Forms of Energy Conversions
... Forms of Energy Conversions: use the back of this page for drawing if you need more room. There are six forms of energy: thermal (heat), electrical (moving electrons), electromagnetic (light), nuclear (energy that binds the nuclei of atoms), chemical and mechanical (a kind of kinetic energy of movin ...
... Forms of Energy Conversions: use the back of this page for drawing if you need more room. There are six forms of energy: thermal (heat), electrical (moving electrons), electromagnetic (light), nuclear (energy that binds the nuclei of atoms), chemical and mechanical (a kind of kinetic energy of movin ...
Microbial Metabolism
... Modes of E Conservation-ATP • Fermentation: in which redox reaction ocurs WITHOUT a terminal electron acceptor (couple oxiation with subsequent reduction of an organic ...
... Modes of E Conservation-ATP • Fermentation: in which redox reaction ocurs WITHOUT a terminal electron acceptor (couple oxiation with subsequent reduction of an organic ...
2010 Q10 - Loreto Balbriggan
... The history of anti-matter begins in 1928 when a young English physicist named Paul Dirac predicted an anti-particle for the electron. (i) What is anti-matter? An anti-matter particle was first discovered during the study of cosmic rays in 1932. Name the anti-particle and give its symbol. What happe ...
... The history of anti-matter begins in 1928 when a young English physicist named Paul Dirac predicted an anti-particle for the electron. (i) What is anti-matter? An anti-matter particle was first discovered during the study of cosmic rays in 1932. Name the anti-particle and give its symbol. What happe ...
chapter 5
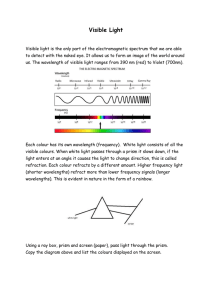
... corpuscular character is exhibited by the high frequencies radiations - ultraviolet, X-ray and, in particular, the gamma-rays. Their photons have enough energy to break chemical bonds in molecules, to produce photoelectric effect, to excite and ionize the atoms and molecules. Hence, these types of r ...
... corpuscular character is exhibited by the high frequencies radiations - ultraviolet, X-ray and, in particular, the gamma-rays. Their photons have enough energy to break chemical bonds in molecules, to produce photoelectric effect, to excite and ionize the atoms and molecules. Hence, these types of r ...
Photosynthesis ppt Honors
... _____ Using a candle and a jar, he observed that plants produce a substance that kept the candle burning _____ He measured the mass of the soil in which a plant grew _____ He observed plants exposed to light ...
... _____ Using a candle and a jar, he observed that plants produce a substance that kept the candle burning _____ He measured the mass of the soil in which a plant grew _____ He observed plants exposed to light ...
Unit 3d - OCCC.edu
... • energy is emitted from an unstable nucleus, indicated by m following the mass number. • the mass number and the atomic number of the new nucleus are the same. • 99m here means metastable (=unstable) isotope ...
... • energy is emitted from an unstable nucleus, indicated by m following the mass number. • the mass number and the atomic number of the new nucleus are the same. • 99m here means metastable (=unstable) isotope ...
Physical and Chemical Tests
... The actual energy difference is small. At 300 MHz, the energy difference for a proton is about 3 x 10-5 kcal mol-1. Because the energy difference is so small and the equilibrium between the two states is so fast, the numbers of nuclei in the two states are nearly equal, however, a slight excess will ...
... The actual energy difference is small. At 300 MHz, the energy difference for a proton is about 3 x 10-5 kcal mol-1. Because the energy difference is so small and the equilibrium between the two states is so fast, the numbers of nuclei in the two states are nearly equal, however, a slight excess will ...