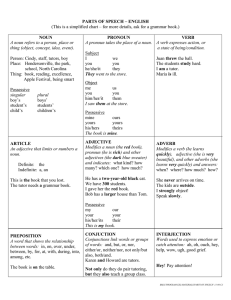
The dreaded grammar cards
... Connect groups of words 1) And, but, or, nor, for, so, yet 2) Either/or, neither/nor, but/and 3) (adverbs) After, although, as, as if, when, where, while, though, unless, until ...
... Connect groups of words 1) And, but, or, nor, for, so, yet 2) Either/or, neither/nor, but/and 3) (adverbs) After, although, as, as if, when, where, while, though, unless, until ...
Parts of Speech- Verbs - VCC Library
... Some verbs do not describe actions. These verbs talk about how things exist, or what they are similar to. These are called verbs of being. Some examples are be (is, are, were, …), have, seem, feel, sound, and taste. Example: ...
... Some verbs do not describe actions. These verbs talk about how things exist, or what they are similar to. These are called verbs of being. Some examples are be (is, are, were, …), have, seem, feel, sound, and taste. Example: ...
Parts of Speech - s3.amazonaws.com
... A noun is the name of anything, As house or garden, hoop, or swing. Instead of nouns, the pronouns standHer head, your face, his arm, my hand. Adjectives tell the kind of noun, As great, small, pretty, white, or brown. Verbs tell of something to be doneTo read, count, sing, talk, laugh, or run. How ...
... A noun is the name of anything, As house or garden, hoop, or swing. Instead of nouns, the pronouns standHer head, your face, his arm, my hand. Adjectives tell the kind of noun, As great, small, pretty, white, or brown. Verbs tell of something to be doneTo read, count, sing, talk, laugh, or run. How ...
File
... S usually we can insert a preposition and the sentence will make sense (its like having an imaginary prepositional phrase that functions as an adverb or time or place) ...
... S usually we can insert a preposition and the sentence will make sense (its like having an imaginary prepositional phrase that functions as an adverb or time or place) ...
To exempt Spanish 101 To exempt Spanish 102
... The preterite vs. the imperfect Hace + time expressions Reflexive verbs and reciprocals Gustar and similar verbs Using the infinitive after prepositions Use of the article Using the participle w/ “estar” Por and para Object pronouns- direct, indirect, reflexive, together The subjunctive (in noun/ind ...
... The preterite vs. the imperfect Hace + time expressions Reflexive verbs and reciprocals Gustar and similar verbs Using the infinitive after prepositions Use of the article Using the participle w/ “estar” Por and para Object pronouns- direct, indirect, reflexive, together The subjunctive (in noun/ind ...
Cornell Notes Topic/Objective: Verb Types Name: Learning Target: I
... These verbs are called linking verbs because they link the _____________ of a sentence with another word in the sentence. A linking verb will ______________ the subject with the verb. be, am, is, are, was, were, been, being appear, become, feel, grow, look, seem, remain, smell, sound, stay, tast ...
... These verbs are called linking verbs because they link the _____________ of a sentence with another word in the sentence. A linking verb will ______________ the subject with the verb. be, am, is, are, was, were, been, being appear, become, feel, grow, look, seem, remain, smell, sound, stay, tast ...
Table of Contents – Overview
... A verb or noun is highlighted in a sentence and students have to sort it (ID it) as a verb or noun. *Use Supplemental Practice Activity 1 (still would use the direct teach in the re-teach unit, but would use these student pages). P2: Action and Linking Verbs Given an action verb (not in a sentence e ...
... A verb or noun is highlighted in a sentence and students have to sort it (ID it) as a verb or noun. *Use Supplemental Practice Activity 1 (still would use the direct teach in the re-teach unit, but would use these student pages). P2: Action and Linking Verbs Given an action verb (not in a sentence e ...
Parts of speech
... A word that can take the place of a noun Example: John is here. He is here. There are many types of pronouns that are not so easily explained. See the lists in your grammar book and read them over frequently. Some pronouns are that, which, his, anyone, its, mine, herself, one . . . The list goes on. ...
... A word that can take the place of a noun Example: John is here. He is here. There are many types of pronouns that are not so easily explained. See the lists in your grammar book and read them over frequently. Some pronouns are that, which, his, anyone, its, mine, herself, one . . . The list goes on. ...
wordclasses_24.09.13
... Possessive pronouns: forms of personal pronouns indicating actual possession or just an abstract relation between the person and some objects(my, your, his, her, one’s , our, their) Wh-pronouns: used in certain question forms, or may act as complementizer (what, who, whom, whoever) ...
... Possessive pronouns: forms of personal pronouns indicating actual possession or just an abstract relation between the person and some objects(my, your, his, her, one’s , our, their) Wh-pronouns: used in certain question forms, or may act as complementizer (what, who, whom, whoever) ...
Subject-Verb Agreement Intro
... A word that refers to one person, place, thing, or idea is singular in number. ...
... A word that refers to one person, place, thing, or idea is singular in number. ...
Slide 1
... An absolute phrase is usually--but not always--a group of words consisting of a noun or pronoun and a participle as well as any related modifiers. An absolute phrase is not a clause because it does not have a true verb. Absolute phrases do not directly connect to or modify any specific word in the s ...
... An absolute phrase is usually--but not always--a group of words consisting of a noun or pronoun and a participle as well as any related modifiers. An absolute phrase is not a clause because it does not have a true verb. Absolute phrases do not directly connect to or modify any specific word in the s ...
VERBS: Action, Linking, Helping
... A verb is one or more words telling what the subject does, how the subject exists, or how it links the subject to another word that describes the subject. There are three forms of verbs: 1. Action Verbs: verbs that show activity, movement, thought, or process. They tell what action the subject perfo ...
... A verb is one or more words telling what the subject does, how the subject exists, or how it links the subject to another word that describes the subject. There are three forms of verbs: 1. Action Verbs: verbs that show activity, movement, thought, or process. They tell what action the subject perfo ...
ONLY - Council Rock School District
... It has no grammatical relation to other words in the sentence. It is set off from the rest of the sentence by an exclamation point or comma! ...
... It has no grammatical relation to other words in the sentence. It is set off from the rest of the sentence by an exclamation point or comma! ...
(PPT, Unknown)
... (noun/pronoun), a verb and an object. The object refers to a person or a thing affected by the action performed by the subject. The following are the examples of S-V-O sentences: ...
... (noun/pronoun), a verb and an object. The object refers to a person or a thing affected by the action performed by the subject. The following are the examples of S-V-O sentences: ...
Parts of Speech:
... i. Magnificently is the adverb because it describes how Joe (subject) played (verb). 2. Adverbs usually end in an “ly,” but not always a. Example: yesterday, earlier, rather 3. Practice: Identify the adverbs: a. Yesterday, the light shone brilliantly. ...
... i. Magnificently is the adverb because it describes how Joe (subject) played (verb). 2. Adverbs usually end in an “ly,” but not always a. Example: yesterday, earlier, rather 3. Practice: Identify the adverbs: a. Yesterday, the light shone brilliantly. ...
the parts of speech
... can stand on its own as a complete sentence. A dependent clause cannot stand on its own; it must be attached to an independent clause. The baby cried is an independent clause; it has a subject and a predicate (a verb). In The baby cried because she was hungry, because she was hungry is a dependent c ...
... can stand on its own as a complete sentence. A dependent clause cannot stand on its own; it must be attached to an independent clause. The baby cried is an independent clause; it has a subject and a predicate (a verb). In The baby cried because she was hungry, because she was hungry is a dependent c ...
Parts of Speech Review
... Her telegram to Nina and Ralph brought good news. object can have modifiers It happened during the last examination. ...
... Her telegram to Nina and Ralph brought good news. object can have modifiers It happened during the last examination. ...
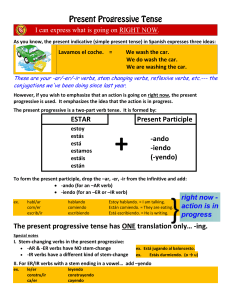
ESTAR Present Participle -ando -iendo (
... We can say "I am studying tomorrow." This puts a present tense verb together with a future time expression. This does NOT happen in Spanish. The present progressive (-ing form) is used ONLY for actions in progress. IR + A + INF (or the future tense, which you will learn later) is used for fu ...
... We can say "I am studying tomorrow." This puts a present tense verb together with a future time expression. This does NOT happen in Spanish. The present progressive (-ing form) is used ONLY for actions in progress. IR + A + INF (or the future tense, which you will learn later) is used for fu ...
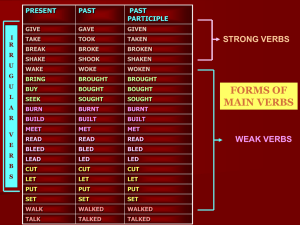
Strong and Weak Verbs
... What is a weak verb? Generally a main verb that needs a ‘t’ or ‘d’ to give its past and past participle forms is called as a weak verb • A main verb that loses an ‘e’ from its usual form to give the past and past participle forms is called as a weak verb e.g. read - read - read , bleed – bled- bled ...
... What is a weak verb? Generally a main verb that needs a ‘t’ or ‘d’ to give its past and past participle forms is called as a weak verb • A main verb that loses an ‘e’ from its usual form to give the past and past participle forms is called as a weak verb e.g. read - read - read , bleed – bled- bled ...
Sentence Building Blocks
... We’ll have to come back to these later! PHRASES: A group of related words that lacks a subject or predicate or both, and that acts as a single part of speech (see next page). Several common types of phrases include the following: Prepositional Phrase: consists of a preposition and its object, plus a ...
... We’ll have to come back to these later! PHRASES: A group of related words that lacks a subject or predicate or both, and that acts as a single part of speech (see next page). Several common types of phrases include the following: Prepositional Phrase: consists of a preposition and its object, plus a ...
Identifying Parts Of Speech
... Identifying Parts Of Speech Once you have learned about nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs, you will be able to identify them in sentences and tell them apart from each other. Some words can be used as more than one part of speech. This is particularly true of words that can be both nou ...
... Identifying Parts Of Speech Once you have learned about nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs, you will be able to identify them in sentences and tell them apart from each other. Some words can be used as more than one part of speech. This is particularly true of words that can be both nou ...