Part I: Introduction
... encapsulation Foreign agent strips off and does a special translation of the mobile nodes IP address to its current hardware address 4: Network Layer 4a-47 ...
... encapsulation Foreign agent strips off and does a special translation of the mobile nodes IP address to its current hardware address 4: Network Layer 4a-47 ...
Node 1 `s Topology Table
... are sent as unicast • The source IP address is the IP address of the interface from which the packet is issued. • Following the IP header is an EIGRP header. ...
... are sent as unicast • The source IP address is the IP address of the interface from which the packet is issued. • Following the IP header is an EIGRP header. ...
Part I: Introduction
... can adapt, perform “dumb” end systems control, error recovery telephones simple inside network, complexity inside complexity at “edge” network many link types different characteristics uniform service difficult 4: Network Layer ...
... can adapt, perform “dumb” end systems control, error recovery telephones simple inside network, complexity inside complexity at “edge” network many link types different characteristics uniform service difficult 4: Network Layer ...
IOSR Journal of Computer Engineering (IOSR-JCE)
... Based on proposed HWN mentioned earlier, the proposed routing algorithm is used to find out the path to send or deliver data packets in the network. We have already discussed that our proposed routing algorithm is based on reactive routing protocol. It is not necessary that every VN require accessin ...
... Based on proposed HWN mentioned earlier, the proposed routing algorithm is used to find out the path to send or deliver data packets in the network. We have already discussed that our proposed routing algorithm is based on reactive routing protocol. It is not necessary that every VN require accessin ...
IOSR Journal of Electronics and Communication Engineering (IOSR-JECE)
... input parameters and throughput and end-to-end delay as output parameters. Based on these input parameters output parameters are calculated. Input and output parameters are as shown in Table I. ...
... input parameters and throughput and end-to-end delay as output parameters. Based on these input parameters output parameters are calculated. Input and output parameters are as shown in Table I. ...
Ch08
... • Need unique address for each device interface on network —MAC address on IEEE 802 network and ATM host address —Enables network to route data units through network and deliver to intended system —Network attachment point address ...
... • Need unique address for each device interface on network —MAC address on IEEE 802 network and ATM host address —Enables network to route data units through network and deliver to intended system —Network attachment point address ...
PPT Version
... reduction without sacrificing performance – large numbers of external LSAs are a concern ...
... reduction without sacrificing performance – large numbers of external LSAs are a concern ...
Optimizing Matrix Multiply - Dipartimento di Matematica
... • Example in 2D torus: all east-west then all north-south (avoids deadlock). • Switching strategy: • Circuit switching: full path reserved for entire message, like the telephone. • Packet switching: message broken into separatelyrouted packets, like the post office. • Flow control (what if there is ...
... • Example in 2D torus: all east-west then all north-south (avoids deadlock). • Switching strategy: • Circuit switching: full path reserved for entire message, like the telephone. • Packet switching: message broken into separatelyrouted packets, like the post office. • Flow control (what if there is ...
Compensation of Asymmetrical Latency for Ethernet Clock
... reception lines, either manually or automatically, after the first set of the PTP timestamps is exchanged. The protocol is then run again, with the exchanged lines, for the second timestamps set, as depicted in figure 2b. With the information of both round-trip measurements, it is possible to calcul ...
... reception lines, either manually or automatically, after the first set of the PTP timestamps is exchanged. The protocol is then run again, with the exchanged lines, for the second timestamps set, as depicted in figure 2b. With the information of both round-trip measurements, it is possible to calcul ...
Complexity theory - College of Computer and Information Science
... The documents listed below have been provided by the contributing authors as a means to ensure timely dissemination of scholarly and technical work on a noncommercial basis. Copyright and all rights therein are maintained by the authors or by other copyright holders, notwithstanding that they have o ...
... The documents listed below have been provided by the contributing authors as a means to ensure timely dissemination of scholarly and technical work on a noncommercial basis. Copyright and all rights therein are maintained by the authors or by other copyright holders, notwithstanding that they have o ...
On the Convexity of Latent Social Network Inference
... feasible, but here we remove this assumption in order to address a more general problem. Furthermore, where [10] is an approximation algorithm, our approach guarantees optimality while easily handling networks with thousands of nodes. ...
... feasible, but here we remove this assumption in order to address a more general problem. Furthermore, where [10] is an approximation algorithm, our approach guarantees optimality while easily handling networks with thousands of nodes. ...
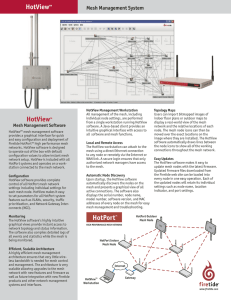
HotViewTM HotView™
... The main HotView screen provides a graphical view of the mesh network, displaying an icon for each of the nodes with lines showing the various connections among the nodes. Icons can be moved to any position on the screen, allowing users to place them in their relative positions over the background i ...
... The main HotView screen provides a graphical view of the mesh network, displaying an icon for each of the nodes with lines showing the various connections among the nodes. Icons can be moved to any position on the screen, allowing users to place them in their relative positions over the background i ...
Uw draadloze beveiligingscode
... What are three characteristics of CSMA/CD? (Choose three.) Devices can be configured with a higher transmission priority. A jam signal indicates that the collision has cleared and the media is not busy. A device listens and waits until the media is not busy before transmitting. The device with the e ...
... What are three characteristics of CSMA/CD? (Choose three.) Devices can be configured with a higher transmission priority. A jam signal indicates that the collision has cleared and the media is not busy. A device listens and waits until the media is not busy before transmitting. The device with the e ...
Document
... While there are many ways to dissect and tear apart the design decisions of the “I”nternet… ...
... While there are many ways to dissect and tear apart the design decisions of the “I”nternet… ...
Π f(Xij)
... With multiple clusters, allocate within clusters In single cluster, allocate to use the same switches ...
... With multiple clusters, allocate within clusters In single cluster, allocate to use the same switches ...
Slide 1
... distance. Yields approx nlog n / 2 entries per routing table. Route flexibility by fixing lower order bits before fixing the higher bits if an optimal path is not available. May result in longer distances as as the lower order bits fixed need not be preserved by later routing. ...
... distance. Yields approx nlog n / 2 entries per routing table. Route flexibility by fixing lower order bits before fixing the higher bits if an optimal path is not available. May result in longer distances as as the lower order bits fixed need not be preserved by later routing. ...
General requirements for improved intelligence in Status polling via
... embedded event correlation engine’s pairwise circuit, but there are problems with this as the last interface down event and interface up event will always be suppressed and this may be undesirable. As an aside, it is important to note that interface status can also be derived by NNM from SNMP MIB-II ...
... embedded event correlation engine’s pairwise circuit, but there are problems with this as the last interface down event and interface up event will always be suppressed and this may be undesirable. As an aside, it is important to note that interface status can also be derived by NNM from SNMP MIB-II ...
PPT Version
... • Opens a “hole” in original design goal tightly confining EAP for configuration to network access keys only – Now, IP address information is configured also – What else will drive through that hole? ...
... • Opens a “hole” in original design goal tightly confining EAP for configuration to network access keys only – Now, IP address information is configured also – What else will drive through that hole? ...
EN33838844
... routing protocol for wireless networks. It’s forms a route on-demand when a transmitting computer request one. However, it uses source routing instead of relying on the routing table at each intermediate device. There are two major phases for the protocol : (a) the route discovery process which is b ...
... routing protocol for wireless networks. It’s forms a route on-demand when a transmitting computer request one. However, it uses source routing instead of relying on the routing table at each intermediate device. There are two major phases for the protocol : (a) the route discovery process which is b ...
More Info »
... The user must configure the hub network defined here, in order for BPM to function as expected. It is required that the traffic management switch use Private VLAN Edge (PVE) – also known as “protected port” – to map the CDD-880’s traffic port to the CTOG-250’s expansion port 1. This is required to p ...
... The user must configure the hub network defined here, in order for BPM to function as expected. It is required that the traffic management switch use Private VLAN Edge (PVE) – also known as “protected port” – to map the CDD-880’s traffic port to the CTOG-250’s expansion port 1. This is required to p ...