9th GRADE CHEMISTRY FINAL STUDY GUIDE
... Protons – have a mass of 1 AMU (atomic mass unit). Found in the nucleus. Have a positive charge. Neutrons – have a mass of 1 AMU. Found in nucleus. No charge (neutral). Electrons – have almost zero mass. Found outside the nucleus. Negative Charge. Subatomic particles – the collective name for proton ...
... Protons – have a mass of 1 AMU (atomic mass unit). Found in the nucleus. Have a positive charge. Neutrons – have a mass of 1 AMU. Found in nucleus. No charge (neutral). Electrons – have almost zero mass. Found outside the nucleus. Negative Charge. Subatomic particles – the collective name for proton ...
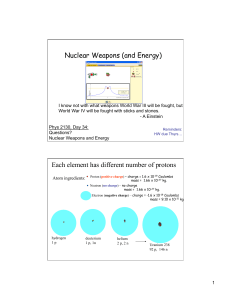
Nuclear Weapons (and Energy) Each element has different number
... b. 20% fewer at. nucl. but about same total neut. and protons. c. about same total neutrons and protons and more atomic nuclei, d. almost no atomic nuclei left, just whole bunch of isolated Neut.s and prot.s., e. almost nothing of Ur or Pl left, all went into energy. ...
... b. 20% fewer at. nucl. but about same total neut. and protons. c. about same total neutrons and protons and more atomic nuclei, d. almost no atomic nuclei left, just whole bunch of isolated Neut.s and prot.s., e. almost nothing of Ur or Pl left, all went into energy. ...
Chemical Basis of Life
... Energy relationship between electrons Energy is the capacity to do work, cause change, or move matter ...
... Energy relationship between electrons Energy is the capacity to do work, cause change, or move matter ...
Radioactivity_Topic
... Radioactivity Topic Many atoms have an unstable nucleus. Such atoms are said to be radioactive and will undergo decay. All radioactive isotopes (radioisotopes) will turn into stable atoms by decaying, but as they do so they give out radiation. ...
... Radioactivity Topic Many atoms have an unstable nucleus. Such atoms are said to be radioactive and will undergo decay. All radioactive isotopes (radioisotopes) will turn into stable atoms by decaying, but as they do so they give out radiation. ...
Atomic Structure What is an atom?
... Large, negatively charged spherical electron ‘cloud’ cloud Tiny, positively charged nucleus That contains ‘all’ of the atom’s mass ...
... Large, negatively charged spherical electron ‘cloud’ cloud Tiny, positively charged nucleus That contains ‘all’ of the atom’s mass ...
Chemistry 1 CP Concept 4 Nuclear Chemistry Study Guide
... Nuclear reaction __________________________________________________________ Radioactive decay ________________________________________________________ 3. What does the 235 in uranium-235 mean? ___________________________________ What do the numbers represent in 4 He? ________________________________ ...
... Nuclear reaction __________________________________________________________ Radioactive decay ________________________________________________________ 3. What does the 235 in uranium-235 mean? ___________________________________ What do the numbers represent in 4 He? ________________________________ ...
Introduction to Atoms
... •Select a depiction for each atomic theory •Define vocabulary: atom, electron, nucleus, proton, energy level, and valence electron ...
... •Select a depiction for each atomic theory •Define vocabulary: atom, electron, nucleus, proton, energy level, and valence electron ...
Nuclear Chemistry
... their nuclei certain radiation, with result in the formation of atoms of a different element or atoms of an isotope of the original element. Stability of the Nucleus The changes in the nucleus of the atom depends on the stability of the nucleus. Of the approximately 2000 known isotopes, there are on ...
... their nuclei certain radiation, with result in the formation of atoms of a different element or atoms of an isotope of the original element. Stability of the Nucleus The changes in the nucleus of the atom depends on the stability of the nucleus. Of the approximately 2000 known isotopes, there are on ...
PHY492: Nuclear & Particle Physics Lecture 5 Angular momentum Nucleon magnetic moments
... Quantum mechanics has only two values of for the projection of the magnetic dipole on the B axis, ±1 . ...
... Quantum mechanics has only two values of for the projection of the magnetic dipole on the B axis, ±1 . ...
2009 Assessment Schedule (90256)
... or heavy”) because the alpha particles were repelled straight back / at large angles. Electrons must be very light and orbit the nucleus in some way since most of the mass is in the positive nucleus because the alpha particles were repelled straight back / at large angles and the positive nucleus re ...
... or heavy”) because the alpha particles were repelled straight back / at large angles. Electrons must be very light and orbit the nucleus in some way since most of the mass is in the positive nucleus because the alpha particles were repelled straight back / at large angles and the positive nucleus re ...
Mindfiesta Page 1 CHAPTER – 13 NUCLEI EXPERT`S TIPS : (1) An
... (35) The stability of a nucleus (in addition to a few other factors) depends upon binding energy per nucleon rather than the total binding energy of the nucleus. (36) The binding energy per nucleon has a low value for both very heavy nuclei. In order to attain higher value of binding energy per nucl ...
... (35) The stability of a nucleus (in addition to a few other factors) depends upon binding energy per nucleon rather than the total binding energy of the nucleus. (36) The binding energy per nucleon has a low value for both very heavy nuclei. In order to attain higher value of binding energy per nucl ...
1 - contentextra
... Bohr theory A classical model of atomic structure with the electron orbiting the nucleus in circular energy levels or orbits. Cancer A malignant growth or tumour caused by abnormal and uncontrolled cell division. It spreads to other parts of the body through the lymphatic system or the blood stream. ...
... Bohr theory A classical model of atomic structure with the electron orbiting the nucleus in circular energy levels or orbits. Cancer A malignant growth or tumour caused by abnormal and uncontrolled cell division. It spreads to other parts of the body through the lymphatic system or the blood stream. ...
Atomic nucleus
The nucleus is the small, dense region consisting of protons and neutrons at the center of an atom. The atomic nucleus was discovered in 1911 by Ernest Rutherford based on the 1909 Geiger–Marsden gold foil experiment. After the discovery of the neutron in 1932, models for a nucleus composed of protons and neutrons were quickly developed by Dmitri Ivanenko and Werner Heisenberg. Almost all of the mass of an atom is located in the nucleus, with a very small contribution from the electron cloud. Protons and neutrons are bound together to form a nucleus by the nuclear force.The diameter of the nucleus is in the range of 6985175000000000000♠1.75 fm (6985175000000000000♠1.75×10−15 m) for hydrogen (the diameter of a single proton) to about 6986150000000000000♠15 fm for the heaviest atoms, such as uranium. These dimensions are much smaller than the diameter of the atom itself (nucleus + electron cloud), by a factor of about 23,000 (uranium) to about 145,000 (hydrogen).The branch of physics concerned with the study and understanding of the atomic nucleus, including its composition and the forces which bind it together, is called nuclear physics.