ABOUT FEASIBILITY OF MEASUREMENT OF ELECTRON
... From (1) it follows that the gain of electrons energy depends from and it enables to measure absolute energy of positrons. The basic purpose of this work is consideration of experimental approbation of RA method on lower energies 10 - 70 MeV. The expediency of approbation of RA method on low energ ...
... From (1) it follows that the gain of electrons energy depends from and it enables to measure absolute energy of positrons. The basic purpose of this work is consideration of experimental approbation of RA method on lower energies 10 - 70 MeV. The expediency of approbation of RA method on low energ ...
File
... • In 1905, Einstein used Planck’s theory to explain the photoelectric effect. – If you shine light on a clean metal surface, electrons can be emitted (in the form of color and light) – Einstein assumed that the radiant energy hitting metal surface behaves like a stream of tiny energy packets (quant ...
... • In 1905, Einstein used Planck’s theory to explain the photoelectric effect. – If you shine light on a clean metal surface, electrons can be emitted (in the form of color and light) – Einstein assumed that the radiant energy hitting metal surface behaves like a stream of tiny energy packets (quant ...
Matter Unit
... distances from the nucleus. RULE 2: Atoms radiate energy when an electron jumps from a higher-energy orbit to a lower-energy orbit. Also, an atom absorbs energy when an electron gets boosted from a low- ...
... distances from the nucleus. RULE 2: Atoms radiate energy when an electron jumps from a higher-energy orbit to a lower-energy orbit. Also, an atom absorbs energy when an electron gets boosted from a low- ...
ELEKTROMAGNETSKO ZRAČENJE
... In each spectroscopy method the photons will interact with matter if their energy corresponds to the energy differences determined by the structure and properties of molecular pattern of the sample. ...
... In each spectroscopy method the photons will interact with matter if their energy corresponds to the energy differences determined by the structure and properties of molecular pattern of the sample. ...
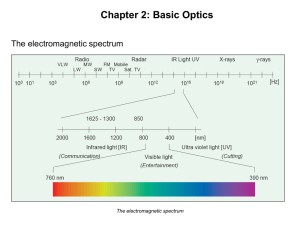
light waves
... 4. Describe convection. Draw a picture to show it. 5. Describe conduction. Draw a picture to show it. ...
... 4. Describe convection. Draw a picture to show it. 5. Describe conduction. Draw a picture to show it. ...
Quantum Mechanics - Haldia Institute of Technology
... Modern physics in the form of quantum mechanics originated in early 20th century from an apparent collapse of classical deterministic physics related with the phenomena both connected to light as electromagnetic waves described by Maxwell's equations: Ultra-violet catastrophe of blackbody radiatio ...
... Modern physics in the form of quantum mechanics originated in early 20th century from an apparent collapse of classical deterministic physics related with the phenomena both connected to light as electromagnetic waves described by Maxwell's equations: Ultra-violet catastrophe of blackbody radiatio ...
Problem set for the lecture Particle Detectors, WS 2015/16 Prof. Dr
... scintillator, each with a width of 5 mm, and the option to insert lead absorber layers in between the scintillators. A ”particle gun” can shoot a single particle with a fixed energy into the detector, by default an electron with 10 GeV, but the particle type and energy can be changed interactively. ...
... scintillator, each with a width of 5 mm, and the option to insert lead absorber layers in between the scintillators. A ”particle gun” can shoot a single particle with a fixed energy into the detector, by default an electron with 10 GeV, but the particle type and energy can be changed interactively. ...
Conservation of Energy Worksheet
... At another time the pendulum has 8-J of potential energy. What is its kinetic energy? ...
... At another time the pendulum has 8-J of potential energy. What is its kinetic energy? ...
Photoelectric Effect
... respectively. If both metals are illuminated by white light (wavelengths between 400nm and 700nm), which one gives off photoelectrons with the greater maximum kinetic energy? Assuming electrons are ejected from both metals, the answer should be cadmium, because it has a lower work function – less en ...
... respectively. If both metals are illuminated by white light (wavelengths between 400nm and 700nm), which one gives off photoelectrons with the greater maximum kinetic energy? Assuming electrons are ejected from both metals, the answer should be cadmium, because it has a lower work function – less en ...