Livestock Marketing
... • Role of the government • Collection and dissemination and timely reporting of prices that were discovered. • Other private treaty buyers and sellers incorporate new information into their negotiation. • Facilitates formula pricing ...
... • Role of the government • Collection and dissemination and timely reporting of prices that were discovered. • Other private treaty buyers and sellers incorporate new information into their negotiation. • Facilitates formula pricing ...
CHAP 16: Marketing 1
... Profit maximising pricing – setting a high price to deliberately make as much profit as soon as possible. ...
... Profit maximising pricing – setting a high price to deliberately make as much profit as soon as possible. ...
Lemonade Stand Game
... Lemonade Stand Game • Your goal in this game is to make as much money as you can within 30 days. • You will have complete control over almost every part of your business: o Inventory/Purchasing supplies o Pricing o Quality Control ...
... Lemonade Stand Game • Your goal in this game is to make as much money as you can within 30 days. • You will have complete control over almost every part of your business: o Inventory/Purchasing supplies o Pricing o Quality Control ...
2.01 Recognize the importance of marketing.
... and improved products to the market, as well as lowering prices.” • List five products you or your family use that are new or have been improved • List five products your family uses that now have lowered or reduced prices • List five stores which have lowered their prices ...
... and improved products to the market, as well as lowering prices.” • List five products you or your family use that are new or have been improved • List five products your family uses that now have lowered or reduced prices • List five stores which have lowered their prices ...
Marketing Management - BYU Marriott School
... Buyer reaction to pricing . When Gibson lowered its prices, sales fell. Why? ...
... Buyer reaction to pricing . When Gibson lowered its prices, sales fell. Why? ...
340 Lamb-JW 17 Prici..
... with selling an extra unit of output, or the change in total revenue with a one-unit change in output. ...
... with selling an extra unit of output, or the change in total revenue with a one-unit change in output. ...
Marketing - Saint Roch's Secondary School
... The customer buys the product (could be another business or individual) The end user ...
... The customer buys the product (could be another business or individual) The end user ...
Lecture_06.1b Monopoly
... Since the early 1980s, economic models based on game theory and the theory of imperfect information have suggested that predatory pricing can be rational and profitable under certain circumstances. For instance, by increasing production and lowering price below costs, a firm may convince its competi ...
... Since the early 1980s, economic models based on game theory and the theory of imperfect information have suggested that predatory pricing can be rational and profitable under certain circumstances. For instance, by increasing production and lowering price below costs, a firm may convince its competi ...
Niche Marketing and the Importance of Product
... Examine Competition Pricing • Penetration Pricing – Lower than competition pricing – Stimulate demand ...
... Examine Competition Pricing • Penetration Pricing – Lower than competition pricing – Stimulate demand ...
Pricing Strategies - PowerPoint Presentation - Full
... • Amazon.com mine their database to gauge specific shoppers desire, measure his or her means, instantaneously tailor products to fit that shoppers behavior, and price products accordingly ...
... • Amazon.com mine their database to gauge specific shoppers desire, measure his or her means, instantaneously tailor products to fit that shoppers behavior, and price products accordingly ...
Ch--11-Pricing
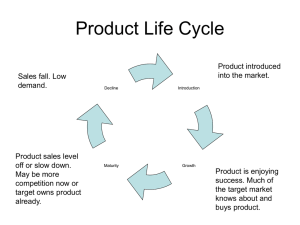
... Price Skimming When the product has no competitors and the product has an extreme uniqueness; The price of the product can be initially high. Often businesses introducing a product need to recoup research and development costs or large capital expenditures. As competitors enter the marketplace, the ...
... Price Skimming When the product has no competitors and the product has an extreme uniqueness; The price of the product can be initially high. Often businesses introducing a product need to recoup research and development costs or large capital expenditures. As competitors enter the marketplace, the ...
Lecture 14 ItM Pricing II
... manufacturer can calculate how much money remains for setting own profitable price). (Compaq made a 3 billion business during 2 years following this pricing approach). Bundle Pricing (marketing several products in one package). (Based on the idea that consumers value the “package” more than individu ...
... manufacturer can calculate how much money remains for setting own profitable price). (Compaq made a 3 billion business during 2 years following this pricing approach). Bundle Pricing (marketing several products in one package). (Based on the idea that consumers value the “package” more than individu ...
International marketing programme
... production occurs in other industrialised countries and then is less developed countries. ...
... production occurs in other industrialised countries and then is less developed countries. ...
Empirical Research on Sketchy Pricing
... • Direct mail/marketing (dominant channel in card market) is conducive to debiasing research. Tight control over content: – Cheap to do randomized-control testing – With less worry than usual than information treatments are undone or diluted by high-touch marketing ...
... • Direct mail/marketing (dominant channel in card market) is conducive to debiasing research. Tight control over content: – Cheap to do randomized-control testing – With less worry than usual than information treatments are undone or diluted by high-touch marketing ...
Marketing Chapters 9-10 Lecture Presentation - MyBC
... – Customer-segment: different customers pay different prices for the same good. – Product-form: different versions are priced differently but not according to cost. – Location pricing: different prices are charged for each location even when the cost of offering the good is the same. – Time pricing: ...
... – Customer-segment: different customers pay different prices for the same good. – Product-form: different versions are priced differently but not according to cost. – Location pricing: different prices are charged for each location even when the cost of offering the good is the same. – Time pricing: ...
Service parts pricing

Service Parts Pricing refers to the aspect of Service Lifecycle Management that deals with setting prices for service parts in the after-sales market. Like other streams of Pricing, Service Parts Pricing is a scientific pursuit aimed at aligning service part prices internally to be logical and consistent, and at the same time aligning them externally with the market. This is done with the overarching aim of extracting the maximum possible price from service parts and thus maximize the profit margins. Pricing analysts have to be cognizant of possible repercussions of pricing their parts too high or too low in the after-sales market; they constantly have to strive to get the prices just right towards achieving maximum margins and maximum possible volumes.The after-sales market consists of service part and after-sales service. These areas often account for a low share in total sales, but for a relatively high share in total profits. It is important to understand that the after-sales supply chain is very different from the manufacturing supply chain, and hence rules that apply to pricing manufacturing parts do not hold good for pricing service parts. Service Parts Pricing requires a different outlook and approach.Service networks deal with a considerably higher number of SKUs and a heterogeneous product portfolio, are more complex, have a sporadic nature of demand AND have minimal response times and strict SLAs. Companies have traditionally been content with outsourcing the after-sales side of their business and have encouraged third-party parts and service providers in the market. The result has been a bevy of these operators in the market with strict price competition and low margins.Increasingly, however, companies are realizing the importance of the after-sales market and its impact on customer retention and loyalty. Increasingly, also, companies have realized that they can extract higher profit margins from the after-sales services market due to the intangible nature of services. Companies are investing in their after-sales service networks to deliver high levels of customer service and in return command higher prices for their parts and services. Customers are being sold the concept of total cost of ownership (TCO) and are being made to realize that buying from OEMs comes packaged with better distribution channels, shorter response times, better knowledge on products, and ultimately higher product uptime.The challenge for companies is to provide reliable service levels in an environment of uncertainty. Unlike factories, businesses can’t produce services in advance of demand. They can manufacture them only when an unpredictable event, such as a product failure, triggers a need. The challenge for Service Parts Pricing is to put a value to this customer need. Parts that are critical, for example, can command higher prices. So can parts that only the OEM provides in the market. Parts that are readily available in the market cannot, and must not, be priced to high. Another problem with after-sales market is that demand cannot be stimulated with price discounts, customers do not stock up service parts just because they are on discount. On the up-side, the fact that most service parts are inelastic means pricing analysts can raise prices without the adverse effects that manufacturing or retail networks witness.These and other characteristics of the after-sales market give Service Parts Pricing a life of its own. Companies are realizing that they can use the lever of service part pricing to increase profitability and don't have to take prices as market determined. Understanding customer needs and expectations, along with the company's internal strengths and weaknesses, goes a long way in designing an effective service part pricing strategy.






![[Product Name] Marketing Plan](http://s1.studyres.com/store/data/008549677_1-ddaa9acefa2928a1938412657a48c300-300x300.png)