Phrases and clauses
... Notes: Phrases and Clauses Definition Phrase – group of words that act as a single part of speech and do not have a verb or a subject 1. verb phrase – includes main verb and any helping verb(s) in a sentence Example: The drama club has been practicing all afternoon for the opening of the play 2. ini ...
... Notes: Phrases and Clauses Definition Phrase – group of words that act as a single part of speech and do not have a verb or a subject 1. verb phrase – includes main verb and any helping verb(s) in a sentence Example: The drama club has been practicing all afternoon for the opening of the play 2. ini ...
The Parts of Speech--2
... plural (both, many); a few may be singular or plural (see 21e). Most indefinite pronouns function as noun equivalents (Something is burning), but some can also function as adjectives (All campers must check in at the lodge). all another any anybody anyone ...
... plural (both, many); a few may be singular or plural (see 21e). Most indefinite pronouns function as noun equivalents (Something is burning), but some can also function as adjectives (All campers must check in at the lodge). all another any anybody anyone ...
Review of Chapter 2 – ENG 314
... “Why do you sit there like that?” “I know it is wet And the sun is not sunny. But we can have lots of good fun …!” “I know some good games we could play,” Said the cat. ...
... “Why do you sit there like that?” “I know it is wet And the sun is not sunny. But we can have lots of good fun …!” “I know some good games we could play,” Said the cat. ...
Grammar Ch 18 Notes - Ohio County Schools
... •A ______________ ______________ is a noun, a pronoun, or an adjective that appears with a ______________ verb and tells something about the ______________. •There are two kinds of subject complements: –______________ ______________ –______________ ______________. •A predicate nominative is a ______ ...
... •A ______________ ______________ is a noun, a pronoun, or an adjective that appears with a ______________ verb and tells something about the ______________. •There are two kinds of subject complements: –______________ ______________ –______________ ______________. •A predicate nominative is a ______ ...
Preposition Notes
... Ex: The boy looked at a magazine. (The preposition is at and the phrase is at a magazine) Infinitive- to + verb The word "to" is not a preposition in this case Ex: The maid wanted to clean the room. (The predicate/verb in this sentence is wanted and the (to clean) is the infinitive. Verb Phrase- con ...
... Ex: The boy looked at a magazine. (The preposition is at and the phrase is at a magazine) Infinitive- to + verb The word "to" is not a preposition in this case Ex: The maid wanted to clean the room. (The predicate/verb in this sentence is wanted and the (to clean) is the infinitive. Verb Phrase- con ...
Compounding in English and Arabic latest
... The meaning of a primary compound can be generally understood from the meaning of its parts, and this is semantically referred to as endocentric compound. 2.1.2. Secondary Compounds In a secondary compound or stem‐compound, no derivational affix is involved, and the constituents of a derived stem ar ...
... The meaning of a primary compound can be generally understood from the meaning of its parts, and this is semantically referred to as endocentric compound. 2.1.2. Secondary Compounds In a secondary compound or stem‐compound, no derivational affix is involved, and the constituents of a derived stem ar ...
Phrases - KoplikEnglish10
... verb. If it is an independent clause, it may stand alone as a sentence: Ex: White dogs are pretty. If it is a dependent (subordinate) clause, it may not stand alone: Ex: Although white dogs are pretty. As shown in the preceding example, a subordinating word is used in dependent clauses. This word re ...
... verb. If it is an independent clause, it may stand alone as a sentence: Ex: White dogs are pretty. If it is a dependent (subordinate) clause, it may not stand alone: Ex: Although white dogs are pretty. As shown in the preceding example, a subordinating word is used in dependent clauses. This word re ...
Prepositions
... 2- Compound (two words as one): within/ underneath/ outside/ without/ underfoot 3- Phrasal (more than one word working as one preposition): on top of/ together with/ by means of/ in back of/ on behalf of/ in between NOTE: the first pronoun or noun following a preposition is its object. Ex. The bug w ...
... 2- Compound (two words as one): within/ underneath/ outside/ without/ underfoot 3- Phrasal (more than one word working as one preposition): on top of/ together with/ by means of/ in back of/ on behalf of/ in between NOTE: the first pronoun or noun following a preposition is its object. Ex. The bug w ...
Grade 8 English Language Arts Exam Review
... Indicate whether the verb tense i n each sentence is present, past, or future. (a) The shipment will arrive next week. (b) We play the game seriously. (c) The baby wailed all night. (d) Our tests will be i n three days. 4. Verbs need to agree with their subjects. Circle the correct verb in parenthes ...
... Indicate whether the verb tense i n each sentence is present, past, or future. (a) The shipment will arrive next week. (b) We play the game seriously. (c) The baby wailed all night. (d) Our tests will be i n three days. 4. Verbs need to agree with their subjects. Circle the correct verb in parenthes ...
English 8: Grammar - SHS
... 4. Sonny, swallow your food very slowly. 5. Some older people were quite happy with the club’s proposal. 6. The architect worked quite methodically. ...
... 4. Sonny, swallow your food very slowly. 5. Some older people were quite happy with the club’s proposal. 6. The architect worked quite methodically. ...
The Preposition - Jessore Govt City College
... (a) Do you sleep on your back or your front?(b) The boy rode on the elephant’s back.(c) We were sitting in the back row.(d) He ran away through the back door.(e) We got seats at the back. (f) He came back home last night. (g) She stepped back to let her brother pass. (h) The barbed wire kept the pro ...
... (a) Do you sleep on your back or your front?(b) The boy rode on the elephant’s back.(c) We were sitting in the back row.(d) He ran away through the back door.(e) We got seats at the back. (f) He came back home last night. (g) She stepped back to let her brother pass. (h) The barbed wire kept the pro ...
Curriculum Map for Progression in Vocabulary, Grammar and
... sentence (eg. I broke the window in the greenhouse versus The window in the greenhouse was broken (by me) The difference between structures of informal speech and structures appropriate for formal speech and writing (*eg. The use of question tags: He’s your friend, isn’t he? Or the use of subjunctiv ...
... sentence (eg. I broke the window in the greenhouse versus The window in the greenhouse was broken (by me) The difference between structures of informal speech and structures appropriate for formal speech and writing (*eg. The use of question tags: He’s your friend, isn’t he? Or the use of subjunctiv ...
3rd grade crct rdgradereadingandlanguageartscrctstudyguide1
... Dictionary – find the definition of a word. Encyclopedia – find detailed information about a topic Glossary – a mini-dictionary at the end of a book Newspaper/Magazine – has news on things that are happening right now Table of Contents – a list of chapters or topics found near the beginning of the b ...
... Dictionary – find the definition of a word. Encyclopedia – find detailed information about a topic Glossary – a mini-dictionary at the end of a book Newspaper/Magazine – has news on things that are happening right now Table of Contents – a list of chapters or topics found near the beginning of the b ...
Linguistic Typology: Word Order
... In the house I take house rather than the as the head. In other words, I follow the old NP analysis, not the more recent DP analysis. Perhaps the latter is more appropriate syntactically, but semantically the noun is clearly the most important element and thus should be the head. ...
... In the house I take house rather than the as the head. In other words, I follow the old NP analysis, not the more recent DP analysis. Perhaps the latter is more appropriate syntactically, but semantically the noun is clearly the most important element and thus should be the head. ...
Business Communication - Tipton County Schools, TN
... pronoun to other words to form a phrase Prepositions introduce phrases Prepositional phrases may modify: Nouns (acting as adjectives) Action verbs Adjectives Adverbs ...
... pronoun to other words to form a phrase Prepositions introduce phrases Prepositional phrases may modify: Nouns (acting as adjectives) Action verbs Adjectives Adverbs ...
NAME
... 14.Everyone in the room cheered when the announcement was made. pronoun 15.The sun was shining as we set out for our first winter camping trip. verb 16.Small children often insist that they can do it by themselves. adjective 17.Dust covered every surface in the locked bedroom. noun 18.The census tak ...
... 14.Everyone in the room cheered when the announcement was made. pronoun 15.The sun was shining as we set out for our first winter camping trip. verb 16.Small children often insist that they can do it by themselves. adjective 17.Dust covered every surface in the locked bedroom. noun 18.The census tak ...
1A Parts of Speech
... [Interrogative adjective: “What books have you read?” “What kind of fruit is that?”] 5. Adverb [Answers the question, “How?” “When?” “Where?” “To what degree?” etc.] Modifying a verb: “He ate quickly.” “She slept soundly.” Modifying an adjective: “They were very smart.” Modifying another adverb: “He ...
... [Interrogative adjective: “What books have you read?” “What kind of fruit is that?”] 5. Adverb [Answers the question, “How?” “When?” “Where?” “To what degree?” etc.] Modifying a verb: “He ate quickly.” “She slept soundly.” Modifying an adjective: “They were very smart.” Modifying another adverb: “He ...
Grammar Notes - Teacher Pages
... him, she, her, hers, it, its, we, our, ours, us, you, your, yours, they, their, theirs, them, who, whom, whose, which, that, these, those, all, another, any, anybody, anyone, anything, both, each, either, everybody, everyone, everything, few, many, more, most, much, neither, nobody, none, no one, on ...
... him, she, her, hers, it, its, we, our, ours, us, you, your, yours, they, their, theirs, them, who, whom, whose, which, that, these, those, all, another, any, anybody, anyone, anything, both, each, either, everybody, everyone, everything, few, many, more, most, much, neither, nobody, none, no one, on ...
Parts of Speech - The Latin Library
... I see but I don't understand. · Subordinate - joins dependent clauses to the main idea of a sentence: Although the night was dark, we found our way. We found our way until the sun set. We found our way because there was a full moon. Preposition - a word that shows the relationship between a noun or ...
... I see but I don't understand. · Subordinate - joins dependent clauses to the main idea of a sentence: Although the night was dark, we found our way. We found our way until the sun set. We found our way because there was a full moon. Preposition - a word that shows the relationship between a noun or ...
All our dreams can come true – if we have the courage to pursue them.
... 17 – An adjective modifies two types of words, they are ____ and ____. ...
... 17 – An adjective modifies two types of words, they are ____ and ____. ...
GrammarVocab
... (That means you need to memorize these.) Parts of Speech Grammar: a way of thinking about language Noun: the name of a person, place, or thing Pronoun: a word that takes the place of a noun List of Subject Pronouns: I, you, he, she, it, we, you, they List of Object Pronouns: me, you, him, her, it, u ...
... (That means you need to memorize these.) Parts of Speech Grammar: a way of thinking about language Noun: the name of a person, place, or thing Pronoun: a word that takes the place of a noun List of Subject Pronouns: I, you, he, she, it, we, you, they List of Object Pronouns: me, you, him, her, it, u ...
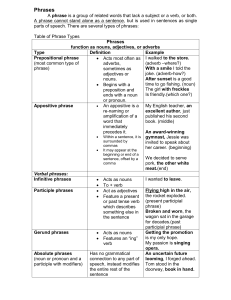
PHRASES
... they may have modifiers and complements. However, verbals are used as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs, not as verbs. The three kinds of verbals are participles, gerunds, and infinitives. 1. Participial Phrases – used as an adjective; consists of a participle and any complements or modifiers the partic ...
... they may have modifiers and complements. However, verbals are used as nouns, adjectives, or adverbs, not as verbs. The three kinds of verbals are participles, gerunds, and infinitives. 1. Participial Phrases – used as an adjective; consists of a participle and any complements or modifiers the partic ...
Phrases: 1.) Prepositional Phrases 2.) Appositives 3.) Gerund 4
... 1. ALWAYS start with a preposition 2. ENDS with the FIRST NOUN /PRONOUN Noun is called the _____________ Abbreviation: ___ ____ 3. Noun may (or may not) have adjectives. in time to you ...
... 1. ALWAYS start with a preposition 2. ENDS with the FIRST NOUN /PRONOUN Noun is called the _____________ Abbreviation: ___ ____ 3. Noun may (or may not) have adjectives. in time to you ...
Parts of Speech PowerPoint
... The predicate nominative and predicate adjective are also called subject complements because they refer to the subject. The direct object and indirect object are also called the objective complements because each is an object that completes the meaning of the ...
... The predicate nominative and predicate adjective are also called subject complements because they refer to the subject. The direct object and indirect object are also called the objective complements because each is an object that completes the meaning of the ...
All our dreams can come true – if we have the courage to pursue them.
... “Atrocious cruelties.” Of a very poor quality; extremely bad or unpleasant: “Atrocious weather.”Which one of the words is a noun– “indolent” or “indolence?” How do you know that this word is probably an adjective by ...
... “Atrocious cruelties.” Of a very poor quality; extremely bad or unpleasant: “Atrocious weather.”Which one of the words is a noun– “indolent” or “indolence?” How do you know that this word is probably an adjective by ...