 receptor selectively and it has been shown to decrease food intake and regulate body-weight gain. The prevalence of obesity worldwide is increasing dramatically and has a great impact on public health. The lack of efficient and well-tolerated drugs to cure obesity has led to an increased interest in research and development of cannabinoid antagonists. Cannabidiol, a naturally occurring cannabinoid, is a non-competitive CB1/2 antagonist.