* Your assessment is very important for improving the work of artificial intelligence, which forms the content of this project
Download Livestock Marketing
Survey
Document related concepts
Transcript
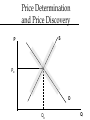
Price Determination and Discovery Price Determination • is the broad forces of supply and demand establishing a market clearing price for a commodity. Price Discovery • is the process by which buyers and sellers arrive a a specific price for a given lot of produce at a given location for a specific time period. Price Discovery A human process, subject to relative bargaining power of the buyer and seller. Two stage process • Evaluate S&D and Pe • Estimate the price for the specific trade. Price Determination and Price Discovery S P Pe D Qe Q Futures Markets in Price Discovery Centralized pricing Global forces in one location Predominate price discovery for grains • Still have local price discovery for basis Livestock price discovery more complicated • Variability – basis a bigger issue • Growing inventory problem Centralized pricing All buyers and sellers in one place at one time, i.e., auction market + Full and immediate information + Competitive bidding + Equalizes market power - Transaction cost - Physical movement of product Decentralized Pricing One-to-one negotiations + Reduced transportation cost + Reduced transaction cost - Depends on skills and information - Higher search cost Where to sell Terminal markets have declined Auction markets important when assembly is needed • Feeder cattle and cull cows • Growing interest in fed cattle in fringe areas Direct sales • Slaughter cattle and hogs • Feeder pigs • Growing in feeder cattle where source verification is important Feeder cattle sales Live weight sales • Various weight classes • In general, lower $/# and heavier weights Auction is major market • Assembly function important Video auctions Direct trade Premium paid for • Large uniform lots • Certification/verification ?????? Important market functions Assembly function • Feeder cattle • Cull cows Sorting function Slaughter Cattle and Hogs Direct sales most common • Animals are delivered directly to the packing plant Spot or cash market • Seller contacts buyer when ready to sell • Negotiate price and terms on each group Contract market • May be for one group or an ongoing agreement between buyer and seller • Terms and pricing method determined ahead of marketing date Hybrid markets Electronic markets • Centralized pricing • Decentralized product movement Examples • • • • Satellite auctions Electronic auctions Tel-o-auction E-commerce Formula pricing Price discovery from elsewhere Formula contracts • • • • Spot market Cutout price Futures Cost of production Do you trust the underlying market for price discovery? Feeder Pig Trade Spot market price Often through a broker USDA report Formula pricing Based on observable price Spot market Hog futures maybe corn & SBM Formula ex: 53% of 5 month out futures Performance issues “Least cost” method of price discovery Effect of the mechanism on price behavior Marketing v. pricing efficiency Information and markets Price reporting • Role of the government • Collection and dissemination and timely reporting of prices that were discovered. • Other private treaty buyers and sellers incorporate new information into their negotiation. • Facilitates formula pricing Packer Offering Price Starts with derived demand from wholesale and retail markets Time lag between sales of product and purchase of animals. • Orders typically booked 3 weeks in advance. » Special features, holidays etc may be longer. » Clean up orders may be few days • Packer is anticipating prices and stands risk Derived Demand S Vertical distance is the difference is price at 3 levels There is cost associated with moving from one level to the next Px Pretail Pwholesale Pfarm Dretail Cuts of meat Dwholesale Carcasses Dfarm Q Animals Qx Derived Demand for Pork Average retail price $/lb $2.50 Value of trim and scrap $/lb $0.10 Costs from whlse -retail $/lb -$1.00 The most retail will pay $/lb $1.60 Retail pounds per carcass 100 The most retail will pay $/head $160 Derived Demand for Hogs Wholesale carcass value $/hd $160 Value hide and offal $/hd $25 Costs to slaughter and fab $/hd -$20 The most packer will pay $/hd $165 Wholesale pounds per carcass 200 The most packer will pay $/lb $82.50 Producer Asking Price Starts with cost of production Reflects current market conditions Time is a huge factor for livestock • Marginal revenue may decrease • Marginal cost increases at increasing rate Farmer has longer time period than packer from start of process to end.