1844
... these forms-s-a fixed plan or form for these several combinations-and that, when once the scheme of inflexion, &c.is well understood, the details are perhaps scarcely more difficult to acquire than the same pronominal, &c. elements in their changeful form and order in European tongues.s ...
... these forms-s-a fixed plan or form for these several combinations-and that, when once the scheme of inflexion, &c.is well understood, the details are perhaps scarcely more difficult to acquire than the same pronominal, &c. elements in their changeful form and order in European tongues.s ...
The semantics of the Turkish accusative marked
... reading is further observed to arise when the accusative definite is unaccented suggesting that the semantic effects stemming from the presence of the accusative objects are intricately related to focus facts. Elaborating this view, the present study argues that an accented accusative definite trigg ...
... reading is further observed to arise when the accusative definite is unaccented suggesting that the semantic effects stemming from the presence of the accusative objects are intricately related to focus facts. Elaborating this view, the present study argues that an accented accusative definite trigg ...
Baule SVCs: Two distinct varieties of missing objects.
... Integrated SVC this missing object is an object gap licensed by a SVC-specific mechanism. This paper will demonstrate that, although there is basis in Baule for the distinction between Clause Chaining SVCs and Integrated SVCs, there is evidence for fundamental similarities between the null object pr ...
... Integrated SVC this missing object is an object gap licensed by a SVC-specific mechanism. This paper will demonstrate that, although there is basis in Baule for the distinction between Clause Chaining SVCs and Integrated SVCs, there is evidence for fundamental similarities between the null object pr ...
An English hAndbook for thE UnivErsity of PrEtoriA 2003
... The aim is not only to help students but also to help those teaching staff who need help with their own usage. Furthermore, all staff have to deal with the language of students and to remedy the grammatical faults of the students. If everyone concentrates on a few of the same basic errors, some prog ...
... The aim is not only to help students but also to help those teaching staff who need help with their own usage. Furthermore, all staff have to deal with the language of students and to remedy the grammatical faults of the students. If everyone concentrates on a few of the same basic errors, some prog ...
Non-finite complements and modality in de-na `allow` in Hindi-Urdu
... In (9) and in many examples below, the =ko postposition is ambiguous between dative and accusative case. The contrast of DOM accusative with the goal dative is even clearer in Kashmiri, a language related to Hindi-Urdu and similar in case marking. The Kashmiri and Hindi-Urdu permissives are very sim ...
... In (9) and in many examples below, the =ko postposition is ambiguous between dative and accusative case. The contrast of DOM accusative with the goal dative is even clearer in Kashmiri, a language related to Hindi-Urdu and similar in case marking. The Kashmiri and Hindi-Urdu permissives are very sim ...
Themes In Literature - LIFE School: LDS Based Home Education
... start by reviewing the eight most common parts of speech. They are: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Nouns and pronouns name. Verbs assert. Adjectives and adverbs describe. Prepositions and conjunctions connect. Interjections exclaim. È Befo ...
... start by reviewing the eight most common parts of speech. They are: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Nouns and pronouns name. Verbs assert. Adjectives and adverbs describe. Prepositions and conjunctions connect. Interjections exclaim. È Befo ...
Grammar Material
... the recipes being used for the meal and construct a grocery list. 8__________ turn your attention to the table décor. 9Decide whether to use formal or casual table settings, which table linens to use, and what sort of centerpiece should be used. 10If fresh flowers will be needed, add them to the sho ...
... the recipes being used for the meal and construct a grocery list. 8__________ turn your attention to the table décor. 9Decide whether to use formal or casual table settings, which table linens to use, and what sort of centerpiece should be used. 10If fresh flowers will be needed, add them to the sho ...
Industrial Ontologies Group
... is given by linking to a normal form of the word (e.g. singular form for nouns or present tense for verbs, etc.). The same idea is usually used in the Lexical Databases - the database itself consists only of normal forms, and also there is some way to get normal form for any arbitrary word we have. ...
... is given by linking to a normal form of the word (e.g. singular form for nouns or present tense for verbs, etc.). The same idea is usually used in the Lexical Databases - the database itself consists only of normal forms, and also there is some way to get normal form for any arbitrary word we have. ...
1. Introduction 1 2. Three Major Types of Actants
... I chose the term actant over other terms for the following three reasons: • First, to emphasize the parallelism between all three types of actants. I want the same term on all levels of representation, and it is preferable to speak of semantic and syntactic actants rather than semantic and syntactic ...
... I chose the term actant over other terms for the following three reasons: • First, to emphasize the parallelism between all three types of actants. I want the same term on all levels of representation, and it is preferable to speak of semantic and syntactic actants rather than semantic and syntactic ...
Shallow-Parsing Stylebook for German
... structure of constituents within topological fields is left open. The model still has some clear advantages from both a theoretical and an annotation perspective: As regards the theoretical perspective it is for example important to point out that a lot of constituent order phenonema can be describe ...
... structure of constituents within topological fields is left open. The model still has some clear advantages from both a theoretical and an annotation perspective: As regards the theoretical perspective it is for example important to point out that a lot of constituent order phenonema can be describe ...
The Syntactic Location of Events
... are strung together in a single clause without overt connective morphology (see for instance Ndimele 1996:127). These verbs express simultaneous or immediately ...
... are strung together in a single clause without overt connective morphology (see for instance Ndimele 1996:127). These verbs express simultaneous or immediately ...
Synthetic compounds
... The part of the definition which is reminiscent of Kant’s synthetic judgement refers to the fact that θεοφιλής ‘dear to the gods’ contains more ideas than those inherent in the single compound members. By this we can understand the argumental relation between head and modifier in the compound as in ...
... The part of the definition which is reminiscent of Kant’s synthetic judgement refers to the fact that θεοφιλής ‘dear to the gods’ contains more ideas than those inherent in the single compound members. By this we can understand the argumental relation between head and modifier in the compound as in ...
Zero Sign (in Morphology - University of Amsterdam
... (within a given language), 2) between impersonal and personal uses of the same verb (Slony sorvali . . . vs. Sorvali . . . ([), and
3) between sentences with impersonal empty non-zero pronouns in some languages and structurally
i ...
... (within a given language), 2) between impersonal and personal uses of the same verb (Slony sorvali . . .
Chapter 4 Extragrammatical expression of
... Chafe and Nichols (1986) paved the way for a more extensive perspective, in which evidentiality is not only restricted to what is ‘formally’ coded by the core of grammatical systems but is also intended as a more general ‘functional category’ expressed by different means, which include lexical eleme ...
... Chafe and Nichols (1986) paved the way for a more extensive perspective, in which evidentiality is not only restricted to what is ‘formally’ coded by the core of grammatical systems but is also intended as a more general ‘functional category’ expressed by different means, which include lexical eleme ...
Document
... pronouns. Use whom or whomever to refer to persons. (me, us, him, her, or them could substitute) Serena Brewer, whom you met last week, saves all her important e-mail on a disk. (You met her last week.) To whom was that last message addressed? (The message was addressed to him.) Business English at ...
... pronouns. Use whom or whomever to refer to persons. (me, us, him, her, or them could substitute) Serena Brewer, whom you met last week, saves all her important e-mail on a disk. (You met her last week.) To whom was that last message addressed? (The message was addressed to him.) Business English at ...
Dagny Taggart`s Ultimate Guide to GMAT Preparation
... “extremely important” for deciding where to apply. Many business schools point to rising scores as evidence of higher standards, neglecting to put them in the context of the rapid climb of average GMAT scores — 57 points in the past 18 years. Women and the MBA: Women graduate from college with highe ...
... “extremely important” for deciding where to apply. Many business schools point to rising scores as evidence of higher standards, neglecting to put them in the context of the rapid climb of average GMAT scores — 57 points in the past 18 years. Women and the MBA: Women graduate from college with highe ...
Tagset Manual
... and a double morphological tag (cf. jnt = in+dat (in+that); Adp()+Art(def) (= adposition + article definite)). Original forms separated. In some cases, orthographic tokens have been split into two or more parts. There are two main reasons for such treatment: ...
... and a double morphological tag (cf. jnt = in+dat (in+that); Adp()+Art(def) (= adposition + article definite)). Original forms separated. In some cases, orthographic tokens have been split into two or more parts. There are two main reasons for such treatment: ...
PROGRESSIVE STRUCTURES OF ENGLISH AND CATALAN
... headed by -ing. The NP/DP which stands for the perceived participant is not treated as an internal argument of the perception verb, but as the external argument of the embedded VP. If we adopt Cowper's analysis, and adapt it to the hypothesis developed in this chapter for other progressive structure ...
... headed by -ing. The NP/DP which stands for the perceived participant is not treated as an internal argument of the perception verb, but as the external argument of the embedded VP. If we adopt Cowper's analysis, and adapt it to the hypothesis developed in this chapter for other progressive structure ...
Non-subject Arguments in Indonesian - ORB
... system as a whole, treating it as the basic transitive system of the language, when certain relationships are recognised as morphological rather than syntactic. This analysis also reveals similarities between Indonesian and more conservative Austronesian languages such as those of the Philippines. A ...
... system as a whole, treating it as the basic transitive system of the language, when certain relationships are recognised as morphological rather than syntactic. This analysis also reveals similarities between Indonesian and more conservative Austronesian languages such as those of the Philippines. A ...
THE POSITION OF THE VERB IN OLD ENGLISH RELATIVE
... similar to the Latin, two examples from the texts under discussion will serve to emphasize the independence of the OE. A Latin phrase can be rendered as a full-blown relative clause in the OE: of þam wife þe wæs genemned thamar of the woman who was named Tamar ...
... similar to the Latin, two examples from the texts under discussion will serve to emphasize the independence of the OE. A Latin phrase can be rendered as a full-blown relative clause in the OE: of þam wife þe wæs genemned thamar of the woman who was named Tamar ...
Linguistic Ambiguity in Language-based Jokes
... be a deficit of research regarding categorization, i.e. identifying frequencies of phonological, lexical, or syntactically-based jokes (for examples see Attardo 1994a, Attardo et al. 1994b, Bucaria 2004). Though a number of studies discuss isolated cases of linguistic ambiguity within the English la ...
... be a deficit of research regarding categorization, i.e. identifying frequencies of phonological, lexical, or syntactically-based jokes (for examples see Attardo 1994a, Attardo et al. 1994b, Bucaria 2004). Though a number of studies discuss isolated cases of linguistic ambiguity within the English la ...
The English relative clause - Machine Translation Archive
... might also generate such sentences as: They called the girl up. He calls the girl up. etc. ...
... might also generate such sentences as: They called the girl up. He calls the girl up. etc. ...
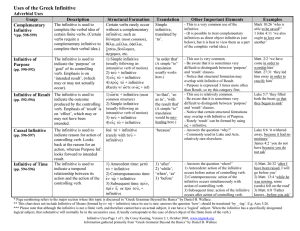
Uses of the Greek Infinitive
... ** This chart does not include Infinitive of Means (formed by ejn tw/: + infinitive) since its use is rare; answers the question ‘how’; should be translated ‘by _-ing’. E.g. Acts 3:26. *** Please note that although the infinitive is not a finite verb, and therefore cannot have an actual subject, it ...
... ** This chart does not include Infinitive of Means (formed by ejn tw/: + infinitive) since its use is rare; answers the question ‘how’; should be translated ‘by _-ing’. E.g. Acts 3:26. *** Please note that although the infinitive is not a finite verb, and therefore cannot have an actual subject, it ...
Quantification in German
... German can cooccur with a (primarily definite) determiner. In this case, they (immediately) follow the determiner. In no case can such a quantifier word be preceded by an adjective in its phrase (but see §2.1.3 for peculiarities of numeral expressions). ...
... German can cooccur with a (primarily definite) determiner. In this case, they (immediately) follow the determiner. In no case can such a quantifier word be preceded by an adjective in its phrase (but see §2.1.3 for peculiarities of numeral expressions). ...