chapter - Human Kinetics
... Purpose of Segmenting • Specialize • Focus on the most likely to buy • Meet wants and needs without exhausting resources • Provide product, price, promotion, place, and public relations in the right way ...
... Purpose of Segmenting • Specialize • Focus on the most likely to buy • Meet wants and needs without exhausting resources • Provide product, price, promotion, place, and public relations in the right way ...
Econ 101, Sections 5 and 7, S03
... *. increased significantly during the mid-to-late 70s but, by 2001 had fallen back below 1973 levels. 7. Assume that a particular bakery faces an elastic demand curve for its donuts. A 10% increase in the price it charges for donuts will have what effect on its total donut sales revenue? Total donut ...
... *. increased significantly during the mid-to-late 70s but, by 2001 had fallen back below 1973 levels. 7. Assume that a particular bakery faces an elastic demand curve for its donuts. A 10% increase in the price it charges for donuts will have what effect on its total donut sales revenue? Total donut ...
Document
... The Other Factors of Production With land and capital, must distinguish between: purchase price – the price a person pays to own that factor indefinitely rental price – the price a person pays to use that factor for a limited period of time ...
... The Other Factors of Production With land and capital, must distinguish between: purchase price – the price a person pays to own that factor indefinitely rental price – the price a person pays to use that factor for a limited period of time ...
MIDTERM EXAMINATION III
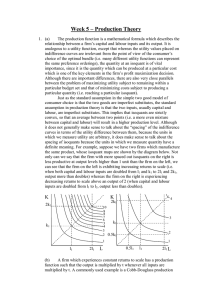
... 1. Let the firm’s production function be given by Q = 4KL. Suppose that r = 4 and w = 2. Also, MPK = 4L and MPL = 4K. a) (8) How much K and L is employed in the efficient production of 32 units of output? b) (5) What is the minimum cost of producing 32 units of output? c) (4) How much capital can th ...
... 1. Let the firm’s production function be given by Q = 4KL. Suppose that r = 4 and w = 2. Also, MPK = 4L and MPL = 4K. a) (8) How much K and L is employed in the efficient production of 32 units of output? b) (5) What is the minimum cost of producing 32 units of output? c) (4) How much capital can th ...
Slide 1
... The Other Factors of Production With land and capital, must distinguish between: purchase price – the price a person pays to own that factor indefinitely rental price – the price a person pays to use that factor for a limited period of time ...
... The Other Factors of Production With land and capital, must distinguish between: purchase price – the price a person pays to own that factor indefinitely rental price – the price a person pays to use that factor for a limited period of time ...
Chapter 6: The Production Process
... • A firm is an organization that comes into being when a person or a group of people decides to produce a good or service to meet a perceived demand. Most firms exist to make a profit. • Production is not limited to firms. ...
... • A firm is an organization that comes into being when a person or a group of people decides to produce a good or service to meet a perceived demand. Most firms exist to make a profit. • Production is not limited to firms. ...
ECON 2105H
... country, you will see that they are linear). b) For each country, compute the opportunity costs of producing one car. In the U.S., producing 100 extra cars requires giving up 200 tons of wheat. The cost of one extra car (the marginal car) is thus 2 tons of wheat. In Japan, producing 200 extra cars r ...
... country, you will see that they are linear). b) For each country, compute the opportunity costs of producing one car. In the U.S., producing 100 extra cars requires giving up 200 tons of wheat. The cost of one extra car (the marginal car) is thus 2 tons of wheat. In Japan, producing 200 extra cars r ...
Questions: Show in a diagram the effect on the demand curve, the
... Case 1: People realize how fattening bagels are. Case 2: People have less time to make themselves a cooked breakfast. a. The market for the Krugman and Wells economics textbook Case 1: Your professor makes it required reading for all of his or her students. Case 2: Printing costs for textbooks are l ...
... Case 1: People realize how fattening bagels are. Case 2: People have less time to make themselves a cooked breakfast. a. The market for the Krugman and Wells economics textbook Case 1: Your professor makes it required reading for all of his or her students. Case 2: Printing costs for textbooks are l ...
Name: Date: ______ 1. An economy is efficient if it is: A) possible to
... 6. The primary difference between a change in supply and a change in the quantity supplied is that: A) a change in quantity supplied is a movement along the supply curve, while a change in supply is a shift in the supply curve. B) both a change in quantity supplied and a change in supply are moveme ...
... 6. The primary difference between a change in supply and a change in the quantity supplied is that: A) a change in quantity supplied is a movement along the supply curve, while a change in supply is a shift in the supply curve. B) both a change in quantity supplied and a change in supply are moveme ...
Price discrimination - McGraw Hill Higher Education
... Marginal Revenue And Elasticity • The less elastic demand is with respect to price, the more price will exceed marginal revenue. – For all elasticity values less than 1 in absolute value marginal revenue will be negative. – For all elasticity values larger than 1 in absolute value marginal revenue ...
... Marginal Revenue And Elasticity • The less elastic demand is with respect to price, the more price will exceed marginal revenue. – For all elasticity values less than 1 in absolute value marginal revenue will be negative. – For all elasticity values larger than 1 in absolute value marginal revenue ...
4. More on Supply and Demand Curves
... scale of the graph, try a Qs about ½ of that. In this case, 50 would take us way off the scale, so we are going to try Ps = 25. Plugging that into the supply function we get Ps = 100, perfect! Now connect the two with your ruler and find out where the supply curve intersects the demand curve, this i ...
... scale of the graph, try a Qs about ½ of that. In this case, 50 would take us way off the scale, so we are going to try Ps = 25. Plugging that into the supply function we get Ps = 100, perfect! Now connect the two with your ruler and find out where the supply curve intersects the demand curve, this i ...
Marketing - Greene Central School District
... information with customer service and marketing communications ▪ Meaningful one-on-one communications via customer intelligence ...
... information with customer service and marketing communications ▪ Meaningful one-on-one communications via customer intelligence ...
Demand and Supply
... Change in Quantity Demanded A change in quantity demanded refers to a change in the amount of the good demanded because of a change in PRICE. This is represented but the movement along the SAME demand curve. P Increase case (vice versa) ...
... Change in Quantity Demanded A change in quantity demanded refers to a change in the amount of the good demanded because of a change in PRICE. This is represented but the movement along the SAME demand curve. P Increase case (vice versa) ...
Ford Motor Company
... Founded in 1903 in Detroit Family owned business Launched very popular Model T in 1908 First moving assembly manufacturing process Very successfully mass marketed Model T Lost market to GM and Chrysler during 1920s by neglecting consumer demands Introduced Ford Escape Hybrid in 2004 Redesigned M ...
... Founded in 1903 in Detroit Family owned business Launched very popular Model T in 1908 First moving assembly manufacturing process Very successfully mass marketed Model T Lost market to GM and Chrysler during 1920s by neglecting consumer demands Introduced Ford Escape Hybrid in 2004 Redesigned M ...