Bioenergetics Key
... 1. Give the equation that relates free energy to the equilibrium constant. ΔG = -RTlnK 2. What does it mean that ΔG are additive. Why is this important in metabolism? It means that if there are several reactions in a process (such as metabolism) that the ΔG for the process is the sum of the ΔG of th ...
... 1. Give the equation that relates free energy to the equilibrium constant. ΔG = -RTlnK 2. What does it mean that ΔG are additive. Why is this important in metabolism? It means that if there are several reactions in a process (such as metabolism) that the ΔG for the process is the sum of the ΔG of th ...
AP Physics HW Name: Photon Scattering and X
... The electron encounters a particle with the same mass and opposite charge (a positron) moving with the same speed in the opposite direction. The two particles undergo a head-on collision, which results in the disappearance of both particles and the production of two photons of the same energy. (c) D ...
... The electron encounters a particle with the same mass and opposite charge (a positron) moving with the same speed in the opposite direction. The two particles undergo a head-on collision, which results in the disappearance of both particles and the production of two photons of the same energy. (c) D ...
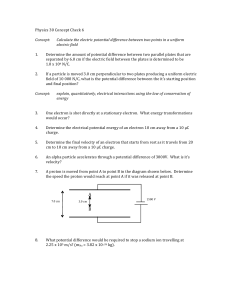
Review & Closure - Little Shop of Physics
... A muon is a lepton that is a higher-mass (rest 105 MeV/c 2) sibling to the electron. Muons are produc the upper atmosphere when incoming cosmic rays co with the nuclei of gas molecules. As the muons travel to the surface of the earth, they lose energy. A muon that tr from the upper atmosphere to the ...
... A muon is a lepton that is a higher-mass (rest 105 MeV/c 2) sibling to the electron. Muons are produc the upper atmosphere when incoming cosmic rays co with the nuclei of gas molecules. As the muons travel to the surface of the earth, they lose energy. A muon that tr from the upper atmosphere to the ...
jaf 02 revision lesson
... In 1678 the Dutch scientist Christian Huygens was the first to ___________that light travels in waves. Since then the work of Albert Einstein and James Maxwell has revealed that light actually _____________ of particles known as photons and travels in electromagnetic waves. Light seems to travel in ...
... In 1678 the Dutch scientist Christian Huygens was the first to ___________that light travels in waves. Since then the work of Albert Einstein and James Maxwell has revealed that light actually _____________ of particles known as photons and travels in electromagnetic waves. Light seems to travel in ...
2nd Semester Review
... What do like charges do with each other & what do opposite charges do with each other? ...
... What do like charges do with each other & what do opposite charges do with each other? ...