Technical Data Sheet
... -gated chloride channels. Chloride conductance of these channels can be modulated by agents such as benzodiazepines that bind to the GABA-A receptor. The GABA-A receptor is generally pentameric and there are five types of subunits: alpha, beta, gamma, delta, and rho. ...
... -gated chloride channels. Chloride conductance of these channels can be modulated by agents such as benzodiazepines that bind to the GABA-A receptor. The GABA-A receptor is generally pentameric and there are five types of subunits: alpha, beta, gamma, delta, and rho. ...
Lecture 9: Cell signaling
... Classification of signaling molecules Peptides: growth factors (EGF), peptide hormones (insulin, glucagon), or neuropeptides (oxytocin, enkephalins) Small molecule neurotransmitters: derived from amino acids like Epinephrine and thyroid hormone (tyrosine), serotonin (tryptophan). Steroids: derived ...
... Classification of signaling molecules Peptides: growth factors (EGF), peptide hormones (insulin, glucagon), or neuropeptides (oxytocin, enkephalins) Small molecule neurotransmitters: derived from amino acids like Epinephrine and thyroid hormone (tyrosine), serotonin (tryptophan). Steroids: derived ...
FPIA - IMGT
... protein, however in the immune system many of the interactions are between membrane proteins. So a ligand can be either a soluble protein or a membrane protein at the cell surface (GPI-anchored or transmembrane). It can be also intracellular in a cell pathway. The notion of receptor is often associa ...
... protein, however in the immune system many of the interactions are between membrane proteins. So a ligand can be either a soluble protein or a membrane protein at the cell surface (GPI-anchored or transmembrane). It can be also intracellular in a cell pathway. The notion of receptor is often associa ...
Leukaemia Section t(5;12)(q33;q24) Atlas of Genetics and Cytogenetics in Oncology and Haematology
... acids; comprises an Arf-GAP domain (amino acids 1124), zinc-fingers (11-34), ankyrin repeats (132-161, 166-195, 199-228, according to Swiss-Prot), a Spa2homology domain, a coiled-coil domain (leucine zipper), and a paxillin-binding site (643-679). GIT1 and GIT2 belong to the family of ADP-ribosylati ...
... acids; comprises an Arf-GAP domain (amino acids 1124), zinc-fingers (11-34), ankyrin repeats (132-161, 166-195, 199-228, according to Swiss-Prot), a Spa2homology domain, a coiled-coil domain (leucine zipper), and a paxillin-binding site (643-679). GIT1 and GIT2 belong to the family of ADP-ribosylati ...
Mouse anti-receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase sigma, RPTPσ
... DATASHEET Product name: receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase sigma (RPTPσ) antibody Background information: Type IIa receptor protein tyrosine phosphatases (RPTPs) are a group of well-characterized proteins that are involved in axon growth and guidance during neural development. Members of this sub ...
... DATASHEET Product name: receptor protein tyrosine phosphatase sigma (RPTPσ) antibody Background information: Type IIa receptor protein tyrosine phosphatases (RPTPs) are a group of well-characterized proteins that are involved in axon growth and guidance during neural development. Members of this sub ...
Model Description Sheet
... Huang, F. Ivy Carroll, S. Wayne Marcarella, Richard B. Westkaemper, Philip D. Mosier, Bryan L. Roth, Vadim Cherezov, Raymond C. Stevens (2012). Structure of the human K-opioid receptor in complex with JDTic. Nature (485): 327-332. Format: Alpha carbon backbone RP: Zcorp with plaster Description: Dan ...
... Huang, F. Ivy Carroll, S. Wayne Marcarella, Richard B. Westkaemper, Philip D. Mosier, Bryan L. Roth, Vadim Cherezov, Raymond C. Stevens (2012). Structure of the human K-opioid receptor in complex with JDTic. Nature (485): 327-332. Format: Alpha carbon backbone RP: Zcorp with plaster Description: Dan ...
Adenosine Transporter Receptor, human (A8352 - Sigma
... Store the product tightly sealed at –70 °C. The receptor remains active for several months when stored at –70 °C. Repeated freeze-thaw of this product is not recommended. Procedure Standard Receptor Binding Assay 1. Prepare Assay Buffer – 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4. 2. Thaw product vial quickly and mix ...
... Store the product tightly sealed at –70 °C. The receptor remains active for several months when stored at –70 °C. Repeated freeze-thaw of this product is not recommended. Procedure Standard Receptor Binding Assay 1. Prepare Assay Buffer – 50 mM Tris-HCl, pH 7.4. 2. Thaw product vial quickly and mix ...
Doc
... COMPUTATIONAL STRUCTURAL PROTEOMICS AND RATIONAL DRUG DESIGN RUBEN ABAGYAN Department of Molecular Biology The Scripps Research Institute Founder, Molsoft, LLC ...
... COMPUTATIONAL STRUCTURAL PROTEOMICS AND RATIONAL DRUG DESIGN RUBEN ABAGYAN Department of Molecular Biology The Scripps Research Institute Founder, Molsoft, LLC ...
3.D.3 Signal Transduction - kromko
... A signal relayed by a signal transduction pathway may trigger an increase in calcium in the cytosol. Pathways leading to the release of calcium involve inositol triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG) as additional second messengers. ...
... A signal relayed by a signal transduction pathway may trigger an increase in calcium in the cytosol. Pathways leading to the release of calcium involve inositol triphosphate (IP3) and diacylglycerol (DAG) as additional second messengers. ...
Hydrophobic signal molecules
... other by sending and receiving chemical signals to each other. This process is known as cell signaling Cell signaling has a number of important steps A signaling cell produces a signal molecule The signal molecule is recognised by a target cell by means of a receptor protein The receptor protein ...
... other by sending and receiving chemical signals to each other. This process is known as cell signaling Cell signaling has a number of important steps A signaling cell produces a signal molecule The signal molecule is recognised by a target cell by means of a receptor protein The receptor protein ...
Chapter 11 Cellular Signaling
... • small water soluble molecules involved in transducing a signal ...
... • small water soluble molecules involved in transducing a signal ...
Slide ()
... Site of action of targeted agents. Signals proceeding from growth factor–related receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) such as EGF-R, erbB2, or c-kit can be interrupted by lapatinib, erlotinib, gefitinib, and imatinib, acting at the ATP binding site; or by cetuximab, trastuzumab, or panitumumab acting at ...
... Site of action of targeted agents. Signals proceeding from growth factor–related receptor tyrosine kinases (RTKs) such as EGF-R, erbB2, or c-kit can be interrupted by lapatinib, erlotinib, gefitinib, and imatinib, acting at the ATP binding site; or by cetuximab, trastuzumab, or panitumumab acting at ...
Example of completed specification
... Images of official documents with terms on covers e.g. Mental Deficiency Act ...
... Images of official documents with terms on covers e.g. Mental Deficiency Act ...
Slide ()
... Pathways of insulin signaling. The binding of insulin to its plasma membrane receptor activates a cascade of downstream signaling events. Insulin binding activates the intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity of the receptor dimer, resulting in the tyrosine phosphorylation (Y-P) of the receptor's β subuni ...
... Pathways of insulin signaling. The binding of insulin to its plasma membrane receptor activates a cascade of downstream signaling events. Insulin binding activates the intrinsic tyrosine kinase activity of the receptor dimer, resulting in the tyrosine phosphorylation (Y-P) of the receptor's β subuni ...
G-Protein Coupled Receptor
... Ion Channels Signal on receptor changes shape Regulate flow of specific ions (Ca2+, Na+) ...
... Ion Channels Signal on receptor changes shape Regulate flow of specific ions (Ca2+, Na+) ...
Model Description Sheet
... The Function and Structure of the Metabotropic Gamma-aminobutyric Acid Receptor PDB: 4F12 Primary Citation: Geng, Y., Xiong, D., Mosyak, L., ...
... The Function and Structure of the Metabotropic Gamma-aminobutyric Acid Receptor PDB: 4F12 Primary Citation: Geng, Y., Xiong, D., Mosyak, L., ...
Chapter 34-4B: Second Messengers
... the surface of target cell membranes. Signals are transferred to the inside of target cell through the transmembrane receptor protein. Signals are converted to some biochemical signals, such as phosphorylation of proteins and GDPGTP exchanges. Responses are produced by “second messengers”, such as 3 ...
... the surface of target cell membranes. Signals are transferred to the inside of target cell through the transmembrane receptor protein. Signals are converted to some biochemical signals, such as phosphorylation of proteins and GDPGTP exchanges. Responses are produced by “second messengers”, such as 3 ...
Slide () - AccessEmergency Medicine
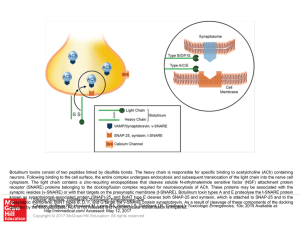
... Botulinum toxins consist of two peptides linked by disulfide bonds. The heavy chain is responsible for specific binding to acetylcholine (ACh) containing neurons. Following binding to the cell surface, the entire complex undergoes endocytosis and subsequent translocation of the light chain into the ...
... Botulinum toxins consist of two peptides linked by disulfide bonds. The heavy chain is responsible for specific binding to acetylcholine (ACh) containing neurons. Following binding to the cell surface, the entire complex undergoes endocytosis and subsequent translocation of the light chain into the ...
SOMAmer® anti-Interleukin-6 receptor subunit alpha
... For long term use, aliquotting is recommended to avoid freeze-thaw cycles. 2 years from date of receipt at -20 °C to -70 °C, as supplied 3 months at 4 °C ...
... For long term use, aliquotting is recommended to avoid freeze-thaw cycles. 2 years from date of receipt at -20 °C to -70 °C, as supplied 3 months at 4 °C ...
Gustation - West Virginia University
... H⁺ blocks K⁺ channels increasing intracellular [K⁺] via the MDEG1 receptor H⁺ also binds to yet another protein which allows Na⁺ ions to flow down the concentration gradient into the cell Bitter ...
... H⁺ blocks K⁺ channels increasing intracellular [K⁺] via the MDEG1 receptor H⁺ also binds to yet another protein which allows Na⁺ ions to flow down the concentration gradient into the cell Bitter ...
Hepatocyte growth factor receptor B-2837-3_2
... autophosphorylation of MET on its intracellular domain that provides docking sites for downstream signaling molecules. Following activation by ligand, interacts with the PI3‐kinase subunit PIK3R1, PLCG1, SRC, GRB2, STAT3 or the adapter GAB1. Recruitment of these downstream effectors by MET leads t ...
... autophosphorylation of MET on its intracellular domain that provides docking sites for downstream signaling molecules. Following activation by ligand, interacts with the PI3‐kinase subunit PIK3R1, PLCG1, SRC, GRB2, STAT3 or the adapter GAB1. Recruitment of these downstream effectors by MET leads t ...
Slide () - Anesthesiology - American Society of Anesthesiologists
... A model summarizing the toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-dependent signaling responses implicated in surgical recovery. In response to tissue damage, damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) molecules including alarmins such as high-mobility group protein B1 (HMGB1) and heat shock proteins (HSPs) bin ...
... A model summarizing the toll-like receptor 4 (TLR4)-dependent signaling responses implicated in surgical recovery. In response to tissue damage, damage-associated molecular patterns (DAMPs) molecules including alarmins such as high-mobility group protein B1 (HMGB1) and heat shock proteins (HSPs) bin ...
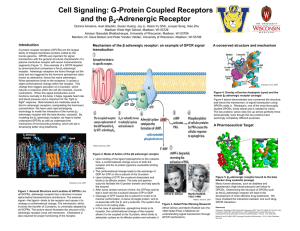
Adrenergic Receptor
... ¾ Upon binding of the ligand (epinephrine) to the cytosolic face, a conformational change occurs to both the receptor and the G protein (guanine nucleotide binding protein). ¾ The conformational change leads to the exchange of GDP for GTP on the α-subunit of the G protein. ¾ Upon binding of GTP, the ...
... ¾ Upon binding of the ligand (epinephrine) to the cytosolic face, a conformational change occurs to both the receptor and the G protein (guanine nucleotide binding protein). ¾ The conformational change leads to the exchange of GDP for GTP on the α-subunit of the G protein. ¾ Upon binding of GTP, the ...