Part of Speech PowerPoint Presentation
... Ms. Caiola is a great history teacher at Penncrest High School. ...
... Ms. Caiola is a great history teacher at Penncrest High School. ...
All our dreams can come true – if we have the courage to pursue them.
... In chapter 4 locate five sentences with adverbs and copy ...
... In chapter 4 locate five sentences with adverbs and copy ...
question bank for written tests [updated Jan 2016]
... What kind of modality is expressed in the phrase PHRASE? Does it refer to reality space, counterfactual space, or potentiality space? What kind of root modality is indicated here by would? What does the choice of was able to INF, as opposed to could INF, tell us about the success of INF? In the fina ...
... What kind of modality is expressed in the phrase PHRASE? Does it refer to reality space, counterfactual space, or potentiality space? What kind of root modality is indicated here by would? What does the choice of was able to INF, as opposed to could INF, tell us about the success of INF? In the fina ...
Appositives: a phrase that
... same grammatical structure (i.e., noun phrases, verb phrases) within a sentence or in a bulleted list. Example of parallel structure: I like to swim, to dance, and to camp. Example of non-parallel structure: I like to swim, to dance, and go ...
... same grammatical structure (i.e., noun phrases, verb phrases) within a sentence or in a bulleted list. Example of parallel structure: I like to swim, to dance, and to camp. Example of non-parallel structure: I like to swim, to dance, and go ...
Grammar Terms Year 1 and 2 - Morley Victoria Primary School
... does, do. Ends with a question mark. E.g. Where are your glasses? Exclamation – Begins how or what and must contain a verb. E.g. What large glasses you have! Command- Begins with an imperative (bossy) verb. E.g. Put your glasses on. Apostrophes Contractions- when two words are shortened to make one ...
... does, do. Ends with a question mark. E.g. Where are your glasses? Exclamation – Begins how or what and must contain a verb. E.g. What large glasses you have! Command- Begins with an imperative (bossy) verb. E.g. Put your glasses on. Apostrophes Contractions- when two words are shortened to make one ...
Because you know you love my sentence structure lectures, here is
... •Consist of a preposition and an object •Function as adjectives or adverbs •Used to show relationship •Can be added or deleted without affecting the meaning or structure of the sentence Life on a raft was an opportunity for adventure. adj. adj. Huck Finn rode the raft down the river by choice. adv. ...
... •Consist of a preposition and an object •Function as adjectives or adverbs •Used to show relationship •Can be added or deleted without affecting the meaning or structure of the sentence Life on a raft was an opportunity for adventure. adj. adj. Huck Finn rode the raft down the river by choice. adv. ...
Spelling Scheme Year 6 - St Mary`s Catholic Primary School
... past: noun or adjective referring to a previous time (e.g. In the past) or preposition or adverb showing place (e.g. he walked past me) passed: past tense of the verb ‘pass’ (e.g. I passed him in the road) precede: go in front of or before proceed: go on principal: adjective – most important (e.g. p ...
... past: noun or adjective referring to a previous time (e.g. In the past) or preposition or adverb showing place (e.g. he walked past me) passed: past tense of the verb ‘pass’ (e.g. I passed him in the road) precede: go in front of or before proceed: go on principal: adjective – most important (e.g. p ...
12.1 phrases and clauses
... Grammar is a complex – as you know – and controversial area of language study! Prescriptive approach/attitude = tends to see other varieties of language other than ‘standard’ English as incorrect or bad and is highly critical to uses of language that ‘deviates’ from established grammatical rules. De ...
... Grammar is a complex – as you know – and controversial area of language study! Prescriptive approach/attitude = tends to see other varieties of language other than ‘standard’ English as incorrect or bad and is highly critical to uses of language that ‘deviates’ from established grammatical rules. De ...
Chapter 11 - EduVenture
... Adverbial conjunctions are adverbs used to connect independent clauses Correlative conjunctions join in pairs ...
... Adverbial conjunctions are adverbs used to connect independent clauses Correlative conjunctions join in pairs ...
Grammar for Grown-ups
... words that begins with a preposition (on, in, over, under, against, with, among…) and ends with a noun or pronoun. It gives extra information about another word in the sentence. The student in the front row is smart. ...
... words that begins with a preposition (on, in, over, under, against, with, among…) and ends with a noun or pronoun. It gives extra information about another word in the sentence. The student in the front row is smart. ...
Preview - Insight Publications
... This list shows many common prepositions: about, above, across, after, against, along, among, around, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, between, beyond, by, despite, down, during, except, for, from, in, inside, into, like, near, of, off, on, out, outside, over, past, since, through, throug ...
... This list shows many common prepositions: about, above, across, after, against, along, among, around, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, between, beyond, by, despite, down, during, except, for, from, in, inside, into, like, near, of, off, on, out, outside, over, past, since, through, throug ...
a sentence which gives information. ( declarative )
... Indirect object: comes first followed by the direct object. Phrase: two or more words that function together as a group. Noun phrase: ( often abbreviated to NP) convenient term for any of the following: noun – nominal group. Modifiers: add to, change or limit the meaning of the head in a phrase. Pro ...
... Indirect object: comes first followed by the direct object. Phrase: two or more words that function together as a group. Noun phrase: ( often abbreviated to NP) convenient term for any of the following: noun – nominal group. Modifiers: add to, change or limit the meaning of the head in a phrase. Pro ...
Grammar: the rules that say how words are combined, arranged and
... Indirect object: comes first followed by the direct object. Phrase: two or more words that function together as a group. Noun phrase: ( often abbreviated to NP) convenient term for any of the following: noun – nominal group. Modifiers: add to, change or limit the meaning of the head in a phrase. Pro ...
... Indirect object: comes first followed by the direct object. Phrase: two or more words that function together as a group. Noun phrase: ( often abbreviated to NP) convenient term for any of the following: noun – nominal group. Modifiers: add to, change or limit the meaning of the head in a phrase. Pro ...
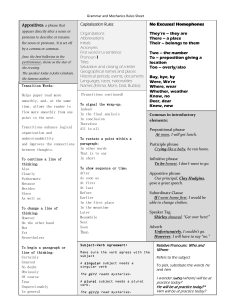
Substance Nouns
... • Voice: Was the subject of the verb giving the action, receiving the action, or acting upon itself? • Mood: What is the relationship of the statement to ...
... • Voice: Was the subject of the verb giving the action, receiving the action, or acting upon itself? • Mood: What is the relationship of the statement to ...
Morphology review
... How high can a native fluent speaker count without resorting to either to words from another language or to a generic word like many? Exemplify the system. Do numerals agree with their head nouns? adverbs: manner, time, direction/location, evidential (source of information), epistemic (degree to whi ...
... How high can a native fluent speaker count without resorting to either to words from another language or to a generic word like many? Exemplify the system. Do numerals agree with their head nouns? adverbs: manner, time, direction/location, evidential (source of information), epistemic (degree to whi ...
Adding Pronoun Constraints to a Grammar
... • other pronouns in subject position occur with plural verb forms – I eat. *I eats. They eat. *They eats. – ignore special case of ‘be’ – J&M treats ‘do’ as aux, so must include number agreement for aux ...
... • other pronouns in subject position occur with plural verb forms – I eat. *I eats. They eat. *They eats. – ignore special case of ‘be’ – J&M treats ‘do’ as aux, so must include number agreement for aux ...
File
... stand alone as a complete sentence. 2. Dependent clause- a clause with a subject and a verb that cannot stand alone as a complete sentence and, therefore, must be combined with an independent clause. Noun clause- dependent clause that function in a sentence any way that a noun can function. Ex: Th ...
... stand alone as a complete sentence. 2. Dependent clause- a clause with a subject and a verb that cannot stand alone as a complete sentence and, therefore, must be combined with an independent clause. Noun clause- dependent clause that function in a sentence any way that a noun can function. Ex: Th ...
6th grade- 2nd semester Language Arts Study Guide Nouns
... pronouns may be used either as subjects or as objects in a sentence. Articles-Articles include a, an, and the. They precede a noun or a noun phrase in a sentence. Example 1: They wanted a house with a big porch. Example 2: He bought the blue sweater on sale. Adjectives-An adjective is a word that mo ...
... pronouns may be used either as subjects or as objects in a sentence. Articles-Articles include a, an, and the. They precede a noun or a noun phrase in a sentence. Example 1: They wanted a house with a big porch. Example 2: He bought the blue sweater on sale. Adjectives-An adjective is a word that mo ...
Of Mice and Men
... Lennie, his opposite, a huge man shapeless of face, with large, pale eyes, with wide sloping shoulders who walked heavily, dragging his feet a little, the way a bear drags his paws. George stopped short in the clearing, and Lenny nearly ran ...
... Lennie, his opposite, a huge man shapeless of face, with large, pale eyes, with wide sloping shoulders who walked heavily, dragging his feet a little, the way a bear drags his paws. George stopped short in the clearing, and Lenny nearly ran ...
Gerund
... One of his duties is attending meetings. The hardest thing about learning English is understanding the gerund. One of life's pleasures is having breakfast in bed. ...
... One of his duties is attending meetings. The hardest thing about learning English is understanding the gerund. One of life's pleasures is having breakfast in bed. ...
GrammarVocab
... List of Subject Pronouns: I, you, he, she, it, we, you, they List of Object Pronouns: me, you, him, her, it, us, you, them Adjective: a word that modifies a noun or pronoun Verb: a word that shows action, being, or links a subject to its subject complement Adverb: a word that modifies a verb, an adj ...
... List of Subject Pronouns: I, you, he, she, it, we, you, they List of Object Pronouns: me, you, him, her, it, us, you, them Adjective: a word that modifies a noun or pronoun Verb: a word that shows action, being, or links a subject to its subject complement Adverb: a word that modifies a verb, an adj ...
A noun is a person, place, thing, or idea. Persons: teacher, Beyonce
... A Pronoun is a word that is used in place of one or more nouns or pronouns. A personal pronoun refers to the one speaking (first person), the one spoken to (second person), or the one spoken about (third person). Personal Pronouns Singular Plural First Person I, me, my, mine We, us, our, ours Secon ...
... A Pronoun is a word that is used in place of one or more nouns or pronouns. A personal pronoun refers to the one speaking (first person), the one spoken to (second person), or the one spoken about (third person). Personal Pronouns Singular Plural First Person I, me, my, mine We, us, our, ours Secon ...
On Your Feet! - Amy Benjamin
... 5. Act out the fact that modifiers, though important, do not form the core of the sentence (ask modifiers to sit down). 6. Act out the difference between an intransitive verb (verb that does not need a direct object: WADDLE) and a transitive verb (verb that needs or wants a direct object: WANT, LIKE ...
... 5. Act out the fact that modifiers, though important, do not form the core of the sentence (ask modifiers to sit down). 6. Act out the difference between an intransitive verb (verb that does not need a direct object: WADDLE) and a transitive verb (verb that needs or wants a direct object: WANT, LIKE ...

![question bank for written tests [updated Jan 2016]](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/014763773_1-774ef9b4ccba79bfa7cb2fb8c0f99e4d-300x300.png)