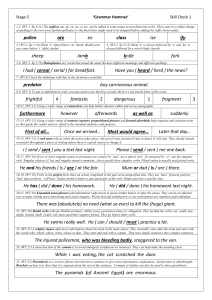
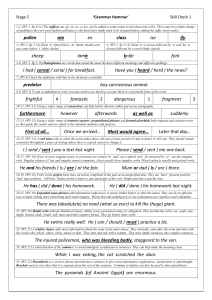
Stage 5 Check 3 – Answers
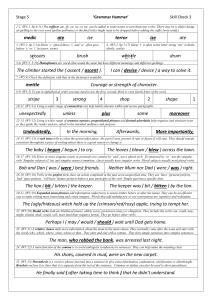
... Perhaps I ( may / would / should ) wait until Dad gets home. 23. (W5:21) A relative clause adds more information about the noun in the main clause. They normally come after the noun and start with the words who, which, where, when, whose or that. They start and end with a comma. They turn simple sen ...
... Perhaps I ( may / would / should ) wait until Dad gets home. 23. (W5:21) A relative clause adds more information about the noun in the main clause. They normally come after the noun and start with the words who, which, where, when, whose or that. They start and end with a comma. They turn simple sen ...
medic ate ize terror ize ate scissors brush whistle drum The climber
... Perhaps I ( may / would / should ) wait until Dad gets home. 23. (W5:21) A relative clause adds more information about the noun in the main clause. They normally come after the noun and start with the words who, which, where, when, whose or that. They start and end with a comma. They turn simple sen ...
... Perhaps I ( may / would / should ) wait until Dad gets home. 23. (W5:21) A relative clause adds more information about the noun in the main clause. They normally come after the noun and start with the words who, which, where, when, whose or that. They start and end with a comma. They turn simple sen ...
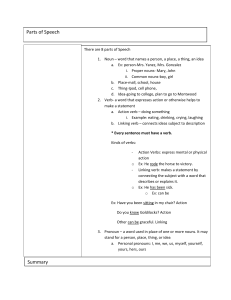
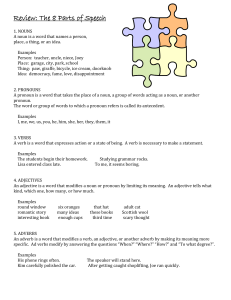
Step One Notes (Parts of Speech)
... objective: me, you, him, her, it plural objective: us, you, them singular possessive: my, your, his, her, its, mine, yours plural possessive: our, your, their, ours, yours, theirs o reflexive (reflect back to "self") myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themse ...
... objective: me, you, him, her, it plural objective: us, you, them singular possessive: my, your, his, her, its, mine, yours plural possessive: our, your, their, ours, yours, theirs o reflexive (reflect back to "self") myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themse ...
The 8 Parts of Speech Conjunction Joins words, phrases, or clauses
... A noun is a word for a person, place, thing, or idea. Nouns are often used with an article (the, a, an), but not always. Proper nouns always start with a capital letter; common nouns do not. Nouns can be singular or plural, concrete or abstract. Nouns show possession by adding's. Nouns can function ...
... A noun is a word for a person, place, thing, or idea. Nouns are often used with an article (the, a, an), but not always. Proper nouns always start with a capital letter; common nouns do not. Nouns can be singular or plural, concrete or abstract. Nouns show possession by adding's. Nouns can function ...
هنا تعاريف مادة النحو والصرف Syntax
... Grammar- The analysis of the structure of phrases and sentences. Morphemes- Parts of words, i.e. stems, prefixes, and suffixes. For example, un + friend + ly contains three morphemes: a prefix un, a stem friend, and a suffix ly. Syntax- The part of grammar dealing with different grammatical units ( ...
... Grammar- The analysis of the structure of phrases and sentences. Morphemes- Parts of words, i.e. stems, prefixes, and suffixes. For example, un + friend + ly contains three morphemes: a prefix un, a stem friend, and a suffix ly. Syntax- The part of grammar dealing with different grammatical units ( ...
Parts of Speech Summary
... Other can be graceful. Linking 3. Pronoun – a word used in place of one or more nouns. It may stand for a person, place, thing, or idea a. Personal pronouns: I, me, we, us, myself, yourself, yours, hers, ours ...
... Other can be graceful. Linking 3. Pronoun – a word used in place of one or more nouns. It may stand for a person, place, thing, or idea a. Personal pronouns: I, me, we, us, myself, yourself, yours, hers, ours ...
for whom - Wikispaces
... A conjunction is a word used to join words or groups of words. Ex. And, but, or, nor, for, so, yet… Both girls and boys went to the park for a ...
... A conjunction is a word used to join words or groups of words. Ex. And, but, or, nor, for, so, yet… Both girls and boys went to the park for a ...
The importance of grammar With the advent of email and text
... adjective meaning not moving) instead of “stationery” (the noun indicating envelopes etc). Nouns are "naming" words for "people, places or things" e.g. the cat, the school Adjectives describe an attribute of a noun, e.g. cold weather, violent storm Verbs are defined as "action" words or "doing" word ...
... adjective meaning not moving) instead of “stationery” (the noun indicating envelopes etc). Nouns are "naming" words for "people, places or things" e.g. the cat, the school Adjectives describe an attribute of a noun, e.g. cold weather, violent storm Verbs are defined as "action" words or "doing" word ...
Polyptoton 1
... B. Polyptoton is the repetition of the same part of speech in different inflections. C. It is from the Greek poluptoton (poluvtwton) which is composed of polus (poluvς), “many,” and ptosis (ptwsiς), “a falling.” D. In grammar, a case (from an assumed form ptovw, ptoo, “to fall.” E. Hence, Polyptoton ...
... B. Polyptoton is the repetition of the same part of speech in different inflections. C. It is from the Greek poluptoton (poluvtwton) which is composed of polus (poluvς), “many,” and ptosis (ptwsiς), “a falling.” D. In grammar, a case (from an assumed form ptovw, ptoo, “to fall.” E. Hence, Polyptoton ...
Adv
... Shaq is a giant tree and he slammed on Kobe, which caused him to run away like a scared rabbit. Prepositional phrase ...
... Shaq is a giant tree and he slammed on Kobe, which caused him to run away like a scared rabbit. Prepositional phrase ...
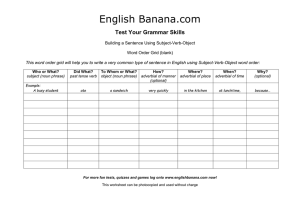
doc - English Banana
... Building a Sentence Using Subject-Verb-Object Word Order Grid (blank) This word order grid will help you to write a very common type of sentence in English using Subject-Verb-Object word order: Who or What? subject (noun phrase) Example: A busy student ...
... Building a Sentence Using Subject-Verb-Object Word Order Grid (blank) This word order grid will help you to write a very common type of sentence in English using Subject-Verb-Object word order: Who or What? subject (noun phrase) Example: A busy student ...
Parts of Speech - Bardstown City Schools
... An adverb is a word that modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb by making its meaning more specific. Ad verbs modify by answering the questions “When?” “Where?” “How?” and “To what degree?”. Examples His phone rings often. Kim carefully polished the car. ...
... An adverb is a word that modifies a verb, an adjective, or another adverb by making its meaning more specific. Ad verbs modify by answering the questions “When?” “Where?” “How?” and “To what degree?”. Examples His phone rings often. Kim carefully polished the car. ...
Parts of Speech
... How many—some ducks, three dogs, few tourists Which one—that man, this table The articles a, an and the are adjectives. Adverb—a word used to describe a verb, adjective or another adverb. Adverbs usually answer one of the following questions: how, when, where, why, to what extent, how often, to what ...
... How many—some ducks, three dogs, few tourists Which one—that man, this table The articles a, an and the are adjectives. Adverb—a word used to describe a verb, adjective or another adverb. Adverbs usually answer one of the following questions: how, when, where, why, to what extent, how often, to what ...
The vast desert of linguistics…
... 1. Tentatively, she opened the book. 2. I have always wanted to live in Canada. 3. What was this he was feeling - love or hate? 4. She had never been one to follow the ‘herd’. ...
... 1. Tentatively, she opened the book. 2. I have always wanted to live in Canada. 3. What was this he was feeling - love or hate? 4. She had never been one to follow the ‘herd’. ...
final ify ize dead ate en sign poster character person I will see you in
... way to make writing more interesting and create imagery. Words that add nothing new or are synonymous are repetitive and redundant. ...
... way to make writing more interesting and create imagery. Words that add nothing new or are synonymous are repetitive and redundant. ...
A word that describes a noun - Seething and Mundham Primary
... present (him – he is receiving the object) ...
... present (him – he is receiving the object) ...
THE PARTS OF SPEECH (BASIC OVERVIEW)
... ADJECTIVE: a word that modifies, adds meaning, or adds specificity to a noun. i.e. blue, sharp, scary, happy, his, Jennifer’s, old ARTICLE: a specific kind of adjective meaning “this, specific, singular.” i.e. the, a, an ADVERB: a word that modifies, adds meaning, or adds specificity to a verb, an a ...
... ADJECTIVE: a word that modifies, adds meaning, or adds specificity to a noun. i.e. blue, sharp, scary, happy, his, Jennifer’s, old ARTICLE: a specific kind of adjective meaning “this, specific, singular.” i.e. the, a, an ADVERB: a word that modifies, adds meaning, or adds specificity to a verb, an a ...
pollen ate en class ise ify sheep lamb knife fork I had ( cereal / serial
... verb. Singular subjects (I, he) and singular nouns (committee, class) usually have singular verbs. Plural subjects usually need plural verbs. ...
... verb. Singular subjects (I, he) and singular nouns (committee, class) usually have singular verbs. Plural subjects usually need plural verbs. ...
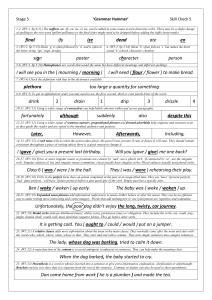
Stage 5 Check 1 Answers
... verb. Singular subjects (I, he) and singular nouns (committee, class) usually have singular verbs. Plural subjects usually need plural verbs. ...
... verb. Singular subjects (I, he) and singular nouns (committee, class) usually have singular verbs. Plural subjects usually need plural verbs. ...
pollen ate en class ise ify sheep lamb knife fork I had ( cereal / serial
... verb. Singular subjects (I, he) and singular nouns (committee, class) usually have singular verbs. Plural subjects usually need plural verbs. ...
... verb. Singular subjects (I, he) and singular nouns (committee, class) usually have singular verbs. Plural subjects usually need plural verbs. ...
English Grammar
... or a phrase or clause functioning in the sentence as a noun. The word or word group that the preposition introduces is its object. ...
... or a phrase or clause functioning in the sentence as a noun. The word or word group that the preposition introduces is its object. ...
Q: What is a Phrase?
... • My hand burned as a result of brilliant idea to stir boiling-hot water with it. • It hurt like a thousand sharp needles, but on the other hand it looked interesting. • My bike was found next to the garbage ...
... • My hand burned as a result of brilliant idea to stir boiling-hot water with it. • It hurt like a thousand sharp needles, but on the other hand it looked interesting. • My bike was found next to the garbage ...