The Wizard Test Maker
... 16. The diagram below shows a moving, 5.00-kilogram cart at the foot of a hill 10.0 meters high. For the cart to reach the top of the hill, what is the minimum kinetic energy of the cart in the position shown? [Neglect energy loss due to friction.] ...
... 16. The diagram below shows a moving, 5.00-kilogram cart at the foot of a hill 10.0 meters high. For the cart to reach the top of the hill, what is the minimum kinetic energy of the cart in the position shown? [Neglect energy loss due to friction.] ...
Chapter 2.4 Periodic properties of the elements
... For calcium, it may be represented as: Ca+(g) + 1145 kJ → Ca2+1(g) + eFor a given element, IE2 is always greater than IE1 because it is always more difficult to remove a negatively charged electron from a positively charged ion than from the corresponding neutral atom. Ionization energies measure ho ...
... For calcium, it may be represented as: Ca+(g) + 1145 kJ → Ca2+1(g) + eFor a given element, IE2 is always greater than IE1 because it is always more difficult to remove a negatively charged electron from a positively charged ion than from the corresponding neutral atom. Ionization energies measure ho ...
Chapter 13 Section 1 The Characteristics of light
... that causes it to move away from the surface. Angle of incidence – the angle between a ray that strikes a surface and the line perpendicular to that surface at the point of contact. Angle of reflection – the angle formed by the line perpendicular to a surface and the direction in which a reflected r ...
... that causes it to move away from the surface. Angle of incidence – the angle between a ray that strikes a surface and the line perpendicular to that surface at the point of contact. Angle of reflection – the angle formed by the line perpendicular to a surface and the direction in which a reflected r ...
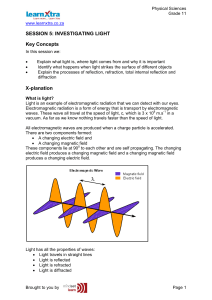
SESSION 5: INVESTIGATING LIGHT Key Concepts X
... X-planation What is light? Light is an example of electromagnetic radiation that we can detect with our eyes. Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that is transport by electromagnetic waves. These wave all travel at the speed of light, c, which is 3 x 108 m.s-1 in a vacuum. As far as we kno ...
... X-planation What is light? Light is an example of electromagnetic radiation that we can detect with our eyes. Electromagnetic radiation is a form of energy that is transport by electromagnetic waves. These wave all travel at the speed of light, c, which is 3 x 108 m.s-1 in a vacuum. As far as we kno ...
Visible Light
... • Still and motion photography both depend on visible light! Chemicals in film react with visible light and create an image that we can see. ...
... • Still and motion photography both depend on visible light! Chemicals in film react with visible light and create an image that we can see. ...
Lecture XVIII_XIX
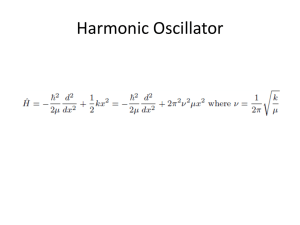
... be approximated by a parabola near the bottom of the well. The parabolic potential leads to harmonic oscillations. • At high excitation energies the parabolic approximation is poor (the true potential is less confining), and does not apply near the dissociation limit. • Must therefore use a asymmetr ...
... be approximated by a parabola near the bottom of the well. The parabolic potential leads to harmonic oscillations. • At high excitation energies the parabolic approximation is poor (the true potential is less confining), and does not apply near the dissociation limit. • Must therefore use a asymmetr ...
Physics - Kalkaska Public Schools
... them in terms of wavelength, frequency, and energy. P4.6B Explain why radio waves can travel through space, but sound waves cannot. P4.6C Explain why there is a time delay between the time we send a radio message to astronauts on the moon and when they receive it. P4.6D Explain why we see a distant ...
... them in terms of wavelength, frequency, and energy. P4.6B Explain why radio waves can travel through space, but sound waves cannot. P4.6C Explain why there is a time delay between the time we send a radio message to astronauts on the moon and when they receive it. P4.6D Explain why we see a distant ...
Romanian Master of Physics 2017 Problem I
... interface between two media, the totally reflected wave beam is laterally displaced, on a distance D (see Fig. 3), that was measured for the first time by Goos and Hänchen in 1947. In Fig. 3, the displacement along the surface is s, and the Goos – Hänchen shift is the lateral shift D indicated in th ...
... interface between two media, the totally reflected wave beam is laterally displaced, on a distance D (see Fig. 3), that was measured for the first time by Goos and Hänchen in 1947. In Fig. 3, the displacement along the surface is s, and the Goos – Hänchen shift is the lateral shift D indicated in th ...