to them
... chercher (to look for), attendre (to wait for) and demander (to ask for) take the direct object in French. In English they take the indirect. This is not so hard to remember as, in French, these verbs are not followed by “à” which introduces the indirect object. ...
... chercher (to look for), attendre (to wait for) and demander (to ask for) take the direct object in French. In English they take the indirect. This is not so hard to remember as, in French, these verbs are not followed by “à” which introduces the indirect object. ...
Verbs, Adverbs, Prepositions, Conjunctions, Interjections
... the list complete. Also, just as some words can be a preposition or an adverb depending on their usage, so also some words can be a subordinating conjunction, a preposition, or some other part of speech depending on usage. after since when although so that whenever as ...
... the list complete. Also, just as some words can be a preposition or an adverb depending on their usage, so also some words can be a subordinating conjunction, a preposition, or some other part of speech depending on usage. after since when although so that whenever as ...
predicator - Rizka Safriyani
... predicator is the word (or a group of words) which does not belong to any of the referring meaning of the sentence. A predicate is any word which can function as the predicator of a sentence. Example; ...
... predicator is the word (or a group of words) which does not belong to any of the referring meaning of the sentence. A predicate is any word which can function as the predicator of a sentence. Example; ...
Formal Writing - University of Kansas
... • Everyone submitted their own paper. • Everyone submitted his or her own paper. • everyone is singular; therefore, the modifying pronoun should be singular. • other words that are singular include: each, someone, nobody, anybody. ...
... • Everyone submitted their own paper. • Everyone submitted his or her own paper. • everyone is singular; therefore, the modifying pronoun should be singular. • other words that are singular include: each, someone, nobody, anybody. ...
Verbs, Adverbs, Prepositions, Conjunctions, Interjections
... the list complete. Also, just as some words can be a preposition or an adverb depending on their usage, so also some words can be a subordinating conjunction, a preposition, or some other part of speech depending on usage. after since when although so that whenever as ...
... the list complete. Also, just as some words can be a preposition or an adverb depending on their usage, so also some words can be a subordinating conjunction, a preposition, or some other part of speech depending on usage. after since when although so that whenever as ...
Active voice cheat sheet, 4 Syllables
... Recognising active and passive voice You can identify the verb voice from the structure of the sentence, or if you’re more familiar with grammar, by the use of certain verb forms. We’ve explained both ways below. Sentence structure To check the voice of your verbs: ...
... Recognising active and passive voice You can identify the verb voice from the structure of the sentence, or if you’re more familiar with grammar, by the use of certain verb forms. We’ve explained both ways below. Sentence structure To check the voice of your verbs: ...
1 MODIFIERS A modifier is a word, phrase, or clause that describes
... Arthur was extremely tired at the end of the day. Here, the adverb extremely describes the adjective tired. (How tired is he? Extremely.) Prepositional Phrases Prepositions are words that describe the place, direction, or time of something. In sentences, they are combined with nouns to form preposit ...
... Arthur was extremely tired at the end of the day. Here, the adverb extremely describes the adjective tired. (How tired is he? Extremely.) Prepositional Phrases Prepositions are words that describe the place, direction, or time of something. In sentences, they are combined with nouns to form preposit ...
Tense, modality, and aspect define the status of the main verb
... of number, that is, whether the noun is singular or plural. It is also based on the category of person, which covers the distinctions of first person, second person and third person (involving any others). The different forms of English pronouns can be described in terms of person and number. ...
... of number, that is, whether the noun is singular or plural. It is also based on the category of person, which covers the distinctions of first person, second person and third person (involving any others). The different forms of English pronouns can be described in terms of person and number. ...
Verbals: Infinitives Verbals: Infinitive Phrases
... Verbals: Infinitives Verbals are formed from verbs and are used as adjectives, nouns, or adverbs. One kind of verbal is the infinitive. An infinitive is a verb form that that can be used as a noun, an adjective, or an adverb. Most infinitives begin with to. ...
... Verbals: Infinitives Verbals are formed from verbs and are used as adjectives, nouns, or adverbs. One kind of verbal is the infinitive. An infinitive is a verb form that that can be used as a noun, an adjective, or an adverb. Most infinitives begin with to. ...
language-and-literacy-levels-across-the-australian-curriculum
... including this one, to refer to sentences that are grammatically complex, having at least two clauses with one or more being a subordinate (dependent) clause. See also ‘subordinate clauses’. In the following examples, the subordinate clauses are indicated in italics: I took my umbrella because it ...
... including this one, to refer to sentences that are grammatically complex, having at least two clauses with one or more being a subordinate (dependent) clause. See also ‘subordinate clauses’. In the following examples, the subordinate clauses are indicated in italics: I took my umbrella because it ...
Grammar Policy - Narrogin Primary School
... ♦ the opportunity to develop a variety of rules and strategies to enable them to apply appropriate written and spoken Grammar. ♦ Recognise that correct Grammar is an important part of written and spoken communications. The Scope and Sequence is to show the Grammatical concepts and terms students may ...
... ♦ the opportunity to develop a variety of rules and strategies to enable them to apply appropriate written and spoken Grammar. ♦ Recognise that correct Grammar is an important part of written and spoken communications. The Scope and Sequence is to show the Grammatical concepts and terms students may ...
Sentence Function and End Punctuation:
... - Phrase = a group of words, without a subject and verb, that functions in a sentence as one part of speech 5 types of phrases: - Prepositional Phrases = begin with a preposition and end with a noun/pronoun (which is the object of the preposition and can be compound); prepositional phrases function ...
... - Phrase = a group of words, without a subject and verb, that functions in a sentence as one part of speech 5 types of phrases: - Prepositional Phrases = begin with a preposition and end with a noun/pronoun (which is the object of the preposition and can be compound); prepositional phrases function ...
Grammar Basics - School of Social Work
... Use colons to connect sentences that have a direct relationship. Example 1: After a sleepless night, the senator made her decision: she would not seek re-election. Example 2: Our mother had one rule: whenever you eat in her kitchen, wash your dish and put it away. Helpful hint: Notice that the first ...
... Use colons to connect sentences that have a direct relationship. Example 1: After a sleepless night, the senator made her decision: she would not seek re-election. Example 2: Our mother had one rule: whenever you eat in her kitchen, wash your dish and put it away. Helpful hint: Notice that the first ...
Glossary - Teaching for Effective Learning @ NPS
... including this one, to refer to sentences that are grammatically complex, having at least two clauses with one or more being a subordinate (dependent) clause. See also ‘subordinate clauses’. In the following examples, the subordinate clauses are indicated in italics: I took my umbrella because it ...
... including this one, to refer to sentences that are grammatically complex, having at least two clauses with one or more being a subordinate (dependent) clause. See also ‘subordinate clauses’. In the following examples, the subordinate clauses are indicated in italics: I took my umbrella because it ...
Tatian Corpus of Deviating Examples T
... clauses introduced by demonstrative pronouns in relative function in Old High German are sometimes ambiguous between main and subordinate clauses. Cf. sum tuomo uuas In sumero burgi/ ther niforhta got (T 200, 3031) lat. Iudex quidam erat In quadam ciuitate/ qui deum non timebat ‘a certain judge was ...
... clauses introduced by demonstrative pronouns in relative function in Old High German are sometimes ambiguous between main and subordinate clauses. Cf. sum tuomo uuas In sumero burgi/ ther niforhta got (T 200, 3031) lat. Iudex quidam erat In quadam ciuitate/ qui deum non timebat ‘a certain judge was ...
I. COMMON GRAMMATICAL ERRORS
... P e r s o n a l :I , w e , m y , m i n e , o u r , o u r s , m e , u s , y o u , y o u r , y o u r s , h e , s h e , i t , t h e y ,h i s , h e r s ,i t s , t h e i r ,t h e i r s ,h i m , h e r , i t , t h e m ...
... P e r s o n a l :I , w e , m y , m i n e , o u r , o u r s , m e , u s , y o u , y o u r , y o u r s , h e , s h e , i t , t h e y ,h i s , h e r s ,i t s , t h e i r ,t h e i r s ,h i m , h e r , i t , t h e m ...
Class Notes / Learning Log / Textbook Notes
... Essential Question: What is are adjectives and adverbs? ...
... Essential Question: What is are adjectives and adverbs? ...
pronoun cases
... As the object of a preposition: He stood in line between you and me. NOTE: Again, watch out for the following scenarios: 1. Compound object—I made sure to call Sam and (she, her). 2. Noun appositive—Everyone blames (we, us) students for the trouble. WHO VS. WHOM, p. 224 Nominative—who, whoever Objec ...
... As the object of a preposition: He stood in line between you and me. NOTE: Again, watch out for the following scenarios: 1. Compound object—I made sure to call Sam and (she, her). 2. Noun appositive—Everyone blames (we, us) students for the trouble. WHO VS. WHOM, p. 224 Nominative—who, whoever Objec ...
Spanish: Direct, Indirect, and Reflexive Pronouns
... 5.) She sits in the chair near the window. ____________________________________ 6.) You take off your shoes. ...
... 5.) She sits in the chair near the window. ____________________________________ 6.) You take off your shoes. ...
ESL-BU095 Syllabus TTH - COM-FSM
... 70% - 80% = C 60% - 70% = D Below 60% = F If you need to miss an exam, you must let me know before the exam! You can send an e-mail, or call and leave a message with one of the secretaries –there is no excuse for not notifying me. I will allow you to take the test at another time if you cannot come ...
... 70% - 80% = C 60% - 70% = D Below 60% = F If you need to miss an exam, you must let me know before the exam! You can send an e-mail, or call and leave a message with one of the secretaries –there is no excuse for not notifying me. I will allow you to take the test at another time if you cannot come ...
possessive pronoun
... It is used for everything non-human, so for things and animals, etc. When your pet animal is referred to you may use ‘he’ and ‘she’. INDIRECT OBJECT AND DIRECT OBJECT. I see him. Where are my trousers, I cannot find them anywhere. ( !! ) Roger likes us all. It rains, my dog likes it. He told me a ni ...
... It is used for everything non-human, so for things and animals, etc. When your pet animal is referred to you may use ‘he’ and ‘she’. INDIRECT OBJECT AND DIRECT OBJECT. I see him. Where are my trousers, I cannot find them anywhere. ( !! ) Roger likes us all. It rains, my dog likes it. He told me a ni ...
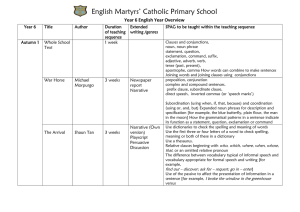
English Martyrs` Catholic Primary School Year 6 English Year
... Subordination (using when, if, that, because) and coordination (using or, and, but) Expanded noun phrases for description and specification [for example, the blue butterfly, plain flour, the man in the moon] How the grammatical patterns in a sentence indicate its function as a statement, question, e ...
... Subordination (using when, if, that, because) and coordination (using or, and, but) Expanded noun phrases for description and specification [for example, the blue butterfly, plain flour, the man in the moon] How the grammatical patterns in a sentence indicate its function as a statement, question, e ...
Spanish: Direct, Indirect, and Reflexive Pronouns
... 5.) She sits in the chair near the window. ____________________________________ 6.) You take off your shoes. ...
... 5.) She sits in the chair near the window. ____________________________________ 6.) You take off your shoes. ...
sentence - Greer Middle College
... as: • He is taller than I (am tall). • This helps you as much as (it helps) me. • She is as noisy as I (am). • Comparisons are really shorthand sentences which usually omit words, such as those in the parentheses in the sentences above. If you complete the comparison in your head, you can choose the ...
... as: • He is taller than I (am tall). • This helps you as much as (it helps) me. • She is as noisy as I (am). • Comparisons are really shorthand sentences which usually omit words, such as those in the parentheses in the sentences above. If you complete the comparison in your head, you can choose the ...
Spanish: Direct, Indirect, and Reflexive Pronouns
... ¾ The indirect object pronouns must always be used even if the indirect object is stated. Use the preposition a to clarify le and les. Also use a mí, a tí, a nosotros/as, a vosotros/as to place emphasis on the indirect object. Pepe regala flores a su madre. Tomas da el dinero a mí. Pepe le regala fl ...
... ¾ The indirect object pronouns must always be used even if the indirect object is stated. Use the preposition a to clarify le and les. Also use a mí, a tí, a nosotros/as, a vosotros/as to place emphasis on the indirect object. Pepe regala flores a su madre. Tomas da el dinero a mí. Pepe le regala fl ...
Chinese grammar
This article concerns Standard Chinese. For the grammars of other forms of Chinese, see their respective articles via links on Chinese language and varieties of Chinese.The grammar of Standard Chinese shares many features with other varieties of Chinese. The language almost entirely lacks inflection, so that words typically have only one grammatical form. Categories such as number (singular or plural) and verb tense are frequently not expressed by any grammatical means, although there are several particles that serve to express verbal aspect, and to some extent mood.The basic word order is subject–verb–object (SVO). Otherwise, Chinese is chiefly a head-last language, meaning that modifiers precede the words they modify – in a noun phrase, for example, the head noun comes last, and all modifiers, including relative clauses, come in front of it. (This phenomenon is more typically found in SOV languages like Turkish and Japanese.)Chinese frequently uses serial verb constructions, which involve two or more verbs or verb phrases in sequence. Chinese prepositions behave similarly to serialized verbs in some respects (several of the common prepositions can also be used as full verbs), and they are often referred to as coverbs. There are also location markers, placed after a noun, and hence often called postpositions; these are often used in combination with a coverb. Predicate adjectives are normally used without a copular verb (""to be""), and can thus be regarded as a type of verb.As in many east Asian languages, classifiers or measure words are required when using numerals (and sometimes other words such as demonstratives) with nouns. There are many different classifiers in the language, and each countable noun generally has a particular classifier associated with it. Informally, however, it is often acceptable to use the general classifier 个 [個] ge in place of other specific classifiers.Examples given in this article use simplified Chinese characters (with the traditional characters following in brackets if they differ) and standard pinyin Romanization.