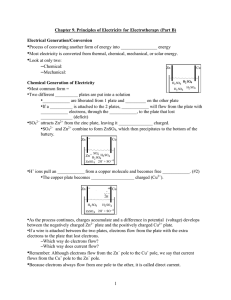
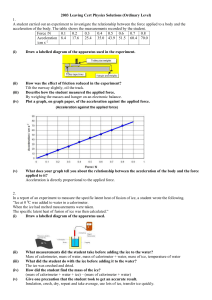
Higher Revision Cards A4
... Weight is a force. The weight of an object is the force on it due to gravitational pull. If an object weighs 100 N on Earth, it weighs 0 N in space (no gravity) and 16 N on the moon. Gravitational field strength is the weight per unit mass of an object in the field. The value of g on Earth is 9.8 N/ ...
... Weight is a force. The weight of an object is the force on it due to gravitational pull. If an object weighs 100 N on Earth, it weighs 0 N in space (no gravity) and 16 N on the moon. Gravitational field strength is the weight per unit mass of an object in the field. The value of g on Earth is 9.8 N/ ...
Book-Abstracts - The Fritz Haber Center for Molecular dynamics
... For incident electron energies higher than ~14 eV H- ESD proceeds also via dipolar dissociation (DD) processes. The 22 eV peak was suggested to be associated with multiple electron scattering or loss events prior to electron attachment leading to DEA. We have showed that that electron trapping induc ...
... For incident electron energies higher than ~14 eV H- ESD proceeds also via dipolar dissociation (DD) processes. The 22 eV peak was suggested to be associated with multiple electron scattering or loss events prior to electron attachment leading to DEA. We have showed that that electron trapping induc ...
beaming, synchrotron and inverse compton
... radial, like in gamma–ray bursts. In this case, assume that the plasma is contained in a conical narrow shell (width smaller than the distance of the shell from the apex of the cone). The observer which is moving together with a portion of the plasma, (the nearest case of a “comoving observer”) will ...
... radial, like in gamma–ray bursts. In this case, assume that the plasma is contained in a conical narrow shell (width smaller than the distance of the shell from the apex of the cone). The observer which is moving together with a portion of the plasma, (the nearest case of a “comoving observer”) will ...
Simulation on the Response of the STAR HFT Pixel Detector Alex Cimaroli 07/23/09
... Collider (RHIC) at Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL). STAR’s main task is to study the characteristics of the matter produced in these collisions, particularly the quark-gluon plasma (QGP), which is expected to have been created a few microseconds after the “Big Bang.” The Heavy Flavor Tracker (H ...
... Collider (RHIC) at Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL). STAR’s main task is to study the characteristics of the matter produced in these collisions, particularly the quark-gluon plasma (QGP), which is expected to have been created a few microseconds after the “Big Bang.” The Heavy Flavor Tracker (H ...
1. Ans: Look at the activities listed below. Reason out... of the term ‘work’.
... (f) Food grains do not move in the presence of solar energy. Hence, the work done is zero during the process of food grains getting dried in the Sun. (g)Wind energy applies a force on the sailboat to push it in the forward direction. Therefore, there is a displacement in the boat in the direction of ...
... (f) Food grains do not move in the presence of solar energy. Hence, the work done is zero during the process of food grains getting dried in the Sun. (g)Wind energy applies a force on the sailboat to push it in the forward direction. Therefore, there is a displacement in the boat in the direction of ...
Test 4 Review
... Covalent Bonds. Covalent bonds are bonds formed by sharing electrons. The electrons of one atom are attracted to the protons of another, but neither atom pulls strongly enough to remove an electron from the other. Covalent bonds form when the electronegativity difference between the elements is less ...
... Covalent Bonds. Covalent bonds are bonds formed by sharing electrons. The electrons of one atom are attracted to the protons of another, but neither atom pulls strongly enough to remove an electron from the other. Covalent bonds form when the electronegativity difference between the elements is less ...
Higher Homework
... b) What form does this emitted energy take when emitted by: (i) an LED (ii) an ordinary junction diode? 3. a) State two advantages of an LED over an ordinary filament lamp. b) An LED is rated as follows: operating p.d. 1·8 V, forward current 20 mA ...
... b) What form does this emitted energy take when emitted by: (i) an LED (ii) an ordinary junction diode? 3. a) State two advantages of an LED over an ordinary filament lamp. b) An LED is rated as follows: operating p.d. 1·8 V, forward current 20 mA ...
J. Zalesak: Optical system for HCAL calibration
... • two intensities of input led light from LED driver • one tile w/ SiPM direct coupling → monitoring of stability (yellow and green) • second measure amplitude (blue and red) ...
... • two intensities of input led light from LED driver • one tile w/ SiPM direct coupling → monitoring of stability (yellow and green) • second measure amplitude (blue and red) ...
Chapter 7 The Quantum Mechanical Model of the Atom
... • in experiments with the photoelectric effect, it was observed that there was a maximum wavelength for electrons to be emitted called the threshold frequency regardless of the intensity ...
... • in experiments with the photoelectric effect, it was observed that there was a maximum wavelength for electrons to be emitted called the threshold frequency regardless of the intensity ...
Topics 3b,c Electron Microscopy 1.0 Introduction and History
... • The transmission electron microscope (TEM) was the first type of Electron Microscope to be developed and is patterned exactly on the light transmission microscope except that a focused beam of electrons is used instead of light to "see through" the specimen. It was developed by Max Knoll and Ernst ...
... • The transmission electron microscope (TEM) was the first type of Electron Microscope to be developed and is patterned exactly on the light transmission microscope except that a focused beam of electrons is used instead of light to "see through" the specimen. It was developed by Max Knoll and Ernst ...
Electric Potential I - Galileo and Einstein
... atom, the electron circles at a radius of 0.53x10-10m, at which V(r) = 27.2 V. • The natural energy unit here is the electron volt : the work needed to take one electron from rest up a one volt hill. But in H the electron already has KE = 13.6eV, so only another 13.6eV is needed for escape. ...
... atom, the electron circles at a radius of 0.53x10-10m, at which V(r) = 27.2 V. • The natural energy unit here is the electron volt : the work needed to take one electron from rest up a one volt hill. But in H the electron already has KE = 13.6eV, so only another 13.6eV is needed for escape. ...