Multicast - Etusivu - Tampereen teknillinen yliopisto
... Multicast forwarding is the procedure of transmitting from one router to another the multicast packets, based on the information derived from multicast routing protocols Routers get information from the end-stations about their group memberships (consequently about the active groups) through IGMP Ro ...
... Multicast forwarding is the procedure of transmitting from one router to another the multicast packets, based on the information derived from multicast routing protocols Routers get information from the end-stations about their group memberships (consequently about the active groups) through IGMP Ro ...
NetComplex: A Complexity Metric for Networked System Designs Byung-Gon Chun Sylvia Ratnasamy
... linked or unlinked. Unused or redundant dependencies, which frequently occur, can be measured in several ways. For example, consider Fig. 1b, where v = f (w, x, y) and let us assume that the value v takes at any point is based on just one of its inputs (for instance, perhaps the active input is chos ...
... linked or unlinked. Unused or redundant dependencies, which frequently occur, can be measured in several ways. For example, consider Fig. 1b, where v = f (w, x, y) and let us assume that the value v takes at any point is based on just one of its inputs (for instance, perhaps the active input is chos ...
Part I: Introduction - Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute
... between host, router and physical link – router’s typically have multiple interfaces – host may have multiple interfaces – IP addresses associated with interface, not host, router Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute ...
... between host, router and physical link – router’s typically have multiple interfaces – host may have multiple interfaces – IP addresses associated with interface, not host, router Rensselaer Polytechnic Institute ...
K1297-G20 Protocol Tester
... the driving factors for the definition of IMA. The standard was defined in the late 1990s by the ATM Forum and describes how to use links with lower bandwidth (such as E1 and DS1) to form a “virtual” link with higher bandwidth. In order to save costs during the early years of 3G network deployment, ...
... the driving factors for the definition of IMA. The standard was defined in the late 1990s by the ATM Forum and describes how to use links with lower bandwidth (such as E1 and DS1) to form a “virtual” link with higher bandwidth. In order to save costs during the early years of 3G network deployment, ...
In recent years, a cost effective Wireless Mesh Networks ( WMNs
... more gateways in the WMNs can improve not only the network capacity but also the reliability. That is, if one gateway fails, the traffic can be delivered by alternative routes and gateways. Client WMNs: Figure 1.2 [1] shows an example of client wireless mesh networks. In the figure, mesh clients for ...
... more gateways in the WMNs can improve not only the network capacity but also the reliability. That is, if one gateway fails, the traffic can be delivered by alternative routes and gateways. Client WMNs: Figure 1.2 [1] shows an example of client wireless mesh networks. In the figure, mesh clients for ...
Media streaming in high quality over long distances
... today and can deliver consistent sustained high video quality for the consumers, and smooth deterministic flows for the network operators. This technology breaks the relationship between distance and quality, making best-effort networks perform like provisioned networks. The technology suite is call ...
... today and can deliver consistent sustained high video quality for the consumers, and smooth deterministic flows for the network operators. This technology breaks the relationship between distance and quality, making best-effort networks perform like provisioned networks. The technology suite is call ...
Adaptive Event Dissemination for Peer-to
... For instance, if a scale-free network is employed, then the network has a low diameter (in general it ranges from log log N to log N , being N the number of nodes). This means that a message requires very few hops to travel from a node to any other node, assuming that routing happens only along shor ...
... For instance, if a scale-free network is employed, then the network has a low diameter (in general it ranges from log log N to log N , being N the number of nodes). This means that a message requires very few hops to travel from a node to any other node, assuming that routing happens only along shor ...
3Com® SuperStack® 3 Switch 3300 Expandable
... These Gigabit Ethernet modules support highperformance, fault-tolerant interworkgroup and workgroup-to-backbone connections. The easy-toinstall modules provide full-duplex Gigabit Ethernet up to 2 Gbps throughput, eliminating network bottlenecks. They support both 802.1D spanning tree and resilient ...
... These Gigabit Ethernet modules support highperformance, fault-tolerant interworkgroup and workgroup-to-backbone connections. The easy-toinstall modules provide full-duplex Gigabit Ethernet up to 2 Gbps throughput, eliminating network bottlenecks. They support both 802.1D spanning tree and resilient ...
Protection and Restoration in Optical Networks - OCW-UMH
... path layer in a ring rather than at the line layer in point-to point ...
... path layer in a ring rather than at the line layer in point-to point ...
Optimizing Device-to-Device Communications in Cellular
... D2D communications could bring great potential benefits to system capacity and spectral efficiency [10]; however it might cause severe interference to the cellular UEs. Thus, an efficient interference management mechanism and routing selection should be developed to guarantee a target level of perfo ...
... D2D communications could bring great potential benefits to system capacity and spectral efficiency [10]; however it might cause severe interference to the cellular UEs. Thus, an efficient interference management mechanism and routing selection should be developed to guarantee a target level of perfo ...
Router Design and Optics
... Switching core is fairly simple, but Support for different traffic classes Signaling software is very complex Technology did not match people’s experience with IP • deploying ATM in LAN is complex (e.g. broadcast) • supporting connection-less service model on connection-based technology ...
... Switching core is fairly simple, but Support for different traffic classes Signaling software is very complex Technology did not match people’s experience with IP • deploying ATM in LAN is complex (e.g. broadcast) • supporting connection-less service model on connection-based technology ...
R33092099
... no longer operate, the rest of the nodes can still communicate with each other, directly or through one or more intermediate nodes. A wireless mesh network can be seen as a special type of wireless ad-hoc network. A wireless mesh network often has a more planned configuration, and may be deployed to ...
... no longer operate, the rest of the nodes can still communicate with each other, directly or through one or more intermediate nodes. A wireless mesh network can be seen as a special type of wireless ad-hoc network. A wireless mesh network often has a more planned configuration, and may be deployed to ...
dccn-ARP - WordPress.com
... If the IP address of the destination host in the ARP query is infact one of the hosts connected to the router, then, the router itself replies the sender with the physical address of the router itself in a unicast ARP response message. When a packet arrives with the destination host’s IP address and ...
... If the IP address of the destination host in the ARP query is infact one of the hosts connected to the router, then, the router itself replies the sender with the physical address of the router itself in a unicast ARP response message. When a packet arrives with the destination host’s IP address and ...
meshed high data rate personal area networks
... DEV searches for any beacon frame, or the DEV ignores all received frames not matching the piconet identifier (PNID) and beacon source identifier (BSID) parameters in the request. The PNID and BSID are used to uniquely identify a piconet. After scanning through all the channels, if the DEV finds a c ...
... DEV searches for any beacon frame, or the DEV ignores all received frames not matching the piconet identifier (PNID) and beacon source identifier (BSID) parameters in the request. The PNID and BSID are used to uniquely identify a piconet. After scanning through all the channels, if the DEV finds a c ...
IP Addresses
... Why use UDP? TCP is more reliable. VoIP uses UDP because it is fast and reliable “enough”. UDP good for applications with very light service. UDP can’t be used if every byte must arrive. UDP good for broadcasting and multicasting (only one socket on the sender end). • TCP is one-to-one; UDP is many- ...
... Why use UDP? TCP is more reliable. VoIP uses UDP because it is fast and reliable “enough”. UDP good for applications with very light service. UDP can’t be used if every byte must arrive. UDP good for broadcasting and multicasting (only one socket on the sender end). • TCP is one-to-one; UDP is many- ...
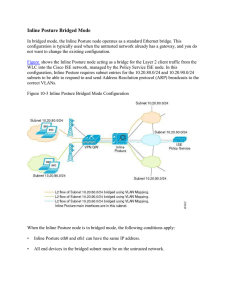
15360608-Inline Posture Bridged Mode
... RADIUS configuration is mandatory. At least one client and one server configuration is necessary for Inline Posture. For more information on RADIUS proxy services, see Proxy Service, page 15-20. Figure 10-11 RADIUS Configuration ...
... RADIUS configuration is mandatory. At least one client and one server configuration is necessary for Inline Posture. For more information on RADIUS proxy services, see Proxy Service, page 15-20. Figure 10-11 RADIUS Configuration ...
Slide 1
... 192.168.10.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 3 masks 192.168.10.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0 192.168.10.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0 192.168.11.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 3 masks 192.168.11.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 192.168.11 ...
... 192.168.10.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 3 masks 192.168.10.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0 192.168.10.1/32 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/0 192.168.11.0/24 is variably subnetted, 2 subnets, 3 masks 192.168.11.0/24 is directly connected, GigabitEthernet0/1 192.168.11 ...