ElectromagneticSpectrumPowerPoint
... • In this figure electrons are flowing in a wire that carries an electric current. As a result, the wire is surrounded by a magnetic field. •Electromagnetic waves are produced by moving charged particles, such as electrons, that move back and forth or vibrate. ...
... • In this figure electrons are flowing in a wire that carries an electric current. As a result, the wire is surrounded by a magnetic field. •Electromagnetic waves are produced by moving charged particles, such as electrons, that move back and forth or vibrate. ...
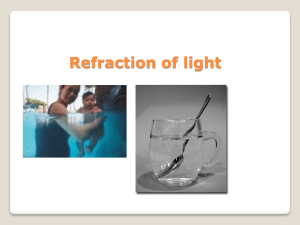
11.4 Refraction of light
... speed of light in a medium. The larger the refractive index the denser the medium and the slower light will move through the it. ...
... speed of light in a medium. The larger the refractive index the denser the medium and the slower light will move through the it. ...
Proceedings (536KB PDF)
... We are not, however, advocating absolute physical correctness in game rendering; such a thing does not exist in any case. Note the use of the word “significant” in the previous paragraph. It is possible to diverge from physical reality in many ways which are not significant to the goal of achieving ...
... We are not, however, advocating absolute physical correctness in game rendering; such a thing does not exist in any case. Note the use of the word “significant” in the previous paragraph. It is possible to diverge from physical reality in many ways which are not significant to the goal of achieving ...
The Chemical Earth
... The name of the element closer to the bottom or left-hand side of the periodic table is written first. The the suffix ‘-ide’ is added to the end of the name of the second element. The number of atoms of each element is indicated by the prefixes ‘mono-’, ‘di-’, ‘tri-’, ‘tetra-’, ‘penta-’ or hexa-’, w ...
... The name of the element closer to the bottom or left-hand side of the periodic table is written first. The the suffix ‘-ide’ is added to the end of the name of the second element. The number of atoms of each element is indicated by the prefixes ‘mono-’, ‘di-’, ‘tri-’, ‘tetra-’, ‘penta-’ or hexa-’, w ...
Slides - nanoHUB
... Screened relativistic Rutherford cross section Can be plotted as an equivalent mean free path vs. incident energy This gives you a good sense on allowable sample thickness! ...
... Screened relativistic Rutherford cross section Can be plotted as an equivalent mean free path vs. incident energy This gives you a good sense on allowable sample thickness! ...
UNIT 5-Ch 11-12 studyguide 2017
... 17) A Carbon atom has 6 protons, 6 neutrons, and 6 electrons. What would be a neutral isotope of this atom? a. 6 protons, 7 neutrons, 6 electrons b. 7 protons, 6 neutrons, 6 electrons c. 7 protons, 7 neutrons, 7 electrons d. 6 protons, 6 neutrons, 7 electrons 18) Which of the following would most l ...
... 17) A Carbon atom has 6 protons, 6 neutrons, and 6 electrons. What would be a neutral isotope of this atom? a. 6 protons, 7 neutrons, 6 electrons b. 7 protons, 6 neutrons, 6 electrons c. 7 protons, 7 neutrons, 7 electrons d. 6 protons, 6 neutrons, 7 electrons 18) Which of the following would most l ...
Energy Types and Forms
... • Electrical energy is based on the position and movement of electrons. • Moving electrons is known as current. This is related to kinetic energy. • The strength of forces acting on stationary electrons is known as voltage. This is related to potential energy. ...
... • Electrical energy is based on the position and movement of electrons. • Moving electrons is known as current. This is related to kinetic energy. • The strength of forces acting on stationary electrons is known as voltage. This is related to potential energy. ...
6.Utilization of photon equation of motion to
... Maxwell’s theory by producing and detecting electromagnetic waves. Unfortunately this wave theory faces a real problem in explaining the Black body radiation phenomenon. In 1900, Max Plank explains blackbody radiation, by proposing light as discrete energy quanta called photons with energy proportio ...
... Maxwell’s theory by producing and detecting electromagnetic waves. Unfortunately this wave theory faces a real problem in explaining the Black body radiation phenomenon. In 1900, Max Plank explains blackbody radiation, by proposing light as discrete energy quanta called photons with energy proportio ...
Slide 1
... Hadron RAA is pt independent as expected by the radiative energy loss (LPM). Direct photons follow the binary scaling. Number of binary scaling works! Unexpected level of suppression for the heavy quarks. Equark,m=0 Equark,m>0 No sign for the color factor effect on energy loss. E CR Egluo ...
... Hadron RAA is pt independent as expected by the radiative energy loss (LPM). Direct photons follow the binary scaling. Number of binary scaling works! Unexpected level of suppression for the heavy quarks. Equark,m=0 Equark,m>0 No sign for the color factor effect on energy loss. E CR Egluo ...