Actividad 3
... Many ______________________ that are used in Spanish are in reality the verb form known as the past participle. To form the past participle for –ar verbs we add _____________________. For most –er and –ir verbs we add _____________________. Some irregular past participles are ______________ ________ ...
... Many ______________________ that are used in Spanish are in reality the verb form known as the past participle. To form the past participle for –ar verbs we add _____________________. For most –er and –ir verbs we add _____________________. Some irregular past participles are ______________ ________ ...
The Fisher King
... epitomizing time and change displaying how very precious every moment is. The magic of this movie is about time within time. It is about how time can be suspended, but never stopping. It is also about how it remains constant, but eternal and how ideas are immortalized through dreams and making them ...
... epitomizing time and change displaying how very precious every moment is. The magic of this movie is about time within time. It is about how time can be suspended, but never stopping. It is also about how it remains constant, but eternal and how ideas are immortalized through dreams and making them ...
Types of Verbs
... Verbs such as smell, look, taste, feel, remain, turn, appear, become, sound, seem, grow, stay can also be linking verbs. How do you know if it is linking or action? You need to ask yourself if the verb is linking the subject to a noun or adjective in the predicate. ...
... Verbs such as smell, look, taste, feel, remain, turn, appear, become, sound, seem, grow, stay can also be linking verbs. How do you know if it is linking or action? You need to ask yourself if the verb is linking the subject to a noun or adjective in the predicate. ...
Inflectional Paradigms
... • In addition to the regular –s plural there are several small groups of irregular plurals. • 1. three nouns still retain the –en plural • 2. another group has a Ø suffixal plural. • The words in this group are the names of edible animals, game animals, fish and birds. Some have both forms. ...
... • In addition to the regular –s plural there are several small groups of irregular plurals. • 1. three nouns still retain the –en plural • 2. another group has a Ø suffixal plural. • The words in this group are the names of edible animals, game animals, fish and birds. Some have both forms. ...
How to determine the part of speech of a word
... (like important, green, inanimate) is an adjective. Once you’ve experimented with these frames, you can probably think up many others. 2. Other parts of speech The nice aspect of the other parts of speech is that they are closed-class words. This means, first, that there aren’t all that many of them ...
... (like important, green, inanimate) is an adjective. Once you’ve experimented with these frames, you can probably think up many others. 2. Other parts of speech The nice aspect of the other parts of speech is that they are closed-class words. This means, first, that there aren’t all that many of them ...
15 - Durov.com
... Class S; suffix -j, most verbs with front vowels, derived from nouns and adj. (ex. styrian(mf), styrede(past), styred(PII)) Class 2: suffix -oja, most numerous, back vowel (locain, locoed, locod) Class 3: habban; sec3an; libban(inf), iifde(past), lifd(PIl). This class disappeared in ME {merged with ...
... Class S; suffix -j, most verbs with front vowels, derived from nouns and adj. (ex. styrian(mf), styrede(past), styred(PII)) Class 2: suffix -oja, most numerous, back vowel (locain, locoed, locod) Class 3: habban; sec3an; libban(inf), iifde(past), lifd(PIl). This class disappeared in ME {merged with ...
LOS ARTÍCULOS
... basic verb form in all languages. In English, it is always preceded by "to," as in "to run," "to love," and "to travel." In Spanish, infinitives consist of only one word and are separated into three different conjugations according to their endings: -ar, -er, or -ir. These endings are attached to th ...
... basic verb form in all languages. In English, it is always preceded by "to," as in "to run," "to love," and "to travel." In Spanish, infinitives consist of only one word and are separated into three different conjugations according to their endings: -ar, -er, or -ir. These endings are attached to th ...
AP Parts of Speech
... Corie knows who made the cake. He made the cake. For whom did you vote? I voted for him. You may go with whomever you choose. I choose him. ...
... Corie knows who made the cake. He made the cake. For whom did you vote? I voted for him. You may go with whomever you choose. I choose him. ...
First Semester Objectives:
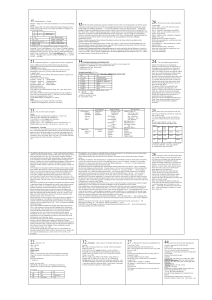
... and radical (stem) changing verbs Know the present-tense usage of all -AR -ER and -IR verbs Usage of subject pronouns, pronouns after prepositions, personal a and direct objects Know the forms and positions of direct and indirect object pronouns Usage of double object pronouns Know the different use ...
... and radical (stem) changing verbs Know the present-tense usage of all -AR -ER and -IR verbs Usage of subject pronouns, pronouns after prepositions, personal a and direct objects Know the forms and positions of direct and indirect object pronouns Usage of double object pronouns Know the different use ...
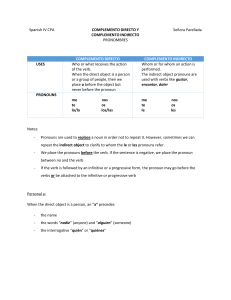
Year 1 Grammar glossary
... question about the other person’s willingness] It was raining. [single-clause sentence] It was raining but we were indoors. [two finite clauses] If you are coming to the party, please let us know. [finite subordinate clause inside a finite main clause] Usha went upstairs to play on her computer. [no ...
... question about the other person’s willingness] It was raining. [single-clause sentence] It was raining but we were indoors. [two finite clauses] If you are coming to the party, please let us know. [finite subordinate clause inside a finite main clause] Usha went upstairs to play on her computer. [no ...
Study Guide for Grammar Assessment Practice for all topics are
... A verbal is a verb form used as some other part of speech. There are three kinds of verbals: gerunds, participles and infinitives. A gerund always ends in ing and is used as a noun. Example: Eating is fun. The gerund can be a subject (Eating is fun.); a direct object (I like eating.); a predicate no ...
... A verbal is a verb form used as some other part of speech. There are three kinds of verbals: gerunds, participles and infinitives. A gerund always ends in ing and is used as a noun. Example: Eating is fun. The gerund can be a subject (Eating is fun.); a direct object (I like eating.); a predicate no ...
Parts of Speech - Rocky View Schools
... Verbs need to agree with the subject of the sentence. A singular subject takes a singular verb. A plural subject takes a plural verb. Look at this example: John (play, plays) baseball. Plays is the singular form of the verb. It agrees with John, a singular subject (noun). Circle the verbs that agree ...
... Verbs need to agree with the subject of the sentence. A singular subject takes a singular verb. A plural subject takes a plural verb. Look at this example: John (play, plays) baseball. Plays is the singular form of the verb. It agrees with John, a singular subject (noun). Circle the verbs that agree ...
Grammar Coverage Y5-6 - Walmore Hill Primary School
... find out / discover ask for / request go in / enter Using question tags for informality: He’s in your class, isn’t he? Use the subjunctive for formal writing: If I were you… Abstract nouns ...
... find out / discover ask for / request go in / enter Using question tags for informality: He’s in your class, isn’t he? Use the subjunctive for formal writing: If I were you… Abstract nouns ...
Genesee County Virtual Summer School
... • Direct/indirect/double object pronouns • The culture of Puerto Rico/Cuba/La República Dominicana • Famous Hispanic artists ...
... • Direct/indirect/double object pronouns • The culture of Puerto Rico/Cuba/La República Dominicana • Famous Hispanic artists ...
Subject Verb Agreement
... person, place, thing, or idea that is doing or being something. You can find the subject of a sentence if you can find the verb. Ask the question, "Who or what 'verbs' or 'verbed'?" and the answer to that question is the subject. ...
... person, place, thing, or idea that is doing or being something. You can find the subject of a sentence if you can find the verb. Ask the question, "Who or what 'verbs' or 'verbed'?" and the answer to that question is the subject. ...
Appendices (Spanish Grammar Book, Enrique Yepes, Bowdoin) http
... another sentence such as “what she writes”, this sentence will be a noun clause: What she writes is good noun clause ...
... another sentence such as “what she writes”, this sentence will be a noun clause: What she writes is good noun clause ...
Verbs in Hittite
... Hittite verbs have two moods: indicative (expressing real actions) and imperative (expressing desired actions). Both moods can be expressed in all grammatical persons, singular and plural. There is no specific grammatical form for modus irrealis, which is expressed instead by the particle -man- appe ...
... Hittite verbs have two moods: indicative (expressing real actions) and imperative (expressing desired actions). Both moods can be expressed in all grammatical persons, singular and plural. There is no specific grammatical form for modus irrealis, which is expressed instead by the particle -man- appe ...
Latin Year 8 Revision Booklet Level 2
... Remember: We often see this case with verbs of giving or speaking or telling! Ablative: This is the one that means 'by', 'with', or 'from'. But it is almost always seen with prepositions. For nouns like servus, the ablative endings are: -o (singular), -is (plural) For nouns like femina, the ablative ...
... Remember: We often see this case with verbs of giving or speaking or telling! Ablative: This is the one that means 'by', 'with', or 'from'. But it is almost always seen with prepositions. For nouns like servus, the ablative endings are: -o (singular), -is (plural) For nouns like femina, the ablative ...
Grammar Terms - GEOCITIES.ws
... The second element in a topic-comment construction. The element that describes, defines, explains, etc. a topic. Topics may be indefinite, which contrasts with narrative function of definite subject-predicate patterns Word, phrase, or clause directly following a verb (verbal complement) or adjective ...
... The second element in a topic-comment construction. The element that describes, defines, explains, etc. a topic. Topics may be indefinite, which contrasts with narrative function of definite subject-predicate patterns Word, phrase, or clause directly following a verb (verbal complement) or adjective ...
Verbs in Hittite
... Hittite verbs have two moods: indicative (expressing real actions) and imperative (expressing desired actions). Both moods can be expressed in all grammatical persons, singular and plural. There is no specific grammatical form for modus irrealis, which is expressed instead by the particle -man- appe ...
... Hittite verbs have two moods: indicative (expressing real actions) and imperative (expressing desired actions). Both moods can be expressed in all grammatical persons, singular and plural. There is no specific grammatical form for modus irrealis, which is expressed instead by the particle -man- appe ...
Spellings for week beginning 29.6.15
... advice advise device devise licence license practice practise prophecy prophesy Task: ...
... advice advise device devise licence license practice practise prophecy prophesy Task: ...