Parts of Speech: Nouns
... 1. Sam dropped his textbook on the floor. 2. The shoppers couldn’t find their car in the parking lot. ...
... 1. Sam dropped his textbook on the floor. 2. The shoppers couldn’t find their car in the parking lot. ...
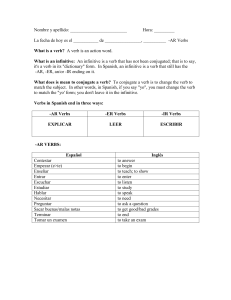
Nombre y apellido
... What is a verb? A verb is an action word. What is an infinitive: An infinitive is a verb that has not been conjugated; that is to say, it's a verb in its "dictionary" form. In Spanish, an infinitive is a verb that still has the -AR, -ER, an/or -IR ending on it. What does is mean to conjugate a verb? ...
... What is a verb? A verb is an action word. What is an infinitive: An infinitive is a verb that has not been conjugated; that is to say, it's a verb in its "dictionary" form. In Spanish, an infinitive is a verb that still has the -AR, -ER, an/or -IR ending on it. What does is mean to conjugate a verb? ...
The Passive Voice
... indefinite or unknown, the Passive voice is used. In the Passive voice, the Subject of the sentence both does and receives the action of the verb. The Passive voice in English is constructed like this: Books are sold in the bookstore. Books , as the subject is also receiving the action of the verb. ...
... indefinite or unknown, the Passive voice is used. In the Passive voice, the Subject of the sentence both does and receives the action of the verb. The Passive voice in English is constructed like this: Books are sold in the bookstore. Books , as the subject is also receiving the action of the verb. ...
final ify ize dead ate en sign poster character person I will see you in
... 1-2. (W5:1. Sp 6:11) The suffixes ate, ify, en, ize ,or ise, can be added to some nouns to turn them into verbs. There may be a slight change of spelling to the root word (pollen-pollinate) or the final letter might need to be dropped before adding the suffix (note-notify). ...
... 1-2. (W5:1. Sp 6:11) The suffixes ate, ify, en, ize ,or ise, can be added to some nouns to turn them into verbs. There may be a slight change of spelling to the root word (pollen-pollinate) or the final letter might need to be dropped before adding the suffix (note-notify). ...
Definitions of grammar Definiciones de la gramática
... complete thought (subject, verb, object): Martha loves the city. Subject [sujeto]Generally, the person or thing that performs the action in a sentence. For example "New York grew rapidly." New York (who grew?) is the subject. Subjunctive Mood [modo subjuntivo].Verb tenses that indicate non-factual a ...
... complete thought (subject, verb, object): Martha loves the city. Subject [sujeto]Generally, the person or thing that performs the action in a sentence. For example "New York grew rapidly." New York (who grew?) is the subject. Subjunctive Mood [modo subjuntivo].Verb tenses that indicate non-factual a ...
The Imperfect
... Mr. Rodriguez Spanish III The Imperfect The imperfect, like the preterit, is used to describe actions that took place in the past. On the other hand, just like prepositions that have the same meaning, “por and para”, or verbs, like “ser & estar”, the imperfect and preterit could also have different ...
... Mr. Rodriguez Spanish III The Imperfect The imperfect, like the preterit, is used to describe actions that took place in the past. On the other hand, just like prepositions that have the same meaning, “por and para”, or verbs, like “ser & estar”, the imperfect and preterit could also have different ...
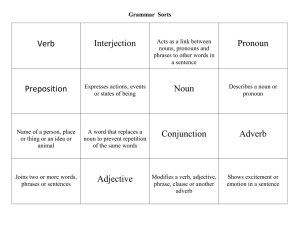
Parts of Speech
... Mood: Indicative, Imperative, Infinitive, Subjunctive, Participle 2 Verbs belong to conjugations. The present active infinitive signals the conjugation of a verb. -āre ...
... Mood: Indicative, Imperative, Infinitive, Subjunctive, Participle 2 Verbs belong to conjugations. The present active infinitive signals the conjugation of a verb. -āre ...
Verbs with reflexive pronouns - Señora Holmes
... pronouns that refer to the ______________ or with direct ______________ that are different from the ______________. • DO NOT use a reflexive pronoun when the action is being done to someone other than the subject • Use ______ when the subject is doing the action to another person. • Modelo: • Juan s ...
... pronouns that refer to the ______________ or with direct ______________ that are different from the ______________. • DO NOT use a reflexive pronoun when the action is being done to someone other than the subject • Use ______ when the subject is doing the action to another person. • Modelo: • Juan s ...
WOW Day 2 corrected
... 3. Subject-verb agreement – if the subject of the sentence is singular, then the verb is also singular - Example: My dog is cute (dog = subject, is = verb) 4. Irregular verbs – in past tense we change the spelling (don’t just add –ed) Examples: tell – told teach – taught swim – swam ride – rode 5. A ...
... 3. Subject-verb agreement – if the subject of the sentence is singular, then the verb is also singular - Example: My dog is cute (dog = subject, is = verb) 4. Irregular verbs – in past tense we change the spelling (don’t just add –ed) Examples: tell – told teach – taught swim – swam ride – rode 5. A ...
Parts of Speech
... He told me that my dog dashed in his backyard. I sprinted as fast as I could and I still lost! (action verbs) I am hungry. (linking verb) I was hoping we could go together. (helping verbs) ...
... He told me that my dog dashed in his backyard. I sprinted as fast as I could and I still lost! (action verbs) I am hungry. (linking verb) I was hoping we could go together. (helping verbs) ...
STUDENT LEARNING OUTCOMES (SLO`s) FOR WORD CLASSES
... Conjugate “new” verbs using the five forms for regular verbs. Explain the formation of some new words. Classify words into one of the four form classes (noun, verb, adjective, adverb) Using the following shared characteristics: derivational affixes, inflectional suffixes, frame sentence, and structu ...
... Conjugate “new” verbs using the five forms for regular verbs. Explain the formation of some new words. Classify words into one of the four form classes (noun, verb, adjective, adverb) Using the following shared characteristics: derivational affixes, inflectional suffixes, frame sentence, and structu ...
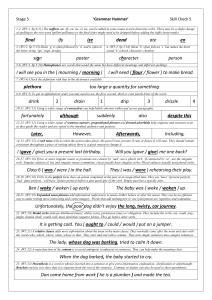
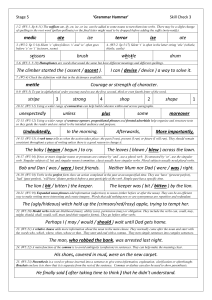
Stage 5 Check 3 – Answers
... Perhaps I ( may / would / should ) wait until Dad gets home. 23. (W5:21) A relative clause adds more information about the noun in the main clause. They normally come after the noun and start with the words who, which, where, when, whose or that. They start and end with a comma. They turn simple sen ...
... Perhaps I ( may / would / should ) wait until Dad gets home. 23. (W5:21) A relative clause adds more information about the noun in the main clause. They normally come after the noun and start with the words who, which, where, when, whose or that. They start and end with a comma. They turn simple sen ...
medic ate ize terror ize ate scissors brush whistle drum The climber
... Perhaps I ( may / would / should ) wait until Dad gets home. 23. (W5:21) A relative clause adds more information about the noun in the main clause. They normally come after the noun and start with the words who, which, where, when, whose or that. They start and end with a comma. They turn simple sen ...
... Perhaps I ( may / would / should ) wait until Dad gets home. 23. (W5:21) A relative clause adds more information about the noun in the main clause. They normally come after the noun and start with the words who, which, where, when, whose or that. They start and end with a comma. They turn simple sen ...
Verbs.English.
... • Some first person pronouns are things like: I, me, we, and us. They usually address the name of the speaker. • Second person pronouns will always address someone else directly, usually using “you”. • And third person pronouns will refer directly to others using: he, she, it, they, and them. • Some ...
... • Some first person pronouns are things like: I, me, we, and us. They usually address the name of the speaker. • Second person pronouns will always address someone else directly, usually using “you”. • And third person pronouns will refer directly to others using: he, she, it, they, and them. • Some ...
Major Parts of Speech
... Sounds we make to convey extreme emotion or to create emphasis when we’re talking, sometimes when we can’t think of a good way to express ourselves. The problem with interjections is that they require a great deal of context to be understood. For instance, hey can mean hello, or that’s great, or sto ...
... Sounds we make to convey extreme emotion or to create emphasis when we’re talking, sometimes when we can’t think of a good way to express ourselves. The problem with interjections is that they require a great deal of context to be understood. For instance, hey can mean hello, or that’s great, or sto ...
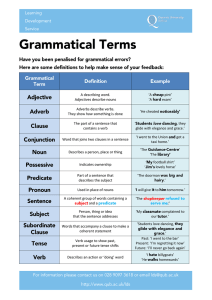
Glossary of Gramatical Terms
... She, he you, mine, hers, yours, himself, yourself. You can’t keep all the apples yourself! This, that, these, those. These are mine Each, any, some, all som ...
... She, he you, mine, hers, yours, himself, yourself. You can’t keep all the apples yourself! This, that, these, those. These are mine Each, any, some, all som ...
A describing word. Adjectives describe nouns `A pint` `A exam
... Adverbs describe verbs. They show how something is done ...
... Adverbs describe verbs. They show how something is done ...
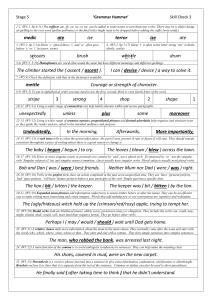
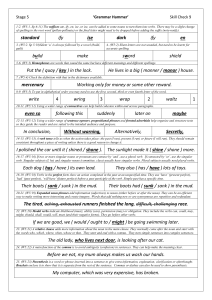
Stage 5 Check 9
... Before we eat, my mum always makes us wash our hands. 25. (W5:23) Parenthesis is a word or phrase inserted into a sentence to give extra information, explanation, clarification or afterthought. Brackets enclose it to show that it is separate from the rest of the sentence. Commas or dashes can also b ...
... Before we eat, my mum always makes us wash our hands. 25. (W5:23) Parenthesis is a word or phrase inserted into a sentence to give extra information, explanation, clarification or afterthought. Brackets enclose it to show that it is separate from the rest of the sentence. Commas or dashes can also b ...
Making Subjects and Verbs Agree • A plural verb should be used
... • Use a singular verb when two or more singular nouns or pronouns are connected by “or” or “nor”. o Neither excessive note card use nor memorization is conducive to an effective presentation. • The verb should agree with the part of the subject nearest to the verb in sentences with compound subjects ...
... • Use a singular verb when two or more singular nouns or pronouns are connected by “or” or “nor”. o Neither excessive note card use nor memorization is conducive to an effective presentation. • The verb should agree with the part of the subject nearest to the verb in sentences with compound subjects ...
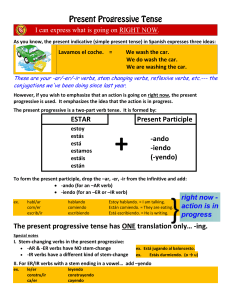
ESTAR Present Participle -ando -iendo (
... -AR & -ER verbs have NO stem-change -IR verbs have a different kind of stem-change ...
... -AR & -ER verbs have NO stem-change -IR verbs have a different kind of stem-change ...
Noun Clauses - 2 - Binus Repository
... • Sometimes in spoken English, no change is made in the noun clause verb, especially if the speaker is reporting something immediately or soon after it was said. • Immediate reporting: A: What did the teacher just say? I didn’t hear him -- B:He said he wants us to read Chapter Six. • Sometimes the p ...
... • Sometimes in spoken English, no change is made in the noun clause verb, especially if the speaker is reporting something immediately or soon after it was said. • Immediate reporting: A: What did the teacher just say? I didn’t hear him -- B:He said he wants us to read Chapter Six. • Sometimes the p ...
a quick english grammar review
... Accusative: Direct Object, reference, manner, subject of infinitive ...
... Accusative: Direct Object, reference, manner, subject of infinitive ...