Courtney Wolfberg
... that introduces a dependent clause, joining it to a main clause. Also called a subordinator after, although, as, because, before, even if, even though, if, in order that once, provided that, rather than, since, so that, than, that, though, unless until, when, whenever, where, whereas, wherever, wh ...
... that introduces a dependent clause, joining it to a main clause. Also called a subordinator after, although, as, because, before, even if, even though, if, in order that once, provided that, rather than, since, so that, than, that, though, unless until, when, whenever, where, whereas, wherever, wh ...
Latin I Final Exam Study Guide (Final Exam is 20% of Course Grade
... Gender: Masc/Fem/Neut; Number: Sing / Pl; Case: Nom, Gen, Dat, Acc, Abl, Voc 1st & 2nd declension adjectives vs. 3rd declension adjectives o Prepositions and the noun cases that follow them in, sub, prope, ad, per, ē/ex, ā/ab, de, apud, cum, et cetera ...
... Gender: Masc/Fem/Neut; Number: Sing / Pl; Case: Nom, Gen, Dat, Acc, Abl, Voc 1st & 2nd declension adjectives vs. 3rd declension adjectives o Prepositions and the noun cases that follow them in, sub, prope, ad, per, ē/ex, ā/ab, de, apud, cum, et cetera ...
Nombre: Fecha: Study guide for final exam. Spanish II. Verb tenses
... Nombre:___________________________________________________________________________ Fecha:__________________________________________ Study guide for final exam. Spanish II. I. ...
... Nombre:___________________________________________________________________________ Fecha:__________________________________________ Study guide for final exam. Spanish II. I. ...
Parallelism - St. Cloud State University
... Boy Scouts learn cooking, canoeing, swimming, and how to make a rope. The last phrase is too heavy; it cannot balance the other –ing words. If we change the phrase to rope-making, it is balanced. A slightly different parallelism involves the common connectors either-or, neither-nor, not only-but als ...
... Boy Scouts learn cooking, canoeing, swimming, and how to make a rope. The last phrase is too heavy; it cannot balance the other –ing words. If we change the phrase to rope-making, it is balanced. A slightly different parallelism involves the common connectors either-or, neither-nor, not only-but als ...
journal-7
... that restrict the meaning of the nouns they follow. Because they are essential to the meaning of the sentence, they are not set off with ...
... that restrict the meaning of the nouns they follow. Because they are essential to the meaning of the sentence, they are not set off with ...
parts of speech here
... 6. Prepositions – words which begin a phrase that shows the relation of a noun to another word in the sentence preposition + noun (object of preposition) = prepositional phrase about, above, across, after, against, along, amid, among, around, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, besides, betw ...
... 6. Prepositions – words which begin a phrase that shows the relation of a noun to another word in the sentence preposition + noun (object of preposition) = prepositional phrase about, above, across, after, against, along, amid, among, around, at, before, behind, below, beneath, beside, besides, betw ...
Adverbs and adverbial phrases
... They usually go AFTER the verb or verb phrase, however, with passive verbs they usually go in mid-position (before the main verb but after an auxiliary verb). He runs very fast. The driver was seriously injured. ...
... They usually go AFTER the verb or verb phrase, however, with passive verbs they usually go in mid-position (before the main verb but after an auxiliary verb). He runs very fast. The driver was seriously injured. ...
Present Progressive Verbs - Catherineandadamportfolio
... end of the verb. Progressive verbs always have helping verbs. These verbs, like am, is, are, and be, come before a progressive verb in a sentence. ...
... end of the verb. Progressive verbs always have helping verbs. These verbs, like am, is, are, and be, come before a progressive verb in a sentence. ...
MBUPLOAD-5373-1
... ____8. This can take the place (or substitute) for a noun: A] Action verb b] pronoun c] preposition ____9. A word functioning as a noun, adjective, or adverb but not functioning as a verb a] action verb b] linking verb c] verbal ____10. This word is always followed by a noun or pronoun and shows rel ...
... ____8. This can take the place (or substitute) for a noun: A] Action verb b] pronoun c] preposition ____9. A word functioning as a noun, adjective, or adverb but not functioning as a verb a] action verb b] linking verb c] verbal ____10. This word is always followed by a noun or pronoun and shows rel ...
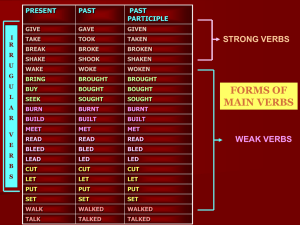
Strong and Weak Verbs
... What is a weak verb? Generally a main verb that needs a ‘t’ or ‘d’ to give its past and past participle forms is called as a weak verb • A main verb that loses an ‘e’ from its usual form to give the past and past participle forms is called as a weak verb e.g. read - read - read , bleed – bled- bled ...
... What is a weak verb? Generally a main verb that needs a ‘t’ or ‘d’ to give its past and past participle forms is called as a weak verb • A main verb that loses an ‘e’ from its usual form to give the past and past participle forms is called as a weak verb e.g. read - read - read , bleed – bled- bled ...
Action Verb Complements An ACTION VERB is a verb that shows
... whom? for whom? after the action verb. An IO must be a noun or a pronoun. Example: Sally gave her mother a check for rent. The DIRECT OBJECT answers the questions what? or whom? after the action verb. A DO must be a noun or a pronoun. Example: Jeff kicked the ball very hard. *Remember: No part of an ...
... whom? for whom? after the action verb. An IO must be a noun or a pronoun. Example: Sally gave her mother a check for rent. The DIRECT OBJECT answers the questions what? or whom? after the action verb. A DO must be a noun or a pronoun. Example: Jeff kicked the ball very hard. *Remember: No part of an ...
Subject / Verb Agreement: subjects and verbs MUST agree in
... Collective Nouns: nouns that encompass a group comprised of individuals; always singular Fields of Study: always singular Compound Subjects: two or more subjects joined by AND: always plural Subjects Joined by OR or NOR: refer to the subject that is after Or or Nor; if that subject is singular; then ...
... Collective Nouns: nouns that encompass a group comprised of individuals; always singular Fields of Study: always singular Compound Subjects: two or more subjects joined by AND: always plural Subjects Joined by OR or NOR: refer to the subject that is after Or or Nor; if that subject is singular; then ...
Verbs - San Jose State University
... Some words can be both verbs and nouns. In the first sentence below, attacks functions as a verb. It is the action of the sentence (performed by the subject—the dog). In the second sentence, we know the word attacks is not a verb because an article or an adjective can go before it. The dog attacks t ...
... Some words can be both verbs and nouns. In the first sentence below, attacks functions as a verb. It is the action of the sentence (performed by the subject—the dog). In the second sentence, we know the word attacks is not a verb because an article or an adjective can go before it. The dog attacks t ...
Q: What is a Phrase?
... • near airports (used as an adjective because it describes were the subject is located) • near busy urban airports (just made it longer…but it’s still an adjective) • near busy urban highways and airports (even longer!) ...
... • near airports (used as an adjective because it describes were the subject is located) • near busy urban airports (just made it longer…but it’s still an adjective) • near busy urban highways and airports (even longer!) ...
What is a Direct Object? A Direct Object is: a noun or pronoun that
... A Direct Object is: a noun or pronoun that takes the action of the verb. Only action verbs that are transitive can take direct objects. The Direct Object answers the question WHAT or WHOM after the verb. What is an Indirect Object? An Indirect Object is: a noun or pronoun that follows a trans ...
... A Direct Object is: a noun or pronoun that takes the action of the verb. Only action verbs that are transitive can take direct objects. The Direct Object answers the question WHAT or WHOM after the verb. What is an Indirect Object? An Indirect Object is: a noun or pronoun that follows a trans ...
Grammar Terms - GEOCITIES.ws
... The part of a sentence in contrast with a subject, generally a verb plus the connected elements (e.g., object, verb complements, etc.) Adverbs that precede verbs and refer either forwards or backwards to other sentence parts (e.g., subjects or objects). Two verbs in succession without a conjunction ...
... The part of a sentence in contrast with a subject, generally a verb plus the connected elements (e.g., object, verb complements, etc.) Adverbs that precede verbs and refer either forwards or backwards to other sentence parts (e.g., subjects or objects). Two verbs in succession without a conjunction ...
Parts of Speech Review - Richard L. Graves Middle School
... – Action verbs: can express physical or mental actions. • Transitive: followed by a direct object. (what? / whom?) – Shawn painted landscapes and portraits. ...
... – Action verbs: can express physical or mental actions. • Transitive: followed by a direct object. (what? / whom?) – Shawn painted landscapes and portraits. ...
ELA THE 12 STEVEN AND TOMMY
... • A verb is a word used to express action or a state of being. • There are two types of verbs, action and linking verbs. • Action - May express physical or mental action. Some action verbs are: run, swim, jump, and dangle. • Linking – Links or connects the subject with a noun, pronoun, or an adject ...
... • A verb is a word used to express action or a state of being. • There are two types of verbs, action and linking verbs. • Action - May express physical or mental action. Some action verbs are: run, swim, jump, and dangle. • Linking – Links or connects the subject with a noun, pronoun, or an adject ...
Parts of Speech
... Parts of Speech Noun – person, place, thing, idea (mom, Wendy’s, school, love) Pronoun – takes place of a noun (he, she, it, you, his, I, my, our) Adjective – describes a noun (flat, gooey, soft, amazing) Verb – action (run, fly, dance, dream, want) or being (am, is, are) Adverb – tells how, when, o ...
... Parts of Speech Noun – person, place, thing, idea (mom, Wendy’s, school, love) Pronoun – takes place of a noun (he, she, it, you, his, I, my, our) Adjective – describes a noun (flat, gooey, soft, amazing) Verb – action (run, fly, dance, dream, want) or being (am, is, are) Adverb – tells how, when, o ...
Infinitives The gerunds
... the infinitive can also be used without to. Read the examples given below. She wants to go. (Here the phrase ‘to go’ is an example of a to-infinitive.) She made me cry. (Here the infinitive ‘cry’ is used without the marker to.) The infinitive is a non-finite verb. In other words, it does not change ...
... the infinitive can also be used without to. Read the examples given below. She wants to go. (Here the phrase ‘to go’ is an example of a to-infinitive.) She made me cry. (Here the infinitive ‘cry’ is used without the marker to.) The infinitive is a non-finite verb. In other words, it does not change ...
I am writing a letter The passive voice is used
... is a verb, by adding to it an idea of time or mood, and must be followed by the base from of the main verb. Auxiliary / Modal verbs : Be, was, were, been, have, had, do, did, can, could, be able to May, might, must, have to, have got to, should, ought to, had better, be supposed to, be to, used to ...
... is a verb, by adding to it an idea of time or mood, and must be followed by the base from of the main verb. Auxiliary / Modal verbs : Be, was, were, been, have, had, do, did, can, could, be able to May, might, must, have to, have got to, should, ought to, had better, be supposed to, be to, used to ...
Negative verbs in other tenses
... The upshot of this is that, in all examples of Swahili verbs, on paper, either interpretation is possible (although I usually only give you one). Please do be aware of this. Note, however, that, when using the 2nd person, i.e. when talking about a person/people you are addressing directly, you are ...
... The upshot of this is that, in all examples of Swahili verbs, on paper, either interpretation is possible (although I usually only give you one). Please do be aware of this. Note, however, that, when using the 2nd person, i.e. when talking about a person/people you are addressing directly, you are ...
nouns-review
... PREDICATE NOUN – the noun following a linking verb (equated to the subject) DIRECT ADDRESS – the noun naming a person being spoken to APPOSITIVE – a noun restating a noun just previous to it DIRECT OBJECT – answers “what?” after an action verb INDIRECT OBJECT – answers “to whom?” or “for whom?” afte ...
... PREDICATE NOUN – the noun following a linking verb (equated to the subject) DIRECT ADDRESS – the noun naming a person being spoken to APPOSITIVE – a noun restating a noun just previous to it DIRECT OBJECT – answers “what?” after an action verb INDIRECT OBJECT – answers “to whom?” or “for whom?” afte ...