1. Verbs can be followed by direct objects, the person or thing
... Verbs can be followed by direct objects, the person or thing receiving the action of the verb. ...
... Verbs can be followed by direct objects, the person or thing receiving the action of the verb. ...
definitions and examples
... The word the pronoun replaces is called the antecedent. It should (but may not) be established before you use a pronoun. ...
... The word the pronoun replaces is called the antecedent. It should (but may not) be established before you use a pronoun. ...
Parts of Speech Definitions
... Verb: (describes action taken by a noun) run, swim, think, eat, hate, love, tease, help Transitive – need to be followed by something that receives the action(a direct object); hit, sawed, helped, painted Intransitive – verbs that can stand alone; ran, thought, shopped, swam Helping/Linking/verbs of ...
... Verb: (describes action taken by a noun) run, swim, think, eat, hate, love, tease, help Transitive – need to be followed by something that receives the action(a direct object); hit, sawed, helped, painted Intransitive – verbs that can stand alone; ran, thought, shopped, swam Helping/Linking/verbs of ...
STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES (SLO`s) FOR WORD CLASSES
... grammatically correct because they are particles in phrsal verbs, elliptical after an infinitive marker, idiomatic, or “postposed” (delayed in WH-questions or in constructions in which the object precedes the preposition). Distinguish between a particle (a preposition that accompanies a verb to conv ...
... grammatically correct because they are particles in phrsal verbs, elliptical after an infinitive marker, idiomatic, or “postposed” (delayed in WH-questions or in constructions in which the object precedes the preposition). Distinguish between a particle (a preposition that accompanies a verb to conv ...
The Nine Parts of Speech Verbs • Action Verb: tells what the subject
... Missouri, Central High School, Emily Pronouns: a word that replaces and refers to a noun. he, she, it, they Adjectives: words that modify, or describe, a noun or pronoun. pretty, stormy, dark Adverb: words that modify, or describe, a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. slowly, very, quickly ...
... Missouri, Central High School, Emily Pronouns: a word that replaces and refers to a noun. he, she, it, they Adjectives: words that modify, or describe, a noun or pronoun. pretty, stormy, dark Adverb: words that modify, or describe, a verb, an adjective, or another adverb. slowly, very, quickly ...
Parts of Speech - Net Start Class
... NOUNS carry important information in a sentence. Almost every sentence has a NOUN. ...
... NOUNS carry important information in a sentence. Almost every sentence has a NOUN. ...
Bell work: September 29, 2011
... Adjectives modify nouns or pronouns and tell which, whose, what kind, and how many. Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs and tell how, when, where, and how much. Prepositions must have an object and show a relationship between its object and some other word in the sentence. Conjunctio ...
... Adjectives modify nouns or pronouns and tell which, whose, what kind, and how many. Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs and tell how, when, where, and how much. Prepositions must have an object and show a relationship between its object and some other word in the sentence. Conjunctio ...
Parts of Speech Notes - Northwest ISD Moodle
... Examples: dog, courage, soldier, Texas, sister, etc… Verbs Action verbs – show action, most common Linking verbs – show a state of being, or that something exists; it does not show action Helping verbs – used to make verb phrases, never stand alone Adjectives – modify nouns and pronouns; the ...
... Examples: dog, courage, soldier, Texas, sister, etc… Verbs Action verbs – show action, most common Linking verbs – show a state of being, or that something exists; it does not show action Helping verbs – used to make verb phrases, never stand alone Adjectives – modify nouns and pronouns; the ...
parts of speech here
... The people who live there are on vacation. Interrogative – who, whom, which, what, whose Used to ask questions Ex/ Who borrowed my pen? Demonstrative – this, these, that, those Used to point out persons or things Ex/ This is my lucky day. Indefinite – all, few, none, another, any, anybody, anyone, b ...
... The people who live there are on vacation. Interrogative – who, whom, which, what, whose Used to ask questions Ex/ Who borrowed my pen? Demonstrative – this, these, that, those Used to point out persons or things Ex/ This is my lucky day. Indefinite – all, few, none, another, any, anybody, anyone, b ...
Parts of Speech Review
... 1. Nouns – child, Chicago, computer, honesty, happiness Nouns can be common (not capitalized) or proper (capitalized). They can sometimes be singular (girl) or plural (girls) Nouns function in many ways. Most commonly we think of them as the subject of a sentence, but they can also be the direct obj ...
... 1. Nouns – child, Chicago, computer, honesty, happiness Nouns can be common (not capitalized) or proper (capitalized). They can sometimes be singular (girl) or plural (girls) Nouns function in many ways. Most commonly we think of them as the subject of a sentence, but they can also be the direct obj ...
NOUNS-VERBS-ADJECTIVES
... Underline once the nouns, twice the verbs, and circle the adjectives. ...
... Underline once the nouns, twice the verbs, and circle the adjectives. ...
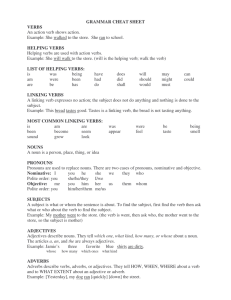
GRAMMAR CHEAT SHEET VERBS An action verb shows action
... Example: Jamie’s three favorite blue shirts are dirty. whose ...
... Example: Jamie’s three favorite blue shirts are dirty. whose ...
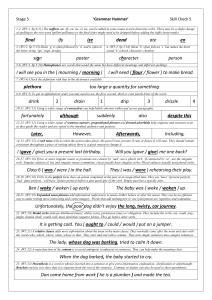
final ify ize dead ate en sign poster character person I will see you in
... 22. (W5:20) Modal verbs indicate likelihood (must), ability (can), permission (may) or obligation. They include the verbs can, could, may, might, should, shall, would, will, must (and their negative forms). They go before other verbs. ...
... 22. (W5:20) Modal verbs indicate likelihood (must), ability (can), permission (may) or obligation. They include the verbs can, could, may, might, should, shall, would, will, must (and their negative forms). They go before other verbs. ...
basic parts of speech
... Noun -- names a person, place, thing, or idea Common noun -- any one of a group My high school held a dance. Proper noun -- a particular person, thing, or idea (capitalized) Penncrest High School held a dance. Pronoun -- takes the place of a noun Adjective -- modifies a noun or a pronoun Verb -- a w ...
... Noun -- names a person, place, thing, or idea Common noun -- any one of a group My high school held a dance. Proper noun -- a particular person, thing, or idea (capitalized) Penncrest High School held a dance. Pronoun -- takes the place of a noun Adjective -- modifies a noun or a pronoun Verb -- a w ...
A noun names a person, place, thing, or idea
... (I am happy. She appears lonely. They are all of the being verbs plus appear, look, feel, smell, taste, sound, remain, become, seem. ...
... (I am happy. She appears lonely. They are all of the being verbs plus appear, look, feel, smell, taste, sound, remain, become, seem. ...
parts of speech
... noun. It is a substitute for a noun. Jim outran the animals. He outran them. Other examples: (he, him, his, she, her, hers, and it) ...
... noun. It is a substitute for a noun. Jim outran the animals. He outran them. Other examples: (he, him, his, she, her, hers, and it) ...
Parts of speech 2
... noun. It is a substitute for a noun. Jim outran the animals. He outran them. Other examples: (he, him, his, she, her, hers, and it) ...
... noun. It is a substitute for a noun. Jim outran the animals. He outran them. Other examples: (he, him, his, she, her, hers, and it) ...
Grammar Study Sheet
... A. English is a subject verb object language: it prefers a sequence of subject–verb–object in its simplest, unmarked declarative statements. B. Interrogative sentences invert word order. C. English also sees some use of the OSV (object-subject-verb) word order, especially when making comparisons usi ...
... A. English is a subject verb object language: it prefers a sequence of subject–verb–object in its simplest, unmarked declarative statements. B. Interrogative sentences invert word order. C. English also sees some use of the OSV (object-subject-verb) word order, especially when making comparisons usi ...
Word - BBC
... 1. When a verb is followed by an infinitive (a verb with no tense, usually after ‘to’): The children didn’t want to go home. 2. When a sentence has two subjects: We’ll talk about the party when Simon comes home. (The two subjects are ‘We’ and ...
... 1. When a verb is followed by an infinitive (a verb with no tense, usually after ‘to’): The children didn’t want to go home. 2. When a sentence has two subjects: We’ll talk about the party when Simon comes home. (The two subjects are ‘We’ and ...
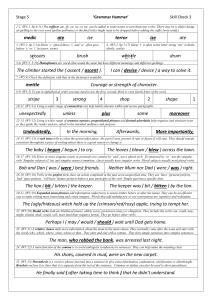
Stage 5 Check 3 – Answers
... 22. (W5:20) Modal verbs indicate likelihood (must), ability (can), permission (may) or obligation. They include the verbs can, could, may, might, should, shall, would, will, must (and their negative forms). They go before other verbs. ...
... 22. (W5:20) Modal verbs indicate likelihood (must), ability (can), permission (may) or obligation. They include the verbs can, could, may, might, should, shall, would, will, must (and their negative forms). They go before other verbs. ...