Two-Sector Circular Flow Model
... $$ Nat’l Income = Rent, Wages, Interest, Profit $$ Resources = Land, Labor, Capital, Entrepreneurship ...
... $$ Nat’l Income = Rent, Wages, Interest, Profit $$ Resources = Land, Labor, Capital, Entrepreneurship ...
Chapter 4: Demand and Supply
... goods, income, etc.) are being held equal. When doing analysis it is important to keep in mind what is being held ...
... goods, income, etc.) are being held equal. When doing analysis it is important to keep in mind what is being held ...
Economic Survey
... As the price increases, consumers demand less. As the price increases, suppliers can earn higher levels of profit or justify higher marginal costs to produce more. None of the Above ...
... As the price increases, consumers demand less. As the price increases, suppliers can earn higher levels of profit or justify higher marginal costs to produce more. None of the Above ...
330Handout Supply and+
... An increase in the price of land (e.g. rent/lease/mortgage), labor (wages, benefits), and/or capital (higher equipment costs/financing of equipment, materials) will increase the firm’s costs, lower their profitability at the current market price, and thus provide an incentive for the firm to reduce ...
... An increase in the price of land (e.g. rent/lease/mortgage), labor (wages, benefits), and/or capital (higher equipment costs/financing of equipment, materials) will increase the firm’s costs, lower their profitability at the current market price, and thus provide an incentive for the firm to reduce ...
Corporate Level Strategy and Long Term Profitability
... noticed. The company won't enjoy the scale economies of the larger players, so it's going to be difficult to make a profit. And because market growth is low, it's going to take a lot of hard work to improve the situation. Example is RC Cola ...
... noticed. The company won't enjoy the scale economies of the larger players, so it's going to be difficult to make a profit. And because market growth is low, it's going to take a lot of hard work to improve the situation. Example is RC Cola ...
Basic Marketing Plan for small businesses Introduction In this
... Basic Marketing Plan for small businesses Introduction In this document I would like to give a few guidelines to small or new businesses to just let you think about your marketing plan. It is important to zoom out every once in a while and just see what is going on around you and see where things ar ...
... Basic Marketing Plan for small businesses Introduction In this document I would like to give a few guidelines to small or new businesses to just let you think about your marketing plan. It is important to zoom out every once in a while and just see what is going on around you and see where things ar ...
AP Micro 6-2 Public Goods (cont)
... Can the government… 1. Prevent the destruction of rain forest? 2. Ensure that no one ever speeds on the freeway? 3. Create a research station on Mars? 4. Stop pollution from fossil fuels? 5. Completely stop illegal immigration? 6. Make sure everyone in the US has a job? YES! But the costs outweigh ...
... Can the government… 1. Prevent the destruction of rain forest? 2. Ensure that no one ever speeds on the freeway? 3. Create a research station on Mars? 4. Stop pollution from fossil fuels? 5. Completely stop illegal immigration? 6. Make sure everyone in the US has a job? YES! But the costs outweigh ...
Pricing management
... Integrate with the firm’s other marketing efforts. Understand consumers’ willingness to pay. Understand pricing effects throughout product line. ...
... Integrate with the firm’s other marketing efforts. Understand consumers’ willingness to pay. Understand pricing effects throughout product line. ...
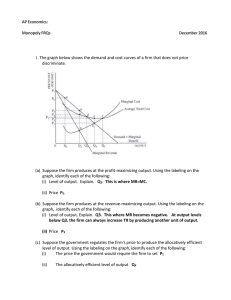
Monopoly FRQs answers
... graph, identify each of the following: (i) Level of output. Explain. Q2. This is where MR=MC. (ii) Price P5. (b) Suppose the firm produces at the revenue-maximizing output. Using the labeling on the graph, identify each of the following: (i) Level of output. Explain. Q3. This where MR becomes negati ...
... graph, identify each of the following: (i) Level of output. Explain. Q2. This is where MR=MC. (ii) Price P5. (b) Suppose the firm produces at the revenue-maximizing output. Using the labeling on the graph, identify each of the following: (i) Level of output. Explain. Q3. This where MR becomes negati ...
adjusting toward equilibrium
... characterized by: unrestricted entry and exit a large number of independent sellers producing differentiated products ...
... characterized by: unrestricted entry and exit a large number of independent sellers producing differentiated products ...
MicroEconomics Oligopoly
... Static Game: Players act simultaneously Strategies: Any Price between 0 and infinity denoted p1 and p2 The Bertand equilibrium is a price level for each firm such that the firm´s profits are maximized given the price level of the other firm. Assuming that firms are selling identical products ...
... Static Game: Players act simultaneously Strategies: Any Price between 0 and infinity denoted p1 and p2 The Bertand equilibrium is a price level for each firm such that the firm´s profits are maximized given the price level of the other firm. Assuming that firms are selling identical products ...
Price ppt
... Setting prices to advantage of a customer’s perception of value of the product. Common for prices to be set below the key price to make the product appear cheaper than it is: $999 instead of $1001; $1.99 instead of $2.01 Prices are set to coincide with market perception of the product even if the pr ...
... Setting prices to advantage of a customer’s perception of value of the product. Common for prices to be set below the key price to make the product appear cheaper than it is: $999 instead of $1001; $1.99 instead of $2.01 Prices are set to coincide with market perception of the product even if the pr ...
ap government summer work 2014-15
... 19. In Figure 3-1, what happens to the quantity demanded of milk as the price increases? What happens when the price decreases? 20. Why does the demand curve have a negative slope? 21. On Figure 3-1, p. 37, what happens to the quantity demanded of milk when the price of milk increases from $1.00 to ...
... 19. In Figure 3-1, what happens to the quantity demanded of milk as the price increases? What happens when the price decreases? 20. Why does the demand curve have a negative slope? 21. On Figure 3-1, p. 37, what happens to the quantity demanded of milk when the price of milk increases from $1.00 to ...
Lecture 2
... Market price (equilibrium price): Profit-maximizing price at which the quantity of goods demanded and the quantity of goods supplied are equal. Surplus: Situation in which quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded. Shortage: Situation in which quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied. Private ...
... Market price (equilibrium price): Profit-maximizing price at which the quantity of goods demanded and the quantity of goods supplied are equal. Surplus: Situation in which quantity supplied exceeds quantity demanded. Shortage: Situation in which quantity demanded exceeds quantity supplied. Private ...
File
... Some markets have only one seller, and this seller sets the price. Such a seller is called a monopoly. Your local cable television company is a monopoly. Residents of your town only have one cable provider from which to buy this service. Some markets have only a few sellers, and these sellers do not ...
... Some markets have only one seller, and this seller sets the price. Such a seller is called a monopoly. Your local cable television company is a monopoly. Residents of your town only have one cable provider from which to buy this service. Some markets have only a few sellers, and these sellers do not ...
Managerial Economics & Business Strategy
... • Firms operating in a Sweezy oligopoly maximize profit by producing where MRS = MC. – The kinked-shaped marginal revenue curve implies that there exists a range over which changes in MC will not impact the profit-maximizing level of output. – Therefore, the firm may have no incentive to change pric ...
... • Firms operating in a Sweezy oligopoly maximize profit by producing where MRS = MC. – The kinked-shaped marginal revenue curve implies that there exists a range over which changes in MC will not impact the profit-maximizing level of output. – Therefore, the firm may have no incentive to change pric ...
Economics - A Contemporary Introduction
... industry, monopolists have control over a. the price they charge for the product b. the quantity of output they produce c. the prices they pay for resources A. A firm in a perfectly competitive industry is a price taker, it has no incentive to charge any other price but the market price. Firms in th ...
... industry, monopolists have control over a. the price they charge for the product b. the quantity of output they produce c. the prices they pay for resources A. A firm in a perfectly competitive industry is a price taker, it has no incentive to charge any other price but the market price. Firms in th ...