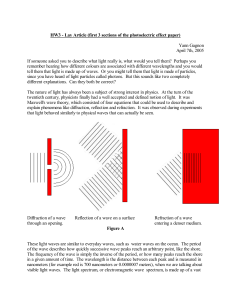
Review 1st Qtr KEY
... 3. For an electron in an atom to change from the ground state to an excited state, a. energy must be released. b. energy must be absorbed. c. radiation must be emitted. d. the electron must make a transition from a higher to a lower energy level. ...
... 3. For an electron in an atom to change from the ground state to an excited state, a. energy must be released. b. energy must be absorbed. c. radiation must be emitted. d. the electron must make a transition from a higher to a lower energy level. ...
Exciter box
... than 1 mm2), and integrated optical components may be used to shape its radiation pattern.[6] LEDs present many advantages over incandescent light sources including lower energy consumption, longer lifetime, improved physical robustness, smaller size, and faster switching. The LED consists of a chip ...
... than 1 mm2), and integrated optical components may be used to shape its radiation pattern.[6] LEDs present many advantages over incandescent light sources including lower energy consumption, longer lifetime, improved physical robustness, smaller size, and faster switching. The LED consists of a chip ...
modern intro timson2
... It was not until later, when Einstein used very similar ideas to explain the Photoelectric Effect in 1905, that it was realized that these assumptions described "real Physics" and were much more than mathematical constructions to provide the right formula. ...
... It was not until later, when Einstein used very similar ideas to explain the Photoelectric Effect in 1905, that it was realized that these assumptions described "real Physics" and were much more than mathematical constructions to provide the right formula. ...
Energy Loss - High Energy Physics at Notre Dame
... It arises from the screening of remote electrons by close electrons, which results in a reduction of energy loss for higher energies (transverse electric field grows with !). The effect is largest in dense matter, i.e. in solids and liquids. ...
... It arises from the screening of remote electrons by close electrons, which results in a reduction of energy loss for higher energies (transverse electric field grows with !). The effect is largest in dense matter, i.e. in solids and liquids. ...