AP Spanish Print Tutorial: Vocabulary Recognition II
... Countless words in Spanish are formed by adding affixes (prefixes and suffixes) to root words. Many of these affixes add a new shade of meaning to the word without changing its grammatical function (part of speech). Others not only change the meaning, but change the grammatical function of the word, ...
... Countless words in Spanish are formed by adding affixes (prefixes and suffixes) to root words. Many of these affixes add a new shade of meaning to the word without changing its grammatical function (part of speech). Others not only change the meaning, but change the grammatical function of the word, ...
8 Parts of Speech
... • Indicates action (mental or visible action) or a state of being • Linking verb – verb that connects a word at or near the beginning of a sentence with a word at or near the end – The most common linking verb is some form of be • Helping verb – verb that can be added to another verb to make a singl ...
... • Indicates action (mental or visible action) or a state of being • Linking verb – verb that connects a word at or near the beginning of a sentence with a word at or near the end – The most common linking verb is some form of be • Helping verb – verb that can be added to another verb to make a singl ...
Passive and Active voices.
... ● Transitive and Intransitive Verbs Transitive verbs are action verbs that have a direct object to perform that action ● I baked some cookies Intransitive verbs are action verbs that don't have a direct object to perform that action. ● I laughed ● Linking Verbs Linking verbs are verbs that won’t mea ...
... ● Transitive and Intransitive Verbs Transitive verbs are action verbs that have a direct object to perform that action ● I baked some cookies Intransitive verbs are action verbs that don't have a direct object to perform that action. ● I laughed ● Linking Verbs Linking verbs are verbs that won’t mea ...
Past participles used as adjectives
... same form as the past tense of the verb. However, you can tell the difference because: • The past tense acts as a verb and has a subject “I” = subject I burned my hand. • The past participle acts as an adjective and describes a noun My hand is burned. ...
... same form as the past tense of the verb. However, you can tell the difference because: • The past tense acts as a verb and has a subject “I” = subject I burned my hand. • The past participle acts as an adjective and describes a noun My hand is burned. ...
Document
... Pronouns include personal pronouns, indefinite pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, interrogative pronouns, possessive pronouns, and reflexive pronouns. It chased her Some like it hot This is very pretty Which is the train to Liverpool? The red book is mine The children hurt themselves Common nouns c ...
... Pronouns include personal pronouns, indefinite pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, interrogative pronouns, possessive pronouns, and reflexive pronouns. It chased her Some like it hot This is very pretty Which is the train to Liverpool? The red book is mine The children hurt themselves Common nouns c ...
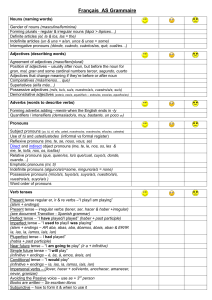
Français AS Grammaire
... Gender of nouns (masculine/feminine) Forming plurals - regular & irregular nouns (lápiz > lápices…) Definite articles (el, la & los, las = the) Indefinite articles (un & una = a/an, unos & unas = some) Interrogative pronouns (dónde, cuándo, cuántos/as, qué, cual/es…) Adjectives (describing words) Ag ...
... Gender of nouns (masculine/feminine) Forming plurals - regular & irregular nouns (lápiz > lápices…) Definite articles (el, la & los, las = the) Indefinite articles (un & una = a/an, unos & unas = some) Interrogative pronouns (dónde, cuándo, cuántos/as, qué, cual/es…) Adjectives (describing words) Ag ...
parts_of_speech_g_8 - Al-Oruba International Schools
... Notice how helping verbs work together with main verbs to form complete verb phrases. Example: is leaving - may become - might have remained Sometimes the parts of a verb phrase are interrupted by other parts of speech. Example : She had always been thinking of her future. Note: the word n ...
... Notice how helping verbs work together with main verbs to form complete verb phrases. Example: is leaving - may become - might have remained Sometimes the parts of a verb phrase are interrupted by other parts of speech. Example : She had always been thinking of her future. Note: the word n ...
Subject – verb agreement
... the verb. Since there is not the subject, the verb agrees with what follows. There are many questions. There is a question. 10. Collective nouns are words that imply more than one person but that are considered singular and take a singular verb, such as: group, team, committee, class, and family. Th ...
... the verb. Since there is not the subject, the verb agrees with what follows. There are many questions. There is a question. 10. Collective nouns are words that imply more than one person but that are considered singular and take a singular verb, such as: group, team, committee, class, and family. Th ...
parts_of_speech-part1_grade_9 - Al
... Notice how helping verbs work together with main verbs to form complete verb phrases. Example: is leaving - may become - might have remained Sometimes the parts of a verb phrase are interrupted by other parts of speech. Example : She had always been thinking of her future. Note: the word n ...
... Notice how helping verbs work together with main verbs to form complete verb phrases. Example: is leaving - may become - might have remained Sometimes the parts of a verb phrase are interrupted by other parts of speech. Example : She had always been thinking of her future. Note: the word n ...
PowerPoint
... Note: If would is the past tense of will, then it is probably not correct to think of will as being simply a future marker. Rather, it’s one of the modals, an “unrealized” marker, which makes sense as long as time goes invariably forward, as it seems to. Many people nevertheless consider will to be ...
... Note: If would is the past tense of will, then it is probably not correct to think of will as being simply a future marker. Rather, it’s one of the modals, an “unrealized” marker, which makes sense as long as time goes invariably forward, as it seems to. Many people nevertheless consider will to be ...
8th-Grade-English-Final-Review-2014
... 1. The bicycle made Charlie very happy. 2. A gusty wind overpowered the captain of the luxurious yacht. 3. That red cabin was musty after the long winter. Part II: Demonstrative, Interrogative, and Indefinite Adjectives B. See pronouns for specifics about what these are. In this section, they are si ...
... 1. The bicycle made Charlie very happy. 2. A gusty wind overpowered the captain of the luxurious yacht. 3. That red cabin was musty after the long winter. Part II: Demonstrative, Interrogative, and Indefinite Adjectives B. See pronouns for specifics about what these are. In this section, they are si ...
plural subjects "we, you, they"
... káru pu'aamtíhap káru pishpíshih. • And they also didn't eat honey. káru = also pu- = not 'aam = eat -tíh = ongoing -ap (see the Comment below!) pishpíshih = honey Comments With negative verbs (pu- "not"), for the subject "they", the suffix -ap is used instead of a prefix! And as we've see ...
... káru pu'aamtíhap káru pishpíshih. • And they also didn't eat honey. káru = also pu- = not 'aam = eat -tíh = ongoing -ap (see the Comment below!) pishpíshih = honey Comments With negative verbs (pu- "not"), for the subject "they", the suffix -ap is used instead of a prefix! And as we've see ...
Predicate Nouns/Pronouns
... Predicate Noun • Also called a predicate nominative OR a completer, or complement, because it completes the verb. • It’s a single noun or a noun phrase that renames the subject of a sentence and follows a form of the verb “to be” or another linking verb. ...
... Predicate Noun • Also called a predicate nominative OR a completer, or complement, because it completes the verb. • It’s a single noun or a noun phrase that renames the subject of a sentence and follows a form of the verb “to be” or another linking verb. ...
CONVERSION IN ENGLISH Caroline University, Prague Attempts to
... division of word-classes has little in common with Jespersen's theory of rank-classes as opposed to word-classes, and that it has nothing to do with syntactic relationships as it is based entirely on the morphological level of a language as viewed from its horizontal axis, i.e. from the viewpoint of ...
... division of word-classes has little in common with Jespersen's theory of rank-classes as opposed to word-classes, and that it has nothing to do with syntactic relationships as it is based entirely on the morphological level of a language as viewed from its horizontal axis, i.e. from the viewpoint of ...
Language Usage - Eastern Florida State College
... Most possessive pronouns have two forms. One form is used with a noun (my house; our car; your, her, their test). The other form (mine, ours, yours, hers, theirs) is used alone (Those boots are mine.) ...
... Most possessive pronouns have two forms. One form is used with a noun (my house; our car; your, her, their test). The other form (mine, ours, yours, hers, theirs) is used alone (Those boots are mine.) ...
Identifying the word class of
... class can be filled in the same slot in a sentence. Each word class has its own specific set of modifying words ...
... class can be filled in the same slot in a sentence. Each word class has its own specific set of modifying words ...
Are the following groups of words sentences?
... Toni bought cars. The eyewitness told us the story. Our mechanic is a poet. Richard feels sad. ...
... Toni bought cars. The eyewitness told us the story. Our mechanic is a poet. Richard feels sad. ...
Comma-Rules-Introductory-Elements
... Use a comma to set off most introductory elements. An introductory element modifies a word or words in the main clause that follows. These elements are usually set off from the rest of the sentence with a comma. Below are the most common types of introductory elements along with examples of each. 1. ...
... Use a comma to set off most introductory elements. An introductory element modifies a word or words in the main clause that follows. These elements are usually set off from the rest of the sentence with a comma. Below are the most common types of introductory elements along with examples of each. 1. ...
Guide to Quiz 2 Review items: 1. The Preterit Tense: Can you
... What verbs require spelling changes (hint: buscar, leer, etc.)? Which stem changing verbs in the present remain stem changing verbs in the preterit? Which forms of the stem changing verbs in the preterit have the stem changes? According to the professor’s system of conjugating, how many semi-irregul ...
... What verbs require spelling changes (hint: buscar, leer, etc.)? Which stem changing verbs in the present remain stem changing verbs in the preterit? Which forms of the stem changing verbs in the preterit have the stem changes? According to the professor’s system of conjugating, how many semi-irregul ...
Glossary of Grammatical Terms and Errors active voice: The
... cloud because one can go through a cloud, be under a cloud, move about a cloud, come from a cloud, travel within a cloud, go to a cloud, etc. As I also explain to my own students, the rule that sentences should never end in prepositions is not some arbitrary invention of difficult English teachers, ...
... cloud because one can go through a cloud, be under a cloud, move about a cloud, come from a cloud, travel within a cloud, go to a cloud, etc. As I also explain to my own students, the rule that sentences should never end in prepositions is not some arbitrary invention of difficult English teachers, ...
Verbals
... general rule is that no word should separate the to of an infinitive from the simple form of the verb that follows. If a word does come between these two components, a split infinitive results. Look at the example that follows: ...
... general rule is that no word should separate the to of an infinitive from the simple form of the verb that follows. If a word does come between these two components, a split infinitive results. Look at the example that follows: ...
Welcome to Latin Class!
... First person singular: I First person plural: We Second person singular: you Second person plural: you all Third person singular: He/she/ it Third person plural: They ...
... First person singular: I First person plural: We Second person singular: you Second person plural: you all Third person singular: He/she/ it Third person plural: They ...
The GPS toolkit - Fishburn Primary School
... If they answer the questions: How? When? Where? or Why? – they are adverbs. If they answer the question: “What is it like?” - they are adjectives, and will be telling you more about a specific noun. Examples: Life is hard. (adjective) Kim works hard. (adverb) The train arrived early. (adverb) I took ...
... If they answer the questions: How? When? Where? or Why? – they are adverbs. If they answer the question: “What is it like?” - they are adjectives, and will be telling you more about a specific noun. Examples: Life is hard. (adjective) Kim works hard. (adverb) The train arrived early. (adverb) I took ...