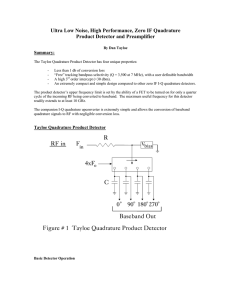
paper - ap pgecet
... In an integrated circuit, the SiO2 layer provides (A) Electrical connection to external circuit (B) Physical strength (C) Isolation (D) Conducting path A PIN diode is frequently used as a (A) Peak clipper (B) Voltage regulator (C) Harmonic regulator (D) Switching diode for frequencies up to 100 MHz ...
... In an integrated circuit, the SiO2 layer provides (A) Electrical connection to external circuit (B) Physical strength (C) Isolation (D) Conducting path A PIN diode is frequently used as a (A) Peak clipper (B) Voltage regulator (C) Harmonic regulator (D) Switching diode for frequencies up to 100 MHz ...
building aq meter
... and was probably patentable before publication. It is one of those rare designs which provide a clean, constant amplitude sine wave output over an enormous frequency range using bog standard devices, and is an ideal oscillator to power things such as aerial bridges, signal generators and other bits ...
... and was probably patentable before publication. It is one of those rare designs which provide a clean, constant amplitude sine wave output over an enormous frequency range using bog standard devices, and is an ideal oscillator to power things such as aerial bridges, signal generators and other bits ...
Wireless Local Area Network Laboratory
... determine which frequency has been received, and convert it back into a digital “0” or “1”. The receiver antenna must be well-matched to both the 2.4 and 2.6 GHz signals. The signal from the antenna is then amplified and split into two identical copies using a 3 dB power divider. The narrow-band fil ...
... determine which frequency has been received, and convert it back into a digital “0” or “1”. The receiver antenna must be well-matched to both the 2.4 and 2.6 GHz signals. The signal from the antenna is then amplified and split into two identical copies using a 3 dB power divider. The narrow-band fil ...
Continuous Coverage V.F.O. for H.F.
... and L5 (9 turns, 0.5 mm wire on a T44-6 core, 0.34 µH) with a buffer stage (2N2222 transistor). L3 is made with 2 wires wound on L4. The mixer alignement can be made in the following manner : - remove the christal so as the oscillator goes off - input a 41.2 MHz signal to gate 1 and tune the capaci ...
... and L5 (9 turns, 0.5 mm wire on a T44-6 core, 0.34 µH) with a buffer stage (2N2222 transistor). L3 is made with 2 wires wound on L4. The mixer alignement can be made in the following manner : - remove the christal so as the oscillator goes off - input a 41.2 MHz signal to gate 1 and tune the capaci ...
hw9notready
... i. the overdrive voltage and current in all devices. For this step you may assume that =0. The simplest order may be Mb1 through Mb6, then M1 through M5. ii. Calculate the bias voltages on all nodes, assuming VI,CM=1V. Specifically: tail, G2, G3, G5, G6, S3B, S4AB, and out. iii. the gm and ro param ...
... i. the overdrive voltage and current in all devices. For this step you may assume that =0. The simplest order may be Mb1 through Mb6, then M1 through M5. ii. Calculate the bias voltages on all nodes, assuming VI,CM=1V. Specifically: tail, G2, G3, G5, G6, S3B, S4AB, and out. iii. the gm and ro param ...
Lock-in amplifiers
... Sum and difference freq generated Compare to signal addition -- interference Signal frequency close to reference freq – low freq beat – DC for equal freq sine waves – DC output level depends on relative phase ...
... Sum and difference freq generated Compare to signal addition -- interference Signal frequency close to reference freq – low freq beat – DC for equal freq sine waves – DC output level depends on relative phase ...
Circuits #3 - Electro Tech Online
... Disturbance to the flow of electricity will cause unwanted or unpredictable effects, such as the timing in a timing circuit being inaccurate ...
... Disturbance to the flow of electricity will cause unwanted or unpredictable effects, such as the timing in a timing circuit being inaccurate ...
Test Procedure for Phase-Frequency Discriminator
... and look at pin 1 or 2 on U1A with a X10 probe. You should see a full ECL logic swing. ...
... and look at pin 1 or 2 on U1A with a X10 probe. You should see a full ECL logic swing. ...
Principles of Electronic Communication Systems
... Open or short-circuited transmission lines will show up on an SWR test. Other problems such as a cable that has been cut, short-circuited, or crushed between the transmitter and receiver can be located with a time domain reflectometer test. ...
... Open or short-circuited transmission lines will show up on an SWR test. Other problems such as a cable that has been cut, short-circuited, or crushed between the transmitter and receiver can be located with a time domain reflectometer test. ...
Basic Principles of Signal Integrity
... As digital circuitry speed increases, output-switching times decrease. Faster switching times cause higher transient currents within the outputs as the load capacitors discharge. If a number of outputs switch simultaneously from logic high to logic low, it causes the charge stored in the I/O load ca ...
... As digital circuitry speed increases, output-switching times decrease. Faster switching times cause higher transient currents within the outputs as the load capacitors discharge. If a number of outputs switch simultaneously from logic high to logic low, it causes the charge stored in the I/O load ca ...
Theoretical Background of a Series RLC Circuit
... We currently are using two different capacitor C values, one value is 1 nF that gives a resonance frequency f0 of about 50 kHz and a second capacitance value of 10 nF that gives a second resonance frequency f0 of about 16 kHz. But, we can easily replace either capacitor with one of larger value, say ...
... We currently are using two different capacitor C values, one value is 1 nF that gives a resonance frequency f0 of about 50 kHz and a second capacitance value of 10 nF that gives a second resonance frequency f0 of about 16 kHz. But, we can easily replace either capacitor with one of larger value, say ...
closedloo
... The main problem associated with the hysteretic type regulator relates to the ability to predict its switching frequency due to the dependence of this parameter on the output filter characteristics and circuit operation. ...
... The main problem associated with the hysteretic type regulator relates to the ability to predict its switching frequency due to the dependence of this parameter on the output filter characteristics and circuit operation. ...
Document
... operating in the 18 34 Gilt range based on AIGaAs/GaAs AIGaAs quantum well uansostors was presented in Reference 5. As far as we know this was the best result ever reported for HEMT circuits and similar to the frequency limit achie'ed by usc of AIGaAs- GaAs·H BTs. A further performance enhancement u ...
... operating in the 18 34 Gilt range based on AIGaAs/GaAs AIGaAs quantum well uansostors was presented in Reference 5. As far as we know this was the best result ever reported for HEMT circuits and similar to the frequency limit achie'ed by usc of AIGaAs- GaAs·H BTs. A further performance enhancement u ...
Variable Inductance Transducers
... • When the core moves the reluctance of the flux path changes and the degree of flux linkage depends on the core position • Since the two secondary windings are connected in series opposition, when the core is at the centre the output is zero (null position) • In the linear operating range o/p volta ...
... • When the core moves the reluctance of the flux path changes and the degree of flux linkage depends on the core position • Since the two secondary windings are connected in series opposition, when the core is at the centre the output is zero (null position) • In the linear operating range o/p volta ...
Frequency Compensation
... The stability of a feedback system, like any other LTI system, is completely determined by the location of its poles in the S-plane. The poles (natural frequencies)of a linear feedback system with closed-loop Transfer function T(s) are defined as the roots of the characteristic equation A(s)=0, wher ...
... The stability of a feedback system, like any other LTI system, is completely determined by the location of its poles in the S-plane. The poles (natural frequencies)of a linear feedback system with closed-loop Transfer function T(s) are defined as the roots of the characteristic equation A(s)=0, wher ...
Heterodyne
Heterodyning is a radio signal processing technique invented in 1901 by Canadian inventor-engineer Reginald Fessenden, in which new frequencies are created by combining or mixing two frequencies. Heterodyning is used to shift one frequency range into another, new one, and is also involved in the processes of modulation and demodulation. The two frequencies are combined in a nonlinear signal-processing device such as a vacuum tube, transistor, or diode, usually called a mixer. In the most common application, two signals at frequencies f1 and f2 are mixed, creating two new signals, one at the sum f1 + f2 of the two frequencies, and the other at the difference f1 − f2. These new frequencies are called heterodynes. Typically only one of the new frequencies is desired, and the other signal is filtered out of the output of the mixer. Heterodynes are related to the phenomenon of ""beats"" in acoustics.A major application of the heterodyne process is in the superheterodyne radio receiver circuit, which is used in virtually all modern radio receivers.