D - sris-physics
... C. one gamma ray photon D. one alpha particle with gamma radiation §A. The process by which a heavy nucleus splits into two lighter nuclei is known as A. fission B. fusion C. beta decay D. a chain reaction ...
... C. one gamma ray photon D. one alpha particle with gamma radiation §A. The process by which a heavy nucleus splits into two lighter nuclei is known as A. fission B. fusion C. beta decay D. a chain reaction ...
Atomic Structure, the Periodic Table, and Nuclear Radiation
... – The closer an electron is to the nucleus, the more strongly it is attracted. – The more protons in a nucleus, the more strongly an electron is attracted. 2. Electrons are repelled by other electrons in an atom. So, if other electrons are between a valence electron and the nucleus, the valence elec ...
... – The closer an electron is to the nucleus, the more strongly it is attracted. – The more protons in a nucleus, the more strongly an electron is attracted. 2. Electrons are repelled by other electrons in an atom. So, if other electrons are between a valence electron and the nucleus, the valence elec ...
Atomic Model - Kendriya Vidyalaya Churu
... positive charge has to be concentrated in a very small volume that repelled and deflected the positively charged alpha particle . 3) Calculation by Rutherford showed the volume occupied by the nucleus is negligibly small as compared to the total volume of the atom. The radius of the atom is about 10 ...
... positive charge has to be concentrated in a very small volume that repelled and deflected the positively charged alpha particle . 3) Calculation by Rutherford showed the volume occupied by the nucleus is negligibly small as compared to the total volume of the atom. The radius of the atom is about 10 ...
Introduction to Atoms
... Atom that has the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons • A. proton • B. electron • C. isotope • D. neutron ...
... Atom that has the same number of protons but different numbers of neutrons • A. proton • B. electron • C. isotope • D. neutron ...
Overview of Particle Physics
... • each element is made of a different kind of atom • atoms are indivisible • the atoms of different elements have different weights ...
... • each element is made of a different kind of atom • atoms are indivisible • the atoms of different elements have different weights ...
Chapter 18 Resource: Matter
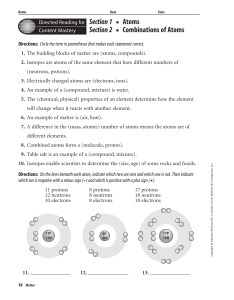
... Directions: Circle the term in parentheses that makes each statement correct. 1. The building blocks of matter are (atoms, compounds). 2. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of (neutrons, protons). 3. Electrically charged atoms are (electrons, ions). 4. An example of a ...
... Directions: Circle the term in parentheses that makes each statement correct. 1. The building blocks of matter are (atoms, compounds). 2. Isotopes are atoms of the same element that have different numbers of (neutrons, protons). 3. Electrically charged atoms are (electrons, ions). 4. An example of a ...
4 slides per page() - Wayne State University Physics and
... The scattering of two electrons via a coulomb force This virtual photon is said to mediate the electromagnetic force. The virtual photon can never be detected because it only lasts for a vanishing small time. ...
... The scattering of two electrons via a coulomb force This virtual photon is said to mediate the electromagnetic force. The virtual photon can never be detected because it only lasts for a vanishing small time. ...
Nuclear Chemistry powerpoint
... ) and no charge ( ). Thus, it causes change in or numbers. Gamma rays almost accompany alpha and beta radiation. However, since there is effect on mass number or atomic number, they are usually from nuclear equations. ...
... ) and no charge ( ). Thus, it causes change in or numbers. Gamma rays almost accompany alpha and beta radiation. However, since there is effect on mass number or atomic number, they are usually from nuclear equations. ...
Ernest Rutherford and the Discovery of the Atomic Nucleus
... This is a talk about history of nuclear physics on the occasion of the centenary of the discovery of the atomic nucleus. It is on the life and discoveries of great physicist and chemist Ernest Rutherford, in particular on his discovery of the atomic nucleus. On 7 March 1911 Ernest Rutherford spoke a ...
... This is a talk about history of nuclear physics on the occasion of the centenary of the discovery of the atomic nucleus. It is on the life and discoveries of great physicist and chemist Ernest Rutherford, in particular on his discovery of the atomic nucleus. On 7 March 1911 Ernest Rutherford spoke a ...
Atomic and Nuclear Terms
... ► Transmutation – Nuclear change of one element into another. • In natural transmutations the nucleus decays spontaneously. There is only one nucleus that undergoes the transformation. • artificial transmutation is induced by the bombardment of the nucleus by high-energy particles. • In order to bal ...
... ► Transmutation – Nuclear change of one element into another. • In natural transmutations the nucleus decays spontaneously. There is only one nucleus that undergoes the transformation. • artificial transmutation is induced by the bombardment of the nucleus by high-energy particles. • In order to bal ...
Lecture 24: The fundamental building blocks of matter 1
... • What does the “Standard Model” have to say about these forces? ...
... • What does the “Standard Model” have to say about these forces? ...
The Strong Nuclear Force and the Stability of the Nucleus
... more stable. This is why radioactive decay happens with heavy elements lying to the right of maximum in the binding energy curve. Energy released is in the form of kinetic energy of the products. ...
... more stable. This is why radioactive decay happens with heavy elements lying to the right of maximum in the binding energy curve. Energy released is in the form of kinetic energy of the products. ...
Chapter 22-23 Review
... a. Electrons than neutrons b. Electrons than protons c. Protons than electrons d. Protons than neutrons e. Neutrons than protons ...
... a. Electrons than neutrons b. Electrons than protons c. Protons than electrons d. Protons than neutrons e. Neutrons than protons ...
nuclear physics - review
... more stable. This is why radioactive decay happens with heavy elements lying to the right of maximum in the binding energy curve. Energy released is in the form of kinetic energy of the products. ...
... more stable. This is why radioactive decay happens with heavy elements lying to the right of maximum in the binding energy curve. Energy released is in the form of kinetic energy of the products. ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.