Chapter-8 - Keep in Touch with Sanjeev Maharjan
... IP provides fragmentation/reassembly of datagrams. The maximum length of an IP datagram is 65,535 octets. When an IP datagram travels from one host to another, it may pass through different physical networks. Each physical network has a maximum frame size, called maximum transmission unit (MTU ...
... IP provides fragmentation/reassembly of datagrams. The maximum length of an IP datagram is 65,535 octets. When an IP datagram travels from one host to another, it may pass through different physical networks. Each physical network has a maximum frame size, called maximum transmission unit (MTU ...
Broadcast Domain
... Broadcast Domain • Network region in which broadcast frames are propagated. • Repeaters, hubs, bridges, & switches propagate broadcasts. • Routers either do or don’t, depending on their configuration. CISCO NETWORKING ACADEMY ...
... Broadcast Domain • Network region in which broadcast frames are propagated. • Repeaters, hubs, bridges, & switches propagate broadcasts. • Routers either do or don’t, depending on their configuration. CISCO NETWORKING ACADEMY ...
The Virtual Local Area Network (VLAN) Technology
... Users can physically move their workstations without having to reconfigure each workstation’s network address. Defining VLAN at layer 3 can eliminate the need for frame tagging in in order to communicate VLAN memberships between switches, reducing transport overhead. ...
... Users can physically move their workstations without having to reconfigure each workstation’s network address. Defining VLAN at layer 3 can eliminate the need for frame tagging in in order to communicate VLAN memberships between switches, reducing transport overhead. ...
IEEE and LAN Protocols
... • It is difficult to implement the polling protocols in large networks with ...
... • It is difficult to implement the polling protocols in large networks with ...
semestr 3 - final
... VLANs can not be deleted until all ports have been removed from the VLAN assignment. VLANs can only be deleted by the user that created them. VLAN 1 can not be deleted until another VLAN has been assigned its duties. *** VLAN1 is the management VLAN by default and can not be deleted. The command was ...
... VLANs can not be deleted until all ports have been removed from the VLAN assignment. VLANs can only be deleted by the user that created them. VLAN 1 can not be deleted until another VLAN has been assigned its duties. *** VLAN1 is the management VLAN by default and can not be deleted. The command was ...
tech brief - Arrow ECS
... router has access to the entire subnet. While this assumption may have been valid for legacy shared LANs, it does not result in very intelligent failover decisions for switched infrastructures. Today’s networks use intelligent switches and routers, which may require multiple router ports to connect ...
... router has access to the entire subnet. While this assumption may have been valid for legacy shared LANs, it does not result in very intelligent failover decisions for switched infrastructures. Today’s networks use intelligent switches and routers, which may require multiple router ports to connect ...
Chap5
... Bridges: traffic isolation • Bridge installation breaks LAN into LAN segments • bridges filter packets: – same-LAN-segment frames not usually ...
... Bridges: traffic isolation • Bridge installation breaks LAN into LAN segments • bridges filter packets: – same-LAN-segment frames not usually ...
H3C S5820X Series 10-Gigabit Switches
... h3C® S5820X Series 10-gigabit Switches are a revolutionary new line of flex chassis switches—the most advanced 10 gigabit Ethernet switches developed by h3C. they deliver a unique combination of unmatched 10 gigabit Ethernet port density, high availability architecture, and full Layer 2 and Layer 3 ...
... h3C® S5820X Series 10-gigabit Switches are a revolutionary new line of flex chassis switches—the most advanced 10 gigabit Ethernet switches developed by h3C. they deliver a unique combination of unmatched 10 gigabit Ethernet port density, high availability architecture, and full Layer 2 and Layer 3 ...
3rd Edition: Chapter 3
... source duplication: how does source determine recipient addresses? Network Layer 4-23 ...
... source duplication: how does source determine recipient addresses? Network Layer 4-23 ...
ppt - Computer Science & Engineering
... bits coming in one link go out all other links at same rate all nodes connected to hub can collide with one another no frame buffering no CSMA/CD at hub: host NICs detect collisions ...
... bits coming in one link go out all other links at same rate all nodes connected to hub can collide with one another no frame buffering no CSMA/CD at hub: host NICs detect collisions ...
1 - Cisco Support Community
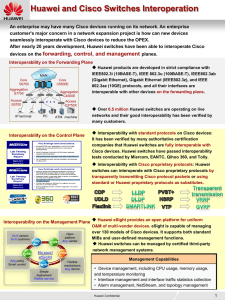
... An enterprise may have many Cisco devices running on its network. An enterprise customer's major concern in a network expansion project is how can new devices seamlessly interoperate with Cisco devices to reduce the OPEX. After nearly 20 years development, Huawei switches have been able to interoper ...
... An enterprise may have many Cisco devices running on its network. An enterprise customer's major concern in a network expansion project is how can new devices seamlessly interoperate with Cisco devices to reduce the OPEX. After nearly 20 years development, Huawei switches have been able to interoper ...
Unsynchronized Networks - Institute of Computer Engineering
... – All end stations are connected to a physical bus (no bridges). – In case multiple end stations start to transmit at about the same point in time – the signals collide on the wire. – End points realize this collision and send a jamming signal. – Retry of transmission after random timeout. • Swi ...
... – All end stations are connected to a physical bus (no bridges). – In case multiple end stations start to transmit at about the same point in time – the signals collide on the wire. – End points realize this collision and send a jamming signal. – Retry of transmission after random timeout. • Swi ...
VLANs
... Intelligent Switches • For most switches there is not enough capacity in the switching fabric / backplane to support all ports if they become active so the switch forms groups of connections and assigns capacity using time division multiplexing. • This means that the switch no longer guarantees sim ...
... Intelligent Switches • For most switches there is not enough capacity in the switching fabric / backplane to support all ports if they become active so the switch forms groups of connections and assigns capacity using time division multiplexing. • This means that the switch no longer guarantees sim ...
Notes
... route computation using Dijkstra’s algorithm OSPF advertisement carries one entry per neighbor ...
... route computation using Dijkstra’s algorithm OSPF advertisement carries one entry per neighbor ...
Addressing - Suraj @ LUMS
... IEEE sets G/L = 0 when giving out the blocks of addresses Addresses with G/L = 1 can be used without paying IEEE but the network administrator is responsible to assign addresses such that there is no collision This leaves with 222 unique OUIs ...
... IEEE sets G/L = 0 when giving out the blocks of addresses Addresses with G/L = 1 can be used without paying IEEE but the network administrator is responsible to assign addresses such that there is no collision This leaves with 222 unique OUIs ...
Routing on the Internet
... T = {s} Set of nodes so far incorporated L(n) = w(s, n) for n ≠ s initial path costs to neighboring nodes are simply link costs find neighboring node not in T with least-cost path from s incorporate node into T also incorporate the edge that is incident on that node and a node in T that contributes ...
... T = {s} Set of nodes so far incorporated L(n) = w(s, n) for n ≠ s initial path costs to neighboring nodes are simply link costs find neighboring node not in T with least-cost path from s incorporate node into T also incorporate the edge that is incident on that node and a node in T that contributes ...
ppt - Suraj @ LUMS
... Another bit in the OUI is designated by the IEEE as G/L bit IEEE sets G/L = 0 when giving out the blocks of addresses Addresses with G/L = 1 can be used without paying IEEE but the network administrator is responsible to assign addresses such that there is no collision This leaves with 222 unique OU ...
... Another bit in the OUI is designated by the IEEE as G/L bit IEEE sets G/L = 0 when giving out the blocks of addresses Addresses with G/L = 1 can be used without paying IEEE but the network administrator is responsible to assign addresses such that there is no collision This leaves with 222 unique OU ...
Edge Port Security using IEEE 802.1x
... dot1x system-auth-control ip radius source-interface Vlan99 radius-server attribute nas-port format c radius-server host 192.168.99.4 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813 key #$TR3g42f34yytV3r4f radius-server vsa send accounting radius-server vsa send authentication ...
... dot1x system-auth-control ip radius source-interface Vlan99 radius-server attribute nas-port format c radius-server host 192.168.99.4 auth-port 1812 acct-port 1813 key #$TR3g42f34yytV3r4f radius-server vsa send accounting radius-server vsa send authentication ...
Some notes on trees and paths
... then it is simple to check that d is well defined and is a metric on vertices making the set of vertices a tree. Thus excursions of simple (random) walks are a convenient (and well studied) way to describe abstract graphical trees. This particular choice for coding a tree with a positive function on ...
... then it is simple to check that d is well defined and is a metric on vertices making the set of vertices a tree. Thus excursions of simple (random) walks are a convenient (and well studied) way to describe abstract graphical trees. This particular choice for coding a tree with a positive function on ...
Link state Routing - 寬頻網路實驗室
... When topology of network changes or failure, the network knowledge base must also change. The knowledge needs to reflect an accurate, consistent view of the new topology. This view is called convergence. When all routers in an inter-network are operating with the same knowledge, the inter-networ ...
... When topology of network changes or failure, the network knowledge base must also change. The knowledge needs to reflect an accurate, consistent view of the new topology. This view is called convergence. When all routers in an inter-network are operating with the same knowledge, the inter-networ ...
Gigabit Fiber Ethernets (Optical Ethernet)
... to be a layer 2/3 switched network and not a flat layer 2 network. An important aspect of switched Gigabit Ethernet network design is where to use layer 2 switching and where to layer 3 routing. It should also be noted that these layer 2/3 switches have non-blocking ...
... to be a layer 2/3 switched network and not a flat layer 2 network. An important aspect of switched Gigabit Ethernet network design is where to use layer 2 switching and where to layer 3 routing. It should also be noted that these layer 2/3 switches have non-blocking ...
20088-2 CCNA3 3.1-08 Questions VLAN
... If the destination port is unknown, a bridge will flood the frame to all ports in the broadcast domain, except for the source port. ...
... If the destination port is unknown, a bridge will flood the frame to all ports in the broadcast domain, except for the source port. ...
Spanning Tree Protocol
The Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) is an older network protocol that ensures a loop-free topology for any bridged Ethernet local area network. The basic function of STP is to prevent bridge loops and the broadcast radiation that results from them. Spanning tree also allows a network design to include spare (redundant) links to provide automatic backup paths if an active link fails, without the danger of bridge loops, or the need for manual enabling/disabling of these backup links.Spanning Tree Protocol (STP) was originally standardized as IEEE 802.1D, in 802.1d-1998, but much of the functionality (spanning tree, rapid spanning tree, multiple spanning tree) previously specified in 802.1D, 801.1s, 802.1w has been incorporated into IEEE 802.1Q-2014 which includes shortest path bridging, the IEEE sanctioned replacement for these spanning tree functions.As the name suggests, it creates a spanning tree within a network of connected layer-2 bridges (typically Ethernet switches), and disables those links that are not part of the spanning tree, leaving a single active path between any two network nodes. STP is based on an algorithm that was invented by Radia Perlman while she was working for Digital Equipment Corporation.