Image Grammar
... • Add one appositive to each of the sentences below: • The volcano spewed forth lava and ash across the mountain. • The old Navajo woman stared blankly. • The fish felt the alligator sink its teeth into his scales. ...
... • Add one appositive to each of the sentences below: • The volcano spewed forth lava and ash across the mountain. • The old Navajo woman stared blankly. • The fish felt the alligator sink its teeth into his scales. ...
Subject/Verb Agreement
... Agreement Cont’d If a subject is plural, its verb must be plural. Example: My dog, Jesse, and Ralph’s dog, Fido, jump over the fence. (2 dogs are jumping over the fence, now) Notice that the verb jump does NOT have a “s”. This is because a verb is plural when it does NOT have an “s”. Remember: A ve ...
... Agreement Cont’d If a subject is plural, its verb must be plural. Example: My dog, Jesse, and Ralph’s dog, Fido, jump over the fence. (2 dogs are jumping over the fence, now) Notice that the verb jump does NOT have a “s”. This is because a verb is plural when it does NOT have an “s”. Remember: A ve ...
ACTGrammar and Usage OH
... "am," "are," "is," "was," and "were." Verbs that may be linking verbs include "appear," "feel," "grow," "look," "smell," and "taste." Singular Verbs and Plural Verbs Most singular third-person verbs end in s. Most plural verbs do not. Look at these examples: Singular ...
... "am," "are," "is," "was," and "were." Verbs that may be linking verbs include "appear," "feel," "grow," "look," "smell," and "taste." Singular Verbs and Plural Verbs Most singular third-person verbs end in s. Most plural verbs do not. Look at these examples: Singular ...
Language_Arts_Literacy_7__Chapter_15
... Remember! If there is an answer to the question WHAT or WHOM, it is TRANSITIVE! An intransitive verb expresses action or tells something about the subject of the sentence but does not direct action toward a noun or pronoun. All linking verbs are intransitive. Examples: Transitive: The captain rang t ...
... Remember! If there is an answer to the question WHAT or WHOM, it is TRANSITIVE! An intransitive verb expresses action or tells something about the subject of the sentence but does not direct action toward a noun or pronoun. All linking verbs are intransitive. Examples: Transitive: The captain rang t ...
Arabic Language (introductory course)
... Reading and writing, the alphabet, writing and comprehension exercises. The scientific transliteration of Arabic letters. Morphology and syntactic notions: roots and form. Nouns: articles and declining nouns. Solar and lunar letters. Nominal propositions, adjectives as attributes and predicates. Int ...
... Reading and writing, the alphabet, writing and comprehension exercises. The scientific transliteration of Arabic letters. Morphology and syntactic notions: roots and form. Nouns: articles and declining nouns. Solar and lunar letters. Nominal propositions, adjectives as attributes and predicates. Int ...
Stem-Changing Verbs (e to ie)
... Stem-changing verbs have a spelling change in the stem of the verb. Stem-changing verbs are also called “shoe verbs” or “boot verbs” because of the pattern of spelling changes. ...
... Stem-changing verbs have a spelling change in the stem of the verb. Stem-changing verbs are also called “shoe verbs” or “boot verbs” because of the pattern of spelling changes. ...
Year 6 ST MARTIN`S SCHOOL VGP LONG TERM PLAN
... This document is to be used in conjunction with the accompanying “Grammar progression” and “Sentence development” documents. It is important to look at the year before and after to be able to differentiate and to identify how the children could develop further. Using these documents will arm you wit ...
... This document is to be used in conjunction with the accompanying “Grammar progression” and “Sentence development” documents. It is important to look at the year before and after to be able to differentiate and to identify how the children could develop further. Using these documents will arm you wit ...
The Subjunctive Basics
... The subjunctive is not a tense; rather, it is a mood. Tense refers when an action takes place (past, present, future), while mood merely reflects how the speaker feels about the action. The subjunctive mood is rarely used in English, but it is widely used in Spanish. Use this verb quizzer to practic ...
... The subjunctive is not a tense; rather, it is a mood. Tense refers when an action takes place (past, present, future), while mood merely reflects how the speaker feels about the action. The subjunctive mood is rarely used in English, but it is widely used in Spanish. Use this verb quizzer to practic ...
Parts of Speech
... Relative pronouns: that, which, who, whom, whose Interrogative pronouns: who, whom, whose, which, that Demonstrative pronouns: this, that, these, those Indefinite pronouns: all, another, any, anybody, anyone, anything, both, each, either, everybody, everyone, everything, few, many, neither, nobody, ...
... Relative pronouns: that, which, who, whom, whose Interrogative pronouns: who, whom, whose, which, that Demonstrative pronouns: this, that, these, those Indefinite pronouns: all, another, any, anybody, anyone, anything, both, each, either, everybody, everyone, everything, few, many, neither, nobody, ...
PARTS OF SPEECH
... Here are some examples: A, An, The A book fell on the floor. An article is used before a noun. The test was easy. ...
... Here are some examples: A, An, The A book fell on the floor. An article is used before a noun. The test was easy. ...
Verb structure
... Notice also how, in English, the form of the verb (e.g., do, doing, done) can change depending on the tense. In Swahili, in most circumstances, only the tense marker needs to change, as above, so the verb stem is usually unaffected by changes in tense. The perfect tense is also used with certain ver ...
... Notice also how, in English, the form of the verb (e.g., do, doing, done) can change depending on the tense. In Swahili, in most circumstances, only the tense marker needs to change, as above, so the verb stem is usually unaffected by changes in tense. The perfect tense is also used with certain ver ...
Working with Writers of English as a Second Language
... Acceptable paraphrase must change both syntax and word choice All words and ideas that are not common knowledge must be documented ...
... Acceptable paraphrase must change both syntax and word choice All words and ideas that are not common knowledge must be documented ...
File
... agree with its antecedent. Examples: The kittens chased the mouse. They chased the mouse. An artist is admired for her skill with a brush. ...
... agree with its antecedent. Examples: The kittens chased the mouse. They chased the mouse. An artist is admired for her skill with a brush. ...
Writing about others` work: verbs for citations (Harvard APA style)
... Martin and Baker (1980) examined the issue from a different perspective. The verb view is used with the conjunction as, placed after the subject of the sentence. For example: Hui (2001, p. 49) views this explanation as too simplistic. She maintains that… Notice that some reporting verbs are more oft ...
... Martin and Baker (1980) examined the issue from a different perspective. The verb view is used with the conjunction as, placed after the subject of the sentence. For example: Hui (2001, p. 49) views this explanation as too simplistic. She maintains that… Notice that some reporting verbs are more oft ...
Grammar Lesson 2, Verbs - Vocab10-3CHS
... can, or will Others: can, may, will, shall, must, ought, need, dare Ex: A better economy may be an eventuality if we work hard to improve. ...
... can, or will Others: can, may, will, shall, must, ought, need, dare Ex: A better economy may be an eventuality if we work hard to improve. ...
Canberra, the capital!
... ▪ Under no circumstances can Paco say he has seen better libraries. After adverbial expressions of place: ▪ Round the corner was the National Library of Australia. After seldom, rarely, never, in comparisons: ▪ Rarely did he go to a library but the one at the university. After hardly, scarcely, no s ...
... ▪ Under no circumstances can Paco say he has seen better libraries. After adverbial expressions of place: ▪ Round the corner was the National Library of Australia. After seldom, rarely, never, in comparisons: ▪ Rarely did he go to a library but the one at the university. After hardly, scarcely, no s ...
the basics
... (mumps, measles, news, mathematics, economics) -plural in form and plural in meaning take a plural verb (scissors, trousers, tidings) “Be” Verbs- make sure to the verb agrees with the subject Collective Nouns- group as a unit takes a singular verb (faculty, team, committee) Indefinite PronounsSingul ...
... (mumps, measles, news, mathematics, economics) -plural in form and plural in meaning take a plural verb (scissors, trousers, tidings) “Be” Verbs- make sure to the verb agrees with the subject Collective Nouns- group as a unit takes a singular verb (faculty, team, committee) Indefinite PronounsSingul ...
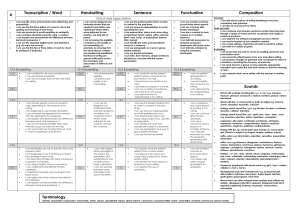
4 Transcription / Word Handwriting Sentence Punctuation
... I can choose specific nouns an powerful verbs depending on the purpose of my writing I am beginning to use fronted adverbials I can compare the apostrophe for omission with the apostrophe for possession. I can explain and demonstrate the difference between plural and possessive ‘s’ I can use the sta ...
... I can choose specific nouns an powerful verbs depending on the purpose of my writing I am beginning to use fronted adverbials I can compare the apostrophe for omission with the apostrophe for possession. I can explain and demonstrate the difference between plural and possessive ‘s’ I can use the sta ...
Nouns * people, places, things, and ideas
... Adjectives – describe, or modify, nouns and pronouns. Adjectives tell the reader what kind, which one, or how many. a, an, the – articles; types of adjectives which explain which one. A man walked down the quiet street. this, that, these, those – demonstrative pronouns which can be used as adjective ...
... Adjectives – describe, or modify, nouns and pronouns. Adjectives tell the reader what kind, which one, or how many. a, an, the – articles; types of adjectives which explain which one. A man walked down the quiet street. this, that, these, those – demonstrative pronouns which can be used as adjective ...
Grammar Verbs Verb: a word that expresses action or otherwise
... A linking verb is a verb that does not show action but connects the subject with a word in the predicate (the part of a sentence that says something about the subject of the sentence). The word that follows the linking verb fills out or completes the meaning of the verb and refers to the subject o ...
... A linking verb is a verb that does not show action but connects the subject with a word in the predicate (the part of a sentence that says something about the subject of the sentence). The word that follows the linking verb fills out or completes the meaning of the verb and refers to the subject o ...
Verbs
... Linking Verbs and Helping Verbs Using your Grammar and Composition textbook, define each part of speech and provide examples. Linking Verbs ...
... Linking Verbs and Helping Verbs Using your Grammar and Composition textbook, define each part of speech and provide examples. Linking Verbs ...
File
... All words may be classified into eight groups called parts of speech. The group to which a word belongs is determined by its use in the sentence; therefore, the same word may be any one of several parts of speech, depending upon its use in a given sentence. The eight parts of speech are noun, pronou ...
... All words may be classified into eight groups called parts of speech. The group to which a word belongs is determined by its use in the sentence; therefore, the same word may be any one of several parts of speech, depending upon its use in a given sentence. The eight parts of speech are noun, pronou ...