Nouns-les noms
... one learn and remember their gender? One usually does this by memorizing. One sometime group words according to their endings, for example,-tion and té are almost always feminine (la nation, la liberté); -ment and –eau are usually masculine (le department, le tableau). Probably the easiest way to ma ...
... one learn and remember their gender? One usually does this by memorizing. One sometime group words according to their endings, for example,-tion and té are almost always feminine (la nation, la liberté); -ment and –eau are usually masculine (le department, le tableau). Probably the easiest way to ma ...
Verbals - Weebly
... Infinitives • Infinitives can also have modifiers or complements. • This can be done because there is a verb form in the infinitive that (if being used as a verb in another sentence) could take a complement such as an indirect or direct object or a predicate complement. ...
... Infinitives • Infinitives can also have modifiers or complements. • This can be done because there is a verb form in the infinitive that (if being used as a verb in another sentence) could take a complement such as an indirect or direct object or a predicate complement. ...
preschoolers` developing morphosyntactic skills
... condition. (That tree is old. The building stands next to the tree.) • Process verbs —internal activity or gradual changes in people or things (thinking, ...
... condition. (That tree is old. The building stands next to the tree.) • Process verbs —internal activity or gradual changes in people or things (thinking, ...
latin i form i - Covington Latin School
... Demonstrative adjectives/pronouns—hic, haec, hoc (this) and ille, illa, illud (that). Imperial Rome. Chapter 27 Personal and reflexive pronouns. Possessive adjectives. Circus Maximus and chariot racing. Word Study VII. Review exercises followed by test. Textbooks: Ecce Romani IA, Longman, 1995 Ecce ...
... Demonstrative adjectives/pronouns—hic, haec, hoc (this) and ille, illa, illud (that). Imperial Rome. Chapter 27 Personal and reflexive pronouns. Possessive adjectives. Circus Maximus and chariot racing. Word Study VII. Review exercises followed by test. Textbooks: Ecce Romani IA, Longman, 1995 Ecce ...
8th 1st Semester Study Guide
... Case is the quality of a noun that shows its relation to some other word or words in the sentence. Nominative Case – subject nouns Subject – the person, place or thing the sentence is about. Subject complement – refers to the same person, place, or thing as the subject. - renames or describes the su ...
... Case is the quality of a noun that shows its relation to some other word or words in the sentence. Nominative Case – subject nouns Subject – the person, place or thing the sentence is about. Subject complement – refers to the same person, place, or thing as the subject. - renames or describes the su ...
3 kinds of verbs Linking verbs: A linking verb is a verb that does She
... Verb is a word that shows action or a state of being. - i hc verb is one otthe toundation worÿls ota S _ . J ...
... Verb is a word that shows action or a state of being. - i hc verb is one otthe toundation worÿls ota S _ . J ...
D.L.P. – Week One Grade eight Day One – Skills Sentence
... A pronoun is a word that takes the place of a noun. An antecedent is the noun that the pronoun replaces. They must agree. For example, if one is singular, then the other must be. If one is masculine, then the other must be. • Negatives – Elimination of Doubles Only one negative word should be used p ...
... A pronoun is a word that takes the place of a noun. An antecedent is the noun that the pronoun replaces. They must agree. For example, if one is singular, then the other must be. If one is masculine, then the other must be. • Negatives – Elimination of Doubles Only one negative word should be used p ...
Turkish personal endings/suffixes
... By the presence of one of the following Before adding this suffixes: -in/ün/ın/un suffix to nouns [or by -nin/nün/nın/nun after a vowel]. ending in k change the k to ğ (yumuşakg) Examples A -1) ...üzümün ...
... By the presence of one of the following Before adding this suffixes: -in/ün/ın/un suffix to nouns [or by -nin/nün/nın/nun after a vowel]. ending in k change the k to ğ (yumuşakg) Examples A -1) ...üzümün ...
commands - cloudfront.net
... COMMANDS Two types of commands may be given. The first is a familiar command, which may be given to someone younger than you, to a friend, or to a family member. The second type of command, a polite command, is used with people older than you are, authority figures, and most likely with your parents ...
... COMMANDS Two types of commands may be given. The first is a familiar command, which may be given to someone younger than you, to a friend, or to a family member. The second type of command, a polite command, is used with people older than you are, authority figures, and most likely with your parents ...
hedgehog - Longton Primary School
... Modal verbs are a type of verb that tell us how likely or necessary something is. They refer to what is going to happen in the future. They normally appear before a main verb. We might go to the pub after the night school. I must work hard at night school or I will be in trouble. would, can, will, c ...
... Modal verbs are a type of verb that tell us how likely or necessary something is. They refer to what is going to happen in the future. They normally appear before a main verb. We might go to the pub after the night school. I must work hard at night school or I will be in trouble. would, can, will, c ...
Reflexive Verbs and Pronouns
... said to have "radical" changes, that is, vowel and consonant changes in the root (or stem of the verb.) Furthermore, these changes occur in all of the conjugations (including the nosotros form.) These Irregular preterite changes are NOT for orthographic (spelling) reasons (like the verbs ending in - ...
... said to have "radical" changes, that is, vowel and consonant changes in the root (or stem of the verb.) Furthermore, these changes occur in all of the conjugations (including the nosotros form.) These Irregular preterite changes are NOT for orthographic (spelling) reasons (like the verbs ending in - ...
Vocabulary Glossary of Terms for Parents.76613177 PDF File
... Many nouns (countable nouns) can be singular (only one) or plural (more than one). The plural is usually marked by the ending -S: cats, houses, wellies. Some plural forms are irregular. For example: women, teeth, lice. Other nouns (mass nouns) do not normally occur in the plural. For example: sheep, ...
... Many nouns (countable nouns) can be singular (only one) or plural (more than one). The plural is usually marked by the ending -S: cats, houses, wellies. Some plural forms are irregular. For example: women, teeth, lice. Other nouns (mass nouns) do not normally occur in the plural. For example: sheep, ...
Grammar fundamentals
... Middle schoolers are very self-conscious about their appearance. Adv adj ...
... Middle schoolers are very self-conscious about their appearance. Adv adj ...
Glossary of Grammatical Terms and Errors active voice: The
... never arise, however, when forms of the infinitive “to be” are omitted; it is the one verb that is always implied and need not be used outright. grammar error: The word “grammar” is commonly used, but somewhat misunderstood. Grammar can be thought of as an overall system of rules for language, synt ...
... never arise, however, when forms of the infinitive “to be” are omitted; it is the one verb that is always implied and need not be used outright. grammar error: The word “grammar” is commonly used, but somewhat misunderstood. Grammar can be thought of as an overall system of rules for language, synt ...
PARTS OF SPEECH
... 1. Denver is a beautiful city to visit, especially if you like cold, snowy weather. 2. The tall Spanish woman turned to her sister and said, “You better put the expensive purse back.” 3. When the baseball catcher dropped the fly ball, the angry crowd at Citizens Bank Park yelled. 4. Tom and Mary hav ...
... 1. Denver is a beautiful city to visit, especially if you like cold, snowy weather. 2. The tall Spanish woman turned to her sister and said, “You better put the expensive purse back.” 3. When the baseball catcher dropped the fly ball, the angry crowd at Citizens Bank Park yelled. 4. Tom and Mary hav ...
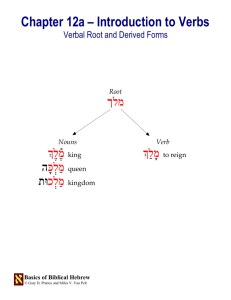
Chapter 12a – Introduction to Verbs
... Masculine referring to masculine subjects Feminine referring to feminine subjects Common referring to masculine or feminine subjects ...
... Masculine referring to masculine subjects Feminine referring to feminine subjects Common referring to masculine or feminine subjects ...
Theme 6 Study Guide
... o Stories have a beginning, middle, and end. In An Important Debate, the beginning is when Speaker Stevens’ dialogue sets up the problem/conflict. Congressman Rock’s dialogue and Congresswoman Green’s dialogue make up the middle of the play and provide the climax. Speaker Stevens’ final dialogue rep ...
... o Stories have a beginning, middle, and end. In An Important Debate, the beginning is when Speaker Stevens’ dialogue sets up the problem/conflict. Congressman Rock’s dialogue and Congresswoman Green’s dialogue make up the middle of the play and provide the climax. Speaker Stevens’ final dialogue rep ...
PRONOUN USAGE
... The quality that distinguishes the entities as masculine or feminine. Some students have a tendency to use masculine pronouns––he, him, his––for nouns which may include female and male subjects. Problematic: Each of the doctors ate his lunch outside. The above use of pronouns should be avoided, unle ...
... The quality that distinguishes the entities as masculine or feminine. Some students have a tendency to use masculine pronouns––he, him, his––for nouns which may include female and male subjects. Problematic: Each of the doctors ate his lunch outside. The above use of pronouns should be avoided, unle ...
Pronoun Notes
... The quality that distinguishes the entities as masculine or feminine. Some students have a tendency to use masculine pronouns––he, him, his––for nouns which may include female and male subjects. Problematic: Each of the doctors ate his lunch outside. The above use of pronouns should be avoided, unle ...
... The quality that distinguishes the entities as masculine or feminine. Some students have a tendency to use masculine pronouns––he, him, his––for nouns which may include female and male subjects. Problematic: Each of the doctors ate his lunch outside. The above use of pronouns should be avoided, unle ...
being verbs
... the car went into the parking lot. • 2. Appositive: The car, a 1936 Ford, went into the parking lot. • 3. Participle: Sliding on the loose gravel, the car went into the parking lot. • 4. Adjectives Out-of-order: The car, dented and rusty, went into the parking lot. • 5. Action verb: The car chugged ...
... the car went into the parking lot. • 2. Appositive: The car, a 1936 Ford, went into the parking lot. • 3. Participle: Sliding on the loose gravel, the car went into the parking lot. • 4. Adjectives Out-of-order: The car, dented and rusty, went into the parking lot. • 5. Action verb: The car chugged ...
Newest parts of speech packet 2008 2009
... TIP for Spotting Nouns: If you can put a word in the slot in the following sentence, it is a noun. A (or An) ________________________ is remarkable. An elephant is remarkable. A rainbow is remarkable. (This works most of the time, but not always.) Underline each noun with one line. Remember that t ...
... TIP for Spotting Nouns: If you can put a word in the slot in the following sentence, it is a noun. A (or An) ________________________ is remarkable. An elephant is remarkable. A rainbow is remarkable. (This works most of the time, but not always.) Underline each noun with one line. Remember that t ...
Sentence elements
... A verbal that modifies a noun is called a participle. It may be in the past or the present tense: a used [past] car with splitting [present] upholstery. ...
... A verbal that modifies a noun is called a participle. It may be in the past or the present tense: a used [past] car with splitting [present] upholstery. ...
Exploring Affixation in English
... inflections are added when all derivational and compositional processes are already complete. This means that one can add inflection on a root and a stem. Let us take for example the word “disinfectants”, the plural inflection –s is added to the stem “disinfectant”. The root of the word is “infect”. ...
... inflections are added when all derivational and compositional processes are already complete. This means that one can add inflection on a root and a stem. Let us take for example the word “disinfectants”, the plural inflection –s is added to the stem “disinfectant”. The root of the word is “infect”. ...