Formula Definition Explanation Example S, conj S sentence comma
... In a series of three or more adjectives modifying a single noun, place a comma after each adjective except the last adjective. An appositive is a parenthetical expression placed between commas after a noun. It provides more information about that noun. *An appositive may be placed at the end of a se ...
... In a series of three or more adjectives modifying a single noun, place a comma after each adjective except the last adjective. An appositive is a parenthetical expression placed between commas after a noun. It provides more information about that noun. *An appositive may be placed at the end of a se ...
Finite and non-finite verbs
... 1. The subject of the verb “emphasis” is “the author”: as the subject is singular, the verb must also be singular and must take the present tense, i.e. “emphasises”. Note, too that the conjunction “and” joins together two predicates: “criticises” and “emphasises”. Each verb must be the same part of ...
... 1. The subject of the verb “emphasis” is “the author”: as the subject is singular, the verb must also be singular and must take the present tense, i.e. “emphasises”. Note, too that the conjunction “and” joins together two predicates: “criticises” and “emphasises”. Each verb must be the same part of ...
Propositions and Sentence Structure
... In this case, the word “John” is equated with the word “student.” It needs to be noted that the author is not saying that they are entirely equal in every respect. John may be many things besides a student, and there may be other students besides John. But the author is stating that at least in some ...
... In this case, the word “John” is equated with the word “student.” It needs to be noted that the author is not saying that they are entirely equal in every respect. John may be many things besides a student, and there may be other students besides John. But the author is stating that at least in some ...
Resume Writing 101
... Rank order by importance to the career objective Do not say Member of … Emphasize your leadership roles Spell out the organization’s name: Do not use abbreviations or acronyms ...
... Rank order by importance to the career objective Do not say Member of … Emphasize your leadership roles Spell out the organization’s name: Do not use abbreviations or acronyms ...
Gerunds and Infinitive Phrases
... GERUNDS Gerund and present participle phrases are easy to confuse because they both begin with an ing word. The difference is that a gerund phrase will always function as a noun while a present participle phrase describes another word in the sentence. Examples: Jamming too much clothing into a wash ...
... GERUNDS Gerund and present participle phrases are easy to confuse because they both begin with an ing word. The difference is that a gerund phrase will always function as a noun while a present participle phrase describes another word in the sentence. Examples: Jamming too much clothing into a wash ...
Narrative Assessment Protocol
... 1. Begin coding after the examiner provides directions for the child to begin telling a story. Do not code while child is supposed to be looking at the pictures, even if the child begins his narrative during this time. 2. Do not code off-topic discourse, such as conversation with the examiner about ...
... 1. Begin coding after the examiner provides directions for the child to begin telling a story. Do not code while child is supposed to be looking at the pictures, even if the child begins his narrative during this time. 2. Do not code off-topic discourse, such as conversation with the examiner about ...
Participles (Part II)
... PARTICIPLES (II) are verbal adjectives, in that they are formed from a verb, conveying an idea of action, but also act like an adjective, agreeing with a noun, e.g. broken glass, sliced tomatoes, a written complaint. Being an adjective, a past participle must agree with its noun in number, gender an ...
... PARTICIPLES (II) are verbal adjectives, in that they are formed from a verb, conveying an idea of action, but also act like an adjective, agreeing with a noun, e.g. broken glass, sliced tomatoes, a written complaint. Being an adjective, a past participle must agree with its noun in number, gender an ...
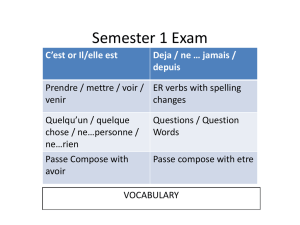
Semester 1 Exam - Sault Ste. Marie Area Public Schools
... – Put ne before the helping verb and personne after the past participle (second verb) – Je n’ai vu personne ...
... – Put ne before the helping verb and personne after the past participle (second verb) – Je n’ai vu personne ...
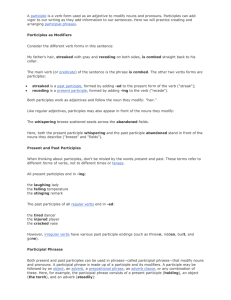
A participle is a verb form used as an adjective to modify nouns and
... A participial phrase should refer clearly to a noun or pronoun in the sentence. We have to be careful when combining sentences such as these: I curled my toes and squinted. The doctor prepared to puncture my arm with a needle. Notice what happens if we drop "I" and change the first sentence to a par ...
... A participial phrase should refer clearly to a noun or pronoun in the sentence. We have to be careful when combining sentences such as these: I curled my toes and squinted. The doctor prepared to puncture my arm with a needle. Notice what happens if we drop "I" and change the first sentence to a par ...
Sentence Patterns
... Pattern #9: Open with an adverb clause. 1. An adverb (adverbial) clause has a subject and a predicate but cannot stand alone as its own sentence. 2. Common adverb clause beginners: after, although, as, because, before, if, in order that, since, so, though, unless, until, when, where, while. 3. Use a ...
... Pattern #9: Open with an adverb clause. 1. An adverb (adverbial) clause has a subject and a predicate but cannot stand alone as its own sentence. 2. Common adverb clause beginners: after, although, as, because, before, if, in order that, since, so, though, unless, until, when, where, while. 3. Use a ...
Verb Reference Sheet – ALL Tenses!
... I want them to eat the bread. I doubt that she lives in Rogers. ...
... I want them to eat the bread. I doubt that she lives in Rogers. ...
En el Agente de Viajes más con… QUERER, PREFERIR, TENER
... You will receive a flashcard that has either a conjugated form of one of the following verbs: PREFERIR, QUERER, or TENER or a subject pronoun. *If you have a verb, you will need to find the person with the appropriate subject pronoun. *If you have a subject pronoun, you will need to find the PEOPLE ...
... You will receive a flashcard that has either a conjugated form of one of the following verbs: PREFERIR, QUERER, or TENER or a subject pronoun. *If you have a verb, you will need to find the person with the appropriate subject pronoun. *If you have a subject pronoun, you will need to find the PEOPLE ...
Noun clauses
... complements, appositives, objects of prepositions, and may be modified by adjectives ...
... complements, appositives, objects of prepositions, and may be modified by adjectives ...
Sentence Patterns - APLangRocksthefreeworld
... • Repetition of the same word or words at the end of successive phrases, clauses, or sentences (opposite of anaphora) • Places emphasis on the last word of the sentence, which causes the reader to neglect less pertinent information that may have preceded Examples: "...and that government of the peop ...
... • Repetition of the same word or words at the end of successive phrases, clauses, or sentences (opposite of anaphora) • Places emphasis on the last word of the sentence, which causes the reader to neglect less pertinent information that may have preceded Examples: "...and that government of the peop ...
Sentence Patterns - APLangRocksthefreeworld
... • Repetition of the same word or words at the end of successive phrases, clauses, or sentences (opposite of anaphora) • Places emphasis on the last word of the sentence, which causes the reader to neglect less pertinent information that may have preceded Examples: "...and that government of the peop ...
... • Repetition of the same word or words at the end of successive phrases, clauses, or sentences (opposite of anaphora) • Places emphasis on the last word of the sentence, which causes the reader to neglect less pertinent information that may have preceded Examples: "...and that government of the peop ...
Systemic Linguistics: Core Linguistics
... relationships by word position in the sentence (= word order) • synthetic languages signal grammatical relationships by the shape of the words (=inflectional endings) • 1500 years ago, English was much more synthetic than it is today. It has changed into a more analytic language ...
... relationships by word position in the sentence (= word order) • synthetic languages signal grammatical relationships by the shape of the words (=inflectional endings) • 1500 years ago, English was much more synthetic than it is today. It has changed into a more analytic language ...
section 4.0 word usage, capitalization, and numbers
... that/which/who: use which, not that, with clauses that do not change the meaning of the basic sentence (nonrestrictive clauses), and place a comma before which; that is used before clauses that would change the meaning of the sentence if removed and do not require a preceding comma; that and which r ...
... that/which/who: use which, not that, with clauses that do not change the meaning of the basic sentence (nonrestrictive clauses), and place a comma before which; that is used before clauses that would change the meaning of the sentence if removed and do not require a preceding comma; that and which r ...
Basic Sentence Parts
... 7. All of these are noun substitutes except one: a) Pronoun b) Gerund c) Infinitive d) Preposition e) None of the above 8. Which one of these adverbs can be used as subject of the sentence? a) Adverb of manner b) Adverb of frequency c) Adverb of place d) Adverb of affirmation e) Adverb of negation ...
... 7. All of these are noun substitutes except one: a) Pronoun b) Gerund c) Infinitive d) Preposition e) None of the above 8. Which one of these adverbs can be used as subject of the sentence? a) Adverb of manner b) Adverb of frequency c) Adverb of place d) Adverb of affirmation e) Adverb of negation ...
Romanian se-verbs: how much we can unify and how much is to be
... Like in the other Romance languages, the so-called “se-verbs” (verbs accompanied by clitic pronouns from the accusative reflexive paradigm) have a variety of uses in Romanian – reflexive, reciprocal, anticausative (also called ‘inchoative’), middle, passive, impersonal (see GALR, Cornilescu 1998, Do ...
... Like in the other Romance languages, the so-called “se-verbs” (verbs accompanied by clitic pronouns from the accusative reflexive paradigm) have a variety of uses in Romanian – reflexive, reciprocal, anticausative (also called ‘inchoative’), middle, passive, impersonal (see GALR, Cornilescu 1998, Do ...
Participles
... Ferens is a participle. In its verbal function,. it expresses an action and takes an object (dona). In its adjectival function, it describes sacerdosrand therefore agrees with saeerdiis in gender, number and case (rnase... sing., nom.). NOTA BE:N'E: . Remember that !Ylpartidples are adjectives and m ...
... Ferens is a participle. In its verbal function,. it expresses an action and takes an object (dona). In its adjectival function, it describes sacerdosrand therefore agrees with saeerdiis in gender, number and case (rnase... sing., nom.). NOTA BE:N'E: . Remember that !Ylpartidples are adjectives and m ...
Morphology-new-lecture5
... It contains more than one morpheme. What do in- and flect mean? This is a case of a non-compositional meaning. In explorationists, if you know the meaning of the parts, you know the meaning of the whole. Not necessarily so for inflect. Non-compositional meaning cannot be derived from its par ...
... It contains more than one morpheme. What do in- and flect mean? This is a case of a non-compositional meaning. In explorationists, if you know the meaning of the parts, you know the meaning of the whole. Not necessarily so for inflect. Non-compositional meaning cannot be derived from its par ...
english 9 - Mona Shores Blogs
... A clause (subordinate or dependent) is two or more related words that contain a verb and its subject, but do not express a complete thought. A clause functions as a single sentence part, either noun, adjective, or adverb. Clauses usually begin with an introductory word. a. The arrow that has left th ...
... A clause (subordinate or dependent) is two or more related words that contain a verb and its subject, but do not express a complete thought. A clause functions as a single sentence part, either noun, adjective, or adverb. Clauses usually begin with an introductory word. a. The arrow that has left th ...
Chapter 2 From meaning to form
... such as irregularly inflected words like children, derived words like kindness, compounds like milk-shake or idioms like kick the bucket. In such cases, grammatical structure also enters into the lexicon. In fact, information about the grammatical properties of each lexical item, such as word class ...
... such as irregularly inflected words like children, derived words like kindness, compounds like milk-shake or idioms like kick the bucket. In such cases, grammatical structure also enters into the lexicon. In fact, information about the grammatical properties of each lexical item, such as word class ...
Unit 2: Make a Difference!
... vowels: ar and or; ur, er and ir. Students will be able to blend sounds to decode words. Students will be able to pronounce high frequency words. ...
... vowels: ar and or; ur, er and ir. Students will be able to blend sounds to decode words. Students will be able to pronounce high frequency words. ...