GRAMMAR REVIEW
... A clause that begins with a subordinate conjunction, making it less important than the main clause in the same sentence It cannot stand alone as a sentence ...
... A clause that begins with a subordinate conjunction, making it less important than the main clause in the same sentence It cannot stand alone as a sentence ...
grammar review
... A clause that begins with a subordinate conjunction, making it less important than the main clause in the same sentence It cannot stand alone as a sentence ...
... A clause that begins with a subordinate conjunction, making it less important than the main clause in the same sentence It cannot stand alone as a sentence ...
Types of Sentences
... 2. a COMPOUND sentence has two or more independent clauses joined by a conjunction or conjunctive adverb, or separated by a semi colon: We went to the Thunderwolves’ hockey game last night, and we met up with our old neighbours from Westfort. We went to a hockey game; needless to say, my team lost. ...
... 2. a COMPOUND sentence has two or more independent clauses joined by a conjunction or conjunctive adverb, or separated by a semi colon: We went to the Thunderwolves’ hockey game last night, and we met up with our old neighbours from Westfort. We went to a hockey game; needless to say, my team lost. ...
28HYD18_Layout 1 - Namasthe Telangana
... I have ten dozens of shoes ( incorrect) I have ten dozen of shoes (correct) Either, neither, each, everyone, many must be followed by a singular verb. Example Neither of the two men was strong. Two or more singular subjects connected by or/nor require singular verb. Example Either the cat or dog has ...
... I have ten dozens of shoes ( incorrect) I have ten dozen of shoes (correct) Either, neither, each, everyone, many must be followed by a singular verb. Example Neither of the two men was strong. Two or more singular subjects connected by or/nor require singular verb. Example Either the cat or dog has ...
subject-verb agreement background
... o Nouns or Pronouns and Words, Phrases, and Clauses can function as subjects A SUBJECT does not have to be a single word – o subjects can be words, phrases or clauses functioning in that role o (however, in most S-V Agreement exercises, we typically use single-word subjects for clarity) A SUBJECT is ...
... o Nouns or Pronouns and Words, Phrases, and Clauses can function as subjects A SUBJECT does not have to be a single word – o subjects can be words, phrases or clauses functioning in that role o (however, in most S-V Agreement exercises, we typically use single-word subjects for clarity) A SUBJECT is ...
Year 5 Programme of Study for English
... proof-read for spelling and punctuation errors perform their own compositions, using appropriate intonation, volume, and movement so that meaning is clear. ...
... proof-read for spelling and punctuation errors perform their own compositions, using appropriate intonation, volume, and movement so that meaning is clear. ...
Year 6 Programme of Study for English
... proof-read for spelling and punctuation errors perform their own compositions, using appropriate intonation, volume, and movement so that meaning is clear. ...
... proof-read for spelling and punctuation errors perform their own compositions, using appropriate intonation, volume, and movement so that meaning is clear. ...
Grammar notes from Friday, October 30th
... Example: Please write your own example here for an adjective clause ...
... Example: Please write your own example here for an adjective clause ...
Grammatical Rules from Harbrace Handbook 3a Punctuating
... Subjects joined by and usually take a plural verb. Agreement errors are common when subjects are joined by or or nor. Inverted word order may lead to agreement errors. Clauses with relative pronouns are common sites for agreement errors. Agreement errors frequently occur with indefinite pronouns. Th ...
... Subjects joined by and usually take a plural verb. Agreement errors are common when subjects are joined by or or nor. Inverted word order may lead to agreement errors. Clauses with relative pronouns are common sites for agreement errors. Agreement errors frequently occur with indefinite pronouns. Th ...
The Subject Complement (SC)
... linking verb (copula) and completes the structure. It is in dependent relationship with the predicator and can be predicted from it. For example: Mary became does not make sense. The predicator became is used here as a linking verb and as such it claims a subject complement to complete meaning. impa ...
... linking verb (copula) and completes the structure. It is in dependent relationship with the predicator and can be predicted from it. For example: Mary became does not make sense. The predicator became is used here as a linking verb and as such it claims a subject complement to complete meaning. impa ...
Adjectives and Adverbs
... I went to the movies with a friend whom my mother dislikes. (modifies the noun “friend”) The musician whose album went platinum was given an award. (modifies the noun “musician”) I think that we should leave now (represents “the thought” hence functions as a noun.) ...
... I went to the movies with a friend whom my mother dislikes. (modifies the noun “friend”) The musician whose album went platinum was given an award. (modifies the noun “musician”) I think that we should leave now (represents “the thought” hence functions as a noun.) ...
Suffixes are groups of letters attached to the ends of... h (noun,
... Suffixes Suffixes are groups of letters attached to the ends of roots, words, and word groups. Suffixes serve a grammatical function. A suffix can indicate what part of speech (noun, verb, adjective, adverb) to which the word belongs. Suffixes can also modify and extend meaning. The following suffix ...
... Suffixes Suffixes are groups of letters attached to the ends of roots, words, and word groups. Suffixes serve a grammatical function. A suffix can indicate what part of speech (noun, verb, adjective, adverb) to which the word belongs. Suffixes can also modify and extend meaning. The following suffix ...
Subject-Verb Agreement
... For more help identifying subjects and verbs, turn to page 693, Subjects, Verbs & Clauses. ...
... For more help identifying subjects and verbs, turn to page 693, Subjects, Verbs & Clauses. ...
Subject-Verb Agreement
... For more help identifying subjects and verbs, turn to page 693, Subjects, Verbs & Clauses. ...
... For more help identifying subjects and verbs, turn to page 693, Subjects, Verbs & Clauses. ...
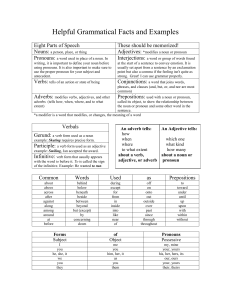
Helpful Grammatical Facts and Examples
... after an introductory adverbial clause Ex. Since you are an experienced swimmer, you can help the beginners. If you have not studied, you will probably not do well on the test. after an introductory participial phrase Ex. Bowing and smiling, the singer acknowledged the audience's applause. Stumb ...
... after an introductory adverbial clause Ex. Since you are an experienced swimmer, you can help the beginners. If you have not studied, you will probably not do well on the test. after an introductory participial phrase Ex. Bowing and smiling, the singer acknowledged the audience's applause. Stumb ...
Singular Plural
... Noun class is often closely linked to grammatical gender; in Indo-European languages, the two generally overlap. Noun class is an arbitrary set of categories and all nouns must belong to one of them. There is no semantic meaning attached to them, although there is a tendency for nouns with similar m ...
... Noun class is often closely linked to grammatical gender; in Indo-European languages, the two generally overlap. Noun class is an arbitrary set of categories and all nouns must belong to one of them. There is no semantic meaning attached to them, although there is a tendency for nouns with similar m ...
Year 6 VGP Appendix - Parklands Primary School, Leeds
... Relative clauses beginning with who, which, where, why, or whose Indicating degrees of possibility using modal verbs (e.g. might, should,will, must) or adverbs (e.g. perhaps, surely) Use of the passive voice to affect the presentation of information in a sentence (e.g. I broke the window in the gree ...
... Relative clauses beginning with who, which, where, why, or whose Indicating degrees of possibility using modal verbs (e.g. might, should,will, must) or adverbs (e.g. perhaps, surely) Use of the passive voice to affect the presentation of information in a sentence (e.g. I broke the window in the gree ...
- SlideBoom
... • Descriptive adjectives, designate qualities or attributes, may come before or after the noun or pronoun they modify for stylistic reasons. • Subject complements are adjectives that describe the subject and follow linking verbs. ...
... • Descriptive adjectives, designate qualities or attributes, may come before or after the noun or pronoun they modify for stylistic reasons. • Subject complements are adjectives that describe the subject and follow linking verbs. ...
Unit 12: Adjectives and Adverbs
... "Fifteen students passed the midterm exam; twelve students passed the final exam." Fifteen and twelve both tell us how many students; midterm and final both tell us which exam. ...
... "Fifteen students passed the midterm exam; twelve students passed the final exam." Fifteen and twelve both tell us how many students; midterm and final both tell us which exam. ...
Grammar ~ List of Topics per Class Level
... o Further ‘tense’ work o Adverbs ~ classifying by ‘where’ ‘when’ ‘how’ o Sentence construction, using adverbs in the sentences. o Finding a number of adverbs that can be used with a list of verbs Fifth Class o Adding prepositions to sentences o In all writing activities, check for the correct use of ...
... o Further ‘tense’ work o Adverbs ~ classifying by ‘where’ ‘when’ ‘how’ o Sentence construction, using adverbs in the sentences. o Finding a number of adverbs that can be used with a list of verbs Fifth Class o Adding prepositions to sentences o In all writing activities, check for the correct use of ...
Unpacked L3.1i
... grammar and usage when writing or speaking. i. Produce simple, compound, and complex sentences. Unpacked Standard: ...
... grammar and usage when writing or speaking. i. Produce simple, compound, and complex sentences. Unpacked Standard: ...
07 - School of Computing | University of Leeds
... or adjective (or other functions…) A hodge-podge (!) General adverb often ends –ly slowly, happily (but NOT early) ...
... or adjective (or other functions…) A hodge-podge (!) General adverb often ends –ly slowly, happily (but NOT early) ...
The Eight Parts of Speech
... Pronoun Replaces a noun. Can be definite (specific) or indefinite. Antecedents are the nouns they replace. Personal pronouns = I, me, my, we, us, our, ours, she, her, hers, he, him, his, it, its, you, your “My name is Edward Cullen,” he continued. “I didn’t have a chance to introduce myself last we ...
... Pronoun Replaces a noun. Can be definite (specific) or indefinite. Antecedents are the nouns they replace. Personal pronouns = I, me, my, we, us, our, ours, she, her, hers, he, him, his, it, its, you, your “My name is Edward Cullen,” he continued. “I didn’t have a chance to introduce myself last we ...