Latin 12 & 13 PPT
... • the reason for this is that English tends to use general Latinbased terms to cover specific things for which there is no existing word – cf. the generalizations cited above were already generalized in antiquity • in general, language tends to move toward more specific terminology as new things com ...
... • the reason for this is that English tends to use general Latinbased terms to cover specific things for which there is no existing word – cf. the generalizations cited above were already generalized in antiquity • in general, language tends to move toward more specific terminology as new things com ...
Slideshow
... solve the student’s questions. (professor is singular therefore “was” is used rather than “were”) ...
... solve the student’s questions. (professor is singular therefore “was” is used rather than “were”) ...
Transitive Vs. Intransitive Verbs
... • What is the difference between the two verbs in the above sentences? At first thought, you may say the definition but forget about the meaning. Instead, concentrate on the grammar. How do the verbs differ grammatically? • Notice that the first sentence has two words following the verb hit. The sec ...
... • What is the difference between the two verbs in the above sentences? At first thought, you may say the definition but forget about the meaning. Instead, concentrate on the grammar. How do the verbs differ grammatically? • Notice that the first sentence has two words following the verb hit. The sec ...
Tom`s Subject/Verb Power Point
... If the subject is plural then the plural verb must be used. The child is outside. The children are outside. The athlete runs fast. The athletes run fast. ...
... If the subject is plural then the plural verb must be used. The child is outside. The children are outside. The athlete runs fast. The athletes run fast. ...
Transitive Vs. Intransitive Verbs
... • What is the difference between the two verbs in the above sentences? At first thought, you may say the definition but forget about the meaning. Instead, concentrate on the grammar. How do the verbs differ grammatically? • Notice that the first sentence has two words following the verb hit. The sec ...
... • What is the difference between the two verbs in the above sentences? At first thought, you may say the definition but forget about the meaning. Instead, concentrate on the grammar. How do the verbs differ grammatically? • Notice that the first sentence has two words following the verb hit. The sec ...
Noun Study Guide
... Examples: damaged shed, shiny star Proper adjectives = describe a specific noun, so it is capitalized Examples: American flag, English book ...
... Examples: damaged shed, shiny star Proper adjectives = describe a specific noun, so it is capitalized Examples: American flag, English book ...
Key Grammatical Terminology - New Hartford Central Schools
... • number – describes how many of something are doing the action of the verb. o singular – one person or thing (sedet – he sits) o plural – more than one person or thing (sedent – they sit) • pronouns – pronouns tell who is doing something ‘I, you, he, she, it, we, they’ in Latin certain pronouns agr ...
... • number – describes how many of something are doing the action of the verb. o singular – one person or thing (sedet – he sits) o plural – more than one person or thing (sedent – they sit) • pronouns – pronouns tell who is doing something ‘I, you, he, she, it, we, they’ in Latin certain pronouns agr ...
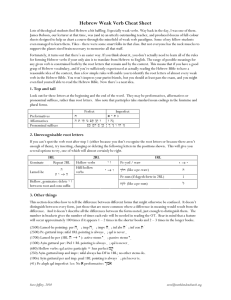
Hebrew Weak Verb Cheat Sheet
... sheets designed to help us chart a course through the minefield of weak verb paradigms. Some of my fellow-students even managed to learn them. Yikes - there were some smart folks in that class. But not everyone has the neck muscles to support the planet-sized brain necessary to memorize all that stu ...
... sheets designed to help us chart a course through the minefield of weak verb paradigms. Some of my fellow-students even managed to learn them. Yikes - there were some smart folks in that class. But not everyone has the neck muscles to support the planet-sized brain necessary to memorize all that stu ...
subject and verb rules
... everybody, everyone, everything, nobody, no one, etc.). However, all, any, none, and some may be either singular or plural, depending on the noun or pronoun they refer to. Everybody on the team is excited about the game. Each of the players is going to the post-game celebration. All of the money is ...
... everybody, everyone, everything, nobody, no one, etc.). However, all, any, none, and some may be either singular or plural, depending on the noun or pronoun they refer to. Everybody on the team is excited about the game. Each of the players is going to the post-game celebration. All of the money is ...
What I`ve Learned Essay - marisa-
... same can be done with adjectives – lumpy becomes lumpiness; free becomes freedom; real becomes reality. Verbs, adjectives, and nouns can be interchangeable with the addition of multiple suffixes. Nouns are, obviously, very versatile. While in possessive form, they may be used as a description (“a da ...
... same can be done with adjectives – lumpy becomes lumpiness; free becomes freedom; real becomes reality. Verbs, adjectives, and nouns can be interchangeable with the addition of multiple suffixes. Nouns are, obviously, very versatile. While in possessive form, they may be used as a description (“a da ...
Capítulo 2A
... example in English we say: "I speak" and "she speaks." Note how the verb changes when the person doing the action changed from "I" to "she." Remember that verbs that have not been conjugated are called “infinitives.” This means that it is a potential action – we don’t know who is doing the action. C ...
... example in English we say: "I speak" and "she speaks." Note how the verb changes when the person doing the action changed from "I" to "she." Remember that verbs that have not been conjugated are called “infinitives.” This means that it is a potential action – we don’t know who is doing the action. C ...
Nouns- people, places, things or ideas
... represent abstract concepts or a collection that does not have an individual state of being. count ...
... represent abstract concepts or a collection that does not have an individual state of being. count ...
Participles
... us it is DATIVE or ABLATIVE plural. You try it. What about the accusative singular? Ridēntem ...
... us it is DATIVE or ABLATIVE plural. You try it. What about the accusative singular? Ridēntem ...
Basic GrammarVerbs
... Hundreds of protesters hurled stones and vegetables at police guarding the courthouse. (Stones and vegetables is the object of hurled.) ...
... Hundreds of protesters hurled stones and vegetables at police guarding the courthouse. (Stones and vegetables is the object of hurled.) ...
All You Need to Know
... His son catches fly balls. Creative children often dream in class. Note: Verbs in the active voice may be either transitive or intransitive. Passive Voice: the subject receives the action: The ball was caught by the first baseman. The duty is performed by the new recruits. The dough was beaten by th ...
... His son catches fly balls. Creative children often dream in class. Note: Verbs in the active voice may be either transitive or intransitive. Passive Voice: the subject receives the action: The ball was caught by the first baseman. The duty is performed by the new recruits. The dough was beaten by th ...
Lesson 14: Verb Usage
... Verbs provide the action in your writing. Choosing the right verbs can make your writing practically jump off the page. On the other hand, few things are more distracting for a reader than mistakes in verb usage. In this lesson, you'll review the skills that will help you avoid the most common verb- ...
... Verbs provide the action in your writing. Choosing the right verbs can make your writing practically jump off the page. On the other hand, few things are more distracting for a reader than mistakes in verb usage. In this lesson, you'll review the skills that will help you avoid the most common verb- ...
ppt
... • Orthography: single word. Not a linguistic argument. • Semantics: they mean something very different from what they are attached to. But same for prefixes. • A syntactic argument: preposition is an autonomous unit in the structure of the sentence that can go apart: in Amsterdam; in the town; in th ...
... • Orthography: single word. Not a linguistic argument. • Semantics: they mean something very different from what they are attached to. But same for prefixes. • A syntactic argument: preposition is an autonomous unit in the structure of the sentence that can go apart: in Amsterdam; in the town; in th ...
a. PPP From the phoneme to the morpheme
... Position and word order Nouns fill certain characteristic positions in relation to other parts of speech. The most obvious is that just before the verb. Examples: The _____ is here. These _____ are beautiful! 5. Function Words –In English, noun determiners immediately precede nouns or precede them ...
... Position and word order Nouns fill certain characteristic positions in relation to other parts of speech. The most obvious is that just before the verb. Examples: The _____ is here. These _____ are beautiful! 5. Function Words –In English, noun determiners immediately precede nouns or precede them ...
PARTS OF SPEECH.pps
... “Linking verbs” show being. Change to show time (tense). Complete verbs include “helping verbs.” ...
... “Linking verbs” show being. Change to show time (tense). Complete verbs include “helping verbs.” ...
HN English I Name_______________________________ Gerund
... Mrs. Stern gives teaching all of her energy and time. ...
... Mrs. Stern gives teaching all of her energy and time. ...
Study Guide for Grammar Test 2
... Sometimes they show degree, as in “too much coffee” or “very excited.” Direct and indirect objects Prepositional phrases. The SAT will give you a sentence like this to confuse you: An increase in applicants have made the selection process more rigorous. The subject of the sentence is “increase,” so ...
... Sometimes they show degree, as in “too much coffee” or “very excited.” Direct and indirect objects Prepositional phrases. The SAT will give you a sentence like this to confuse you: An increase in applicants have made the selection process more rigorous. The subject of the sentence is “increase,” so ...
Present Perfect
... Mostly, we use it to talk about experience. For situations, which happened in the past, but their results stand in the present. For questions (When you ask if someone has ever done something.) – Have you ever eaten a shark? ...
... Mostly, we use it to talk about experience. For situations, which happened in the past, but their results stand in the present. For questions (When you ask if someone has ever done something.) – Have you ever eaten a shark? ...
Subject verb agreement
... 5. Meandering downriver toward a deer, three grizzly cubs comes within 15 yards of it. 6.Female grizzlies mates every third year in summer, without their fertilized eggs implanting in the womb until fall. 7.To a grizzly almost anything are food except rocks. 8. Lingering snow patches often become p ...
... 5. Meandering downriver toward a deer, three grizzly cubs comes within 15 yards of it. 6.Female grizzlies mates every third year in summer, without their fertilized eggs implanting in the womb until fall. 7.To a grizzly almost anything are food except rocks. 8. Lingering snow patches often become p ...
Grammar A-Z_marketing.indd
... This is a sentence that gives orders or instructions. The verb used for commands is called ‘the imperative’ and is usually found at the start of the sentence. It can end with a full stop or, if extra importance needs to be emphasised, an exclamation mark: ...
... This is a sentence that gives orders or instructions. The verb used for commands is called ‘the imperative’ and is usually found at the start of the sentence. It can end with a full stop or, if extra importance needs to be emphasised, an exclamation mark: ...