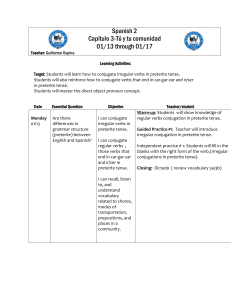
湖南省第一师范学院外语系备课用纸
... Practice (30 minutes) through questions about meaning changes and sentence pattern variations. IV. Summary (15 minutes) through discussions about usages of English verb forms for different moods. V. Detailed information about English moods and their semantic relations. ...
... Practice (30 minutes) through questions about meaning changes and sentence pattern variations. IV. Summary (15 minutes) through discussions about usages of English verb forms for different moods. V. Detailed information about English moods and their semantic relations. ...
sentence ([the, girl, sing, a, song], []).
... as the difference of the following pair of lists [1, 2, 3, 5, 8] and [5, 8] [1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8, 9] and [6, 7, 8, 9] [1,2,3] and [ ]. Each of these are instances of the pair of two incomplete lists [1,2,3 | X] and X. We call such pair a ...
... as the difference of the following pair of lists [1, 2, 3, 5, 8] and [5, 8] [1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8, 9] and [6, 7, 8, 9] [1,2,3] and [ ]. Each of these are instances of the pair of two incomplete lists [1,2,3 | X] and X. We call such pair a ...
pronouns - YuhhediEnglish
... I wrote a letter to the president, who responded quickly. In that sentence, president is antecedent of the pronoun who. A pronoun must agree with its antecedent in person, number, and gender. Personal pronouns In order to use personal pronouns, it is important to know about case (subject, object, ...
... I wrote a letter to the president, who responded quickly. In that sentence, president is antecedent of the pronoun who. A pronoun must agree with its antecedent in person, number, and gender. Personal pronouns In order to use personal pronouns, it is important to know about case (subject, object, ...
Chapter 5 Prepositional phrases
... phrase they head, although, their function can be extended to other uses as well. Some of the prepositions have clearly developed from verbs and still co-exist with their verbal counterparts, which occasionally may lead to semantic ambiguity, notably when they are used with another verb in a serial ...
... phrase they head, although, their function can be extended to other uses as well. Some of the prepositions have clearly developed from verbs and still co-exist with their verbal counterparts, which occasionally may lead to semantic ambiguity, notably when they are used with another verb in a serial ...
Passive Sentences
... 1. The object of the active verb is the subject of the passive verb (“English” in the example sentences below). Therefore, verbs which cannot be followed by objects (intransitive verbs) cannot be used in passive voice. These are some common intransitive verbs: appear, arrive, come, cry, die, go, hap ...
... 1. The object of the active verb is the subject of the passive verb (“English” in the example sentences below). Therefore, verbs which cannot be followed by objects (intransitive verbs) cannot be used in passive voice. These are some common intransitive verbs: appear, arrive, come, cry, die, go, hap ...
Practice and Apply
... Pay attention to the placement of participial phrases in your writing. A phrase in the wrong place is known as a misplaced modifier or dangling participle. ...
... Pay attention to the placement of participial phrases in your writing. A phrase in the wrong place is known as a misplaced modifier or dangling participle. ...
Grammar for Grade 9 IV Clauses and Sentence
... • May not have an expressed subject. Since the speaker is commanding “you” to do something, the understood subject is “you”. – Close the door. • While the sentence doesn’t say who is supposed to do the closing, the subject is “you”: whoever the speaker is ...
... • May not have an expressed subject. Since the speaker is commanding “you” to do something, the understood subject is “you”. – Close the door. • While the sentence doesn’t say who is supposed to do the closing, the subject is “you”: whoever the speaker is ...
1 Introduction
... the verb takes additional suffixes. First, an obligatory suffix marks gender: an a marks feminine, an o masculine. Following the gender suffix, either a plural suffix, s, appears or else there is no suffix at all. The lack of an explicit plural suffix marks singular. The Gender and Number columns of ...
... the verb takes additional suffixes. First, an obligatory suffix marks gender: an a marks feminine, an o masculine. Following the gender suffix, either a plural suffix, s, appears or else there is no suffix at all. The lack of an explicit plural suffix marks singular. The Gender and Number columns of ...
The Roots of Nominality, the Nominality of Roots - LingBuzz
... is not all there until all of it has occurred in time. In this sense, because verbal meaning is based on event structure (cf. especially Ramchand 2008), it has a temporal dimension built in. Nominal meaning, by contrast, does not have a temporal dimension built in. Most nouns refer to continuants, o ...
... is not all there until all of it has occurred in time. In this sense, because verbal meaning is based on event structure (cf. especially Ramchand 2008), it has a temporal dimension built in. Nominal meaning, by contrast, does not have a temporal dimension built in. Most nouns refer to continuants, o ...
The English Gerund-Participle in Cognitive Grammar
... When nominal uses of the type illustrated in (11) below are treated, Langacker’s cognitive grammar analysis shifts from the word-level to that of the clause: (11) Zelda’s reluctantly signing the contract Such ‘factive nominalizations’ are held to apply to a higher-level structure: reluctantly signi ...
... When nominal uses of the type illustrated in (11) below are treated, Langacker’s cognitive grammar analysis shifts from the word-level to that of the clause: (11) Zelda’s reluctantly signing the contract Such ‘factive nominalizations’ are held to apply to a higher-level structure: reluctantly signi ...
Analysis ACT Rubric
... logical use of verb tense and pronoun person on the basis of information in the paragraph or essay as a whole ...
... logical use of verb tense and pronoun person on the basis of information in the paragraph or essay as a whole ...
Slides
... Davidson (1967) verbs stand for kinds of events Verbs are like common nouns rather than proper nouns Thus, ‘hit’ is a kind of action, or event (∃e) [hitting (e)] There is an event and it’s a hitting event (with particular hittings as its instances) Panini (4th century BC), Davidson (1967) ...
... Davidson (1967) verbs stand for kinds of events Verbs are like common nouns rather than proper nouns Thus, ‘hit’ is a kind of action, or event (∃e) [hitting (e)] There is an event and it’s a hitting event (with particular hittings as its instances) Panini (4th century BC), Davidson (1967) ...
Analogy Sentence “Cheatsheet”
... Analogy Sentence “Cheatsheet” When posed with a word-pair from an analogy, use the following sentences to help determine their relationship. These sentences are meant to help you, but they are not the ONLY sentences that can be formed to show the relationship between the 2 words in a word-pair. ...
... Analogy Sentence “Cheatsheet” When posed with a word-pair from an analogy, use the following sentences to help determine their relationship. These sentences are meant to help you, but they are not the ONLY sentences that can be formed to show the relationship between the 2 words in a word-pair. ...
segmentation of french sentences - Association for Computational
... clause. It is a striking peculiarity of the French language that every (or nearly every) subordinate clause is introduced by some kind of introductory word, a conjunction or the like. Or to put it otherwise: the first word in a subordinate clause is always a word that belongs to a very limited class ...
... clause. It is a striking peculiarity of the French language that every (or nearly every) subordinate clause is introduced by some kind of introductory word, a conjunction or the like. Or to put it otherwise: the first word in a subordinate clause is always a word that belongs to a very limited class ...
Document
... • The Simple Subject tells WHAT or WHOM the sentence is about. Chad, my next door neighbor, went to the store to buy some apples. Simple Subject Complete Subject The Complete Subject tells about the WHOLE subject of the sentence. ...
... • The Simple Subject tells WHAT or WHOM the sentence is about. Chad, my next door neighbor, went to the store to buy some apples. Simple Subject Complete Subject The Complete Subject tells about the WHOLE subject of the sentence. ...
ENGLISH FOR PRACTICAL PURPOSES
... The main relative pronouns in English are who (with its derived forms whom and whose), which, and that. The relative pronoun which refers to things rather than persons, as in the shirt, which used to be red, is faded. For persons, who is used (the man who saw me was tall). The oblique case form of ...
... The main relative pronouns in English are who (with its derived forms whom and whose), which, and that. The relative pronoun which refers to things rather than persons, as in the shirt, which used to be red, is faded. For persons, who is used (the man who saw me was tall). The oblique case form of ...
PROLOG Family Knowledge Base Assignment 2004
... the noun). Here the verb_phrase means this word order: adores the spoons inordinately. The first three words (an irksome instrumentalist) are well for singular noun phrase. This example would be successful for phrase sentence in singular form. Query b) phrase(verb_phrase(N),[reviles,the,spoons,a,lot ...
... the noun). Here the verb_phrase means this word order: adores the spoons inordinately. The first three words (an irksome instrumentalist) are well for singular noun phrase. This example would be successful for phrase sentence in singular form. Query b) phrase(verb_phrase(N),[reviles,the,spoons,a,lot ...
ENGLISH FOR PRACTICAL PURPOSES
... The main relative pronouns in English are who (with its derived forms whom and whose), which, and that. The relative pronoun which refers to things rather than persons, as in the shirt, which used to be red, is faded. For persons, who is used (the man who saw me was tall). The oblique case form of ...
... The main relative pronouns in English are who (with its derived forms whom and whose), which, and that. The relative pronoun which refers to things rather than persons, as in the shirt, which used to be red, is faded. For persons, who is used (the man who saw me was tall). The oblique case form of ...
MODES OF LINGUISTIC COMMUNICATION
... A base is the form to which an affix is added. In many cases, the base is also the root. In books, for example, book is the root to which the affix –s is added. In other cases, however, the base can be larger than the root, which is always just a single morpheme. This happens in words such as blacke ...
... A base is the form to which an affix is added. In many cases, the base is also the root. In books, for example, book is the root to which the affix –s is added. In other cases, however, the base can be larger than the root, which is always just a single morpheme. This happens in words such as blacke ...
The Phrase… - Cloudfront.net
... A group of words that does NOT have a subject and a verb, and acts as 1 part of speech. In other words…. NOT a complete sentence, but part of a sentence! ...
... A group of words that does NOT have a subject and a verb, and acts as 1 part of speech. In other words…. NOT a complete sentence, but part of a sentence! ...
Final Exam
... 43- In the sentence "Many students enjoyed the concert", the noun phrase the concert functions as a/an: a. predicator complement b. subject attribute c. direct object d. indirect object 44- In the sentence "Last night,' they revealed who had done it", the function ‘direct object’ is realized by: a. ...
... 43- In the sentence "Many students enjoyed the concert", the noun phrase the concert functions as a/an: a. predicator complement b. subject attribute c. direct object d. indirect object 44- In the sentence "Last night,' they revealed who had done it", the function ‘direct object’ is realized by: a. ...
граматика англійської та української мов
... languages but also on the basis of dead languages like Sanskrit, ancient Greek or Latin. Also the hypothetic abstract etalon language created by typologists for the sake of investigation is widely made use of by universal typology. This “language” plays a very important role in foreseeing the quanti ...
... languages but also on the basis of dead languages like Sanskrit, ancient Greek or Latin. Also the hypothetic abstract etalon language created by typologists for the sake of investigation is widely made use of by universal typology. This “language” plays a very important role in foreseeing the quanti ...
final exam b
... a. non-finite clause functioning as an object attribute b. non-finite clause functioning as a predicator complement c. prepositional phrase functioning as a postmodifier d. non-finite clause functioning as an adverbial 47- in the sentence "My mother knitted me a sweater", the underlined noun phrase ...
... a. non-finite clause functioning as an object attribute b. non-finite clause functioning as a predicator complement c. prepositional phrase functioning as a postmodifier d. non-finite clause functioning as an adverbial 47- in the sentence "My mother knitted me a sweater", the underlined noun phrase ...
![sentence ([the, girl, sing, a, song], []).](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008435180_1-1401b6c76d4c5a85cc857ddb5452dfe9-300x300.png)