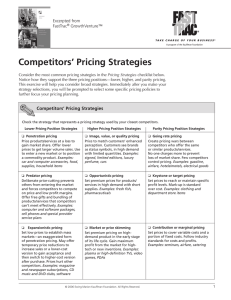
Pricing Strategies - Business Lincolnshire
... Cost-based pricing involves the determination of all fixed and variable costs associated with a product or service. After the total costs attributable to the product or servi ce have been determined, companies add a desired profit margin to each unit such as a 5 or 10 percent markup. The goal of the ...
... Cost-based pricing involves the determination of all fixed and variable costs associated with a product or service. After the total costs attributable to the product or servi ce have been determined, companies add a desired profit margin to each unit such as a 5 or 10 percent markup. The goal of the ...
Customer-based Marketing Strategies
... In recent times, companies are experiencing an increased level of complexity in managing their markets, due to different causes: globalization, digitalization, technological development and new forms of social interaction. In the new competitive context, customer-based marketing strategies aimed at ...
... In recent times, companies are experiencing an increased level of complexity in managing their markets, due to different causes: globalization, digitalization, technological development and new forms of social interaction. In the new competitive context, customer-based marketing strategies aimed at ...
Price - Student Handout
... prices because they believe an item is different from that offered by competition. Companies try to achieve this status by developing brand loyalty. o Example: Red Sox tickets. Different prices based on location of seats. All will see same performance – but from different vantage points. o Example: ...
... prices because they believe an item is different from that offered by competition. Companies try to achieve this status by developing brand loyalty. o Example: Red Sox tickets. Different prices based on location of seats. All will see same performance – but from different vantage points. o Example: ...
Chapter 11 and 12 Questions pdf
... 1. Compare and contrast market-skimming and market-penetration pricing strategies and discuss the conditions under which each is appropriate. For each strategy, give an example of a recent introduced product that used that pricing strategy. Market-skimming pricing is, “Setting a high price for a new ...
... 1. Compare and contrast market-skimming and market-penetration pricing strategies and discuss the conditions under which each is appropriate. For each strategy, give an example of a recent introduced product that used that pricing strategy. Market-skimming pricing is, “Setting a high price for a new ...
MLSP to Accompany Essentials of Marketing
... that really gives the target market superior customer value. There are Price choices in most markets Value pricers define the target market and the competition Meeting competitors' prices may be necessary Value pricing fits with market-oriented strategy planning LEGALITY OF PRICING POLICIES ...
... that really gives the target market superior customer value. There are Price choices in most markets Value pricers define the target market and the competition Meeting competitors' prices may be necessary Value pricing fits with market-oriented strategy planning LEGALITY OF PRICING POLICIES ...
Pride/Hughes/Kapoor Business, 10th Edition
... Competition, or the rivalry among businesses for sales to potential customers, is a hallmark of our market economy. The four types of competition include pure competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and monopoly. Pure, or perfect, competition is the market situation in which there are many ...
... Competition, or the rivalry among businesses for sales to potential customers, is a hallmark of our market economy. The four types of competition include pure competition, monopolistic competition, oligopoly, and monopoly. Pure, or perfect, competition is the market situation in which there are many ...
Developing Your Marketing Mix
... Marketers use different tools in order to get the desired response from the customer or best satisfy their needs. These tools are known as The Marketing Mix. Marketing Mix is probably the most famous term in marketing. ...
... Marketers use different tools in order to get the desired response from the customer or best satisfy their needs. These tools are known as The Marketing Mix. Marketing Mix is probably the most famous term in marketing. ...
International marketing programme
... Pricing across products (product line pricing) Pricing across countries Total package price Psychological pricing In comparison to domestic pricing strategies, the decisions are much more complex, because they are affected by a number of additional external factors, such as fluctuations in exchange ...
... Pricing across products (product line pricing) Pricing across countries Total package price Psychological pricing In comparison to domestic pricing strategies, the decisions are much more complex, because they are affected by a number of additional external factors, such as fluctuations in exchange ...
La Madre
... Inelastic Price Structure – High value creates the ability to adjust price without affecting the sales. ...
... Inelastic Price Structure – High value creates the ability to adjust price without affecting the sales. ...
Retail Pricing Strategies
... Vallaya, Ravi Bajaj, Moan Pali, Sunit Verma and Rohit Bal, and manyother designer labels selling high fashion ladies garments in India, also offer high quality prducts and services without compromising on prices. The common factor that is common to all such retail formats in India and anywhere acros ...
... Vallaya, Ravi Bajaj, Moan Pali, Sunit Verma and Rohit Bal, and manyother designer labels selling high fashion ladies garments in India, also offer high quality prducts and services without compromising on prices. The common factor that is common to all such retail formats in India and anywhere acros ...
诚实考试吾心不虚 ,公平竞争方显实力,
... 2b) A franchise is described as what type of vertical marketing system? How does this system differ from the other two types? (10 marks) Answers Franchising is on contractual base. The other two are based on: corporate control or administrative control. ...
... 2b) A franchise is described as what type of vertical marketing system? How does this system differ from the other two types? (10 marks) Answers Franchising is on contractual base. The other two are based on: corporate control or administrative control. ...
Emergence of Sport Marketing
... – “… pricing in the lower range of expected prices, in the belief that an elastic market exists and the lower price will increase the quantity purchased.” ...
... – “… pricing in the lower range of expected prices, in the belief that an elastic market exists and the lower price will increase the quantity purchased.” ...
parallel market
... Such prices may be arranged through the cooperation of competitors; through national, state, or local governments; or by international agreement. The legality of administered pricing arrangements of various kinds differs from country to country and from time to time. A country may condone(宽恕) ...
... Such prices may be arranged through the cooperation of competitors; through national, state, or local governments; or by international agreement. The legality of administered pricing arrangements of various kinds differs from country to country and from time to time. A country may condone(宽恕) ...
Marketing Plan
... Width of mix -- number of lines Depth of mix -- number of different products in line ...
... Width of mix -- number of lines Depth of mix -- number of different products in line ...
Service parts pricing

Service Parts Pricing refers to the aspect of Service Lifecycle Management that deals with setting prices for service parts in the after-sales market. Like other streams of Pricing, Service Parts Pricing is a scientific pursuit aimed at aligning service part prices internally to be logical and consistent, and at the same time aligning them externally with the market. This is done with the overarching aim of extracting the maximum possible price from service parts and thus maximize the profit margins. Pricing analysts have to be cognizant of possible repercussions of pricing their parts too high or too low in the after-sales market; they constantly have to strive to get the prices just right towards achieving maximum margins and maximum possible volumes.The after-sales market consists of service part and after-sales service. These areas often account for a low share in total sales, but for a relatively high share in total profits. It is important to understand that the after-sales supply chain is very different from the manufacturing supply chain, and hence rules that apply to pricing manufacturing parts do not hold good for pricing service parts. Service Parts Pricing requires a different outlook and approach.Service networks deal with a considerably higher number of SKUs and a heterogeneous product portfolio, are more complex, have a sporadic nature of demand AND have minimal response times and strict SLAs. Companies have traditionally been content with outsourcing the after-sales side of their business and have encouraged third-party parts and service providers in the market. The result has been a bevy of these operators in the market with strict price competition and low margins.Increasingly, however, companies are realizing the importance of the after-sales market and its impact on customer retention and loyalty. Increasingly, also, companies have realized that they can extract higher profit margins from the after-sales services market due to the intangible nature of services. Companies are investing in their after-sales service networks to deliver high levels of customer service and in return command higher prices for their parts and services. Customers are being sold the concept of total cost of ownership (TCO) and are being made to realize that buying from OEMs comes packaged with better distribution channels, shorter response times, better knowledge on products, and ultimately higher product uptime.The challenge for companies is to provide reliable service levels in an environment of uncertainty. Unlike factories, businesses can’t produce services in advance of demand. They can manufacture them only when an unpredictable event, such as a product failure, triggers a need. The challenge for Service Parts Pricing is to put a value to this customer need. Parts that are critical, for example, can command higher prices. So can parts that only the OEM provides in the market. Parts that are readily available in the market cannot, and must not, be priced to high. Another problem with after-sales market is that demand cannot be stimulated with price discounts, customers do not stock up service parts just because they are on discount. On the up-side, the fact that most service parts are inelastic means pricing analysts can raise prices without the adverse effects that manufacturing or retail networks witness.These and other characteristics of the after-sales market give Service Parts Pricing a life of its own. Companies are realizing that they can use the lever of service part pricing to increase profitability and don't have to take prices as market determined. Understanding customer needs and expectations, along with the company's internal strengths and weaknesses, goes a long way in designing an effective service part pricing strategy.